Sewage disposal and energy recovery method based on three-stage membrane separation technology
A technology for sewage treatment and energy recovery, applied in water/sewage treatment, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of easy clogging of separation membrane, limited treatment effect and high treatment load , to achieve the effect of realizing reuse, realizing efficient utilization, and reducing processing load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
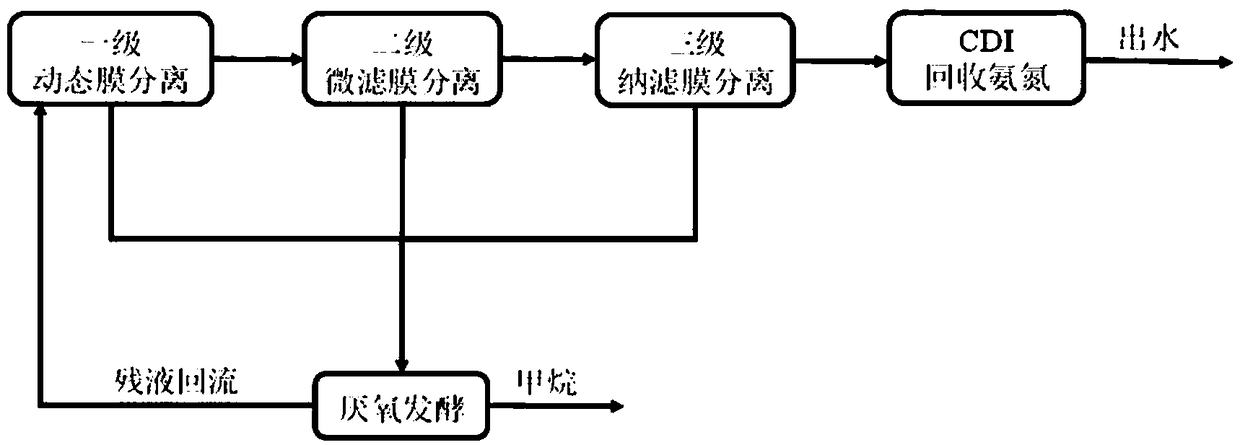
[0022] A method for sewage treatment and energy recovery based on three-stage membrane separation technology, comprising the steps of:
[0023] (1) The raw sewage (average COD is 396.8mg / L, ammonia nitrogen concentration is 44.83mg / L) is sequentially passed through the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor, the second-stage microfiltration membrane reactor and the third-stage nanofiltration membrane reactor for solid-liquid separation. Separation, wherein, the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor uses 250-mesh polyester mesh with a thickness of 0.8mm as the base membrane, and after the sewage enters the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor, 50mg / L polyferric chloride is used as a coagulant to assist the coagulation and sedimentation of organic matter; the second-stage microfiltration membrane reactor uses PVDF microfiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm as the base membrane, and the sewage is automatically dosed after entering the second-stage microfiltration membrane ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A method for sewage treatment and energy recovery based on three-stage membrane separation technology, comprising the steps of:
[0027] (1) The raw sewage (average COD is 396.8mg / L, ammonia nitrogen concentration is 44.83mg / L) is sequentially passed through the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor, the second-stage microfiltration membrane reactor and the third-stage nanofiltration membrane reactor for solid-liquid separation. Separation, wherein, the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor uses 800-mesh polyester mesh with a thickness of 0.8mm as the base membrane, and after the sewage enters the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor, 50mg / L polymerized ferric chloride is used as a coagulant to assist the coagulation and sedimentation of organic matter; the second-stage microfiltration membrane reactor uses a PVDF microfiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.50 μm as the base membrane, and the sewage is automatically dosed after entering the second-stage microfiltration...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A method for sewage treatment and energy recovery based on three-stage membrane separation technology, comprising the steps of:
[0031](1) The raw sewage (average COD is 396.8mg / L, ammonia nitrogen concentration is 44.83mg / L) is sequentially passed through the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor, the second-stage microfiltration membrane reactor and the third-stage nanofiltration membrane reactor for solid-liquid separation. Separation, wherein, the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor uses 450-mesh polyester mesh with a thickness of 0.8mm as the base membrane, and after the sewage enters the first-stage dynamic membrane reactor, 50mg / L polymerized ferric chloride is used as a coagulant to assist the coagulation and sedimentation of organic matter; the second-stage microfiltration membrane reactor uses a PVDF microfiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.11 μm as the base membrane, and the sewage is automatically dosed after entering the second-stage microfiltration ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com