A screening method for heavy metal-resistant microorganisms
A screening method and microbial technology, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms, can solve the problems of substandard concentration of culture medium, false positives of strains, and easy destruction of culture medium components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
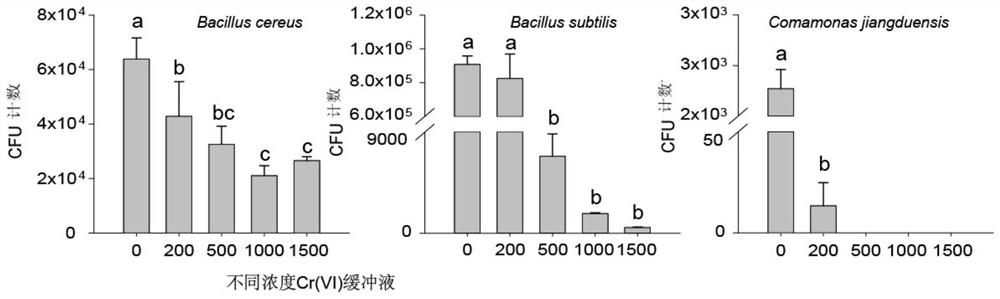
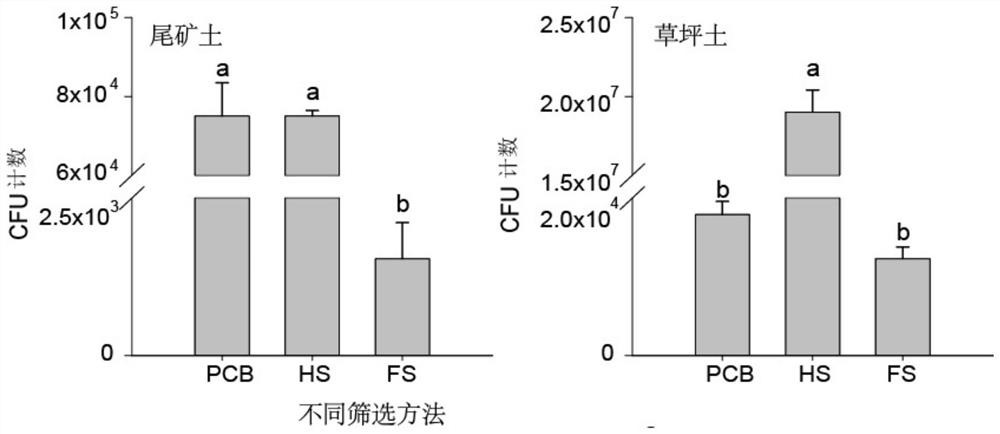
[0030] Embodiment 1: A kind of screening method of resistance to Cr (VI) microorganism
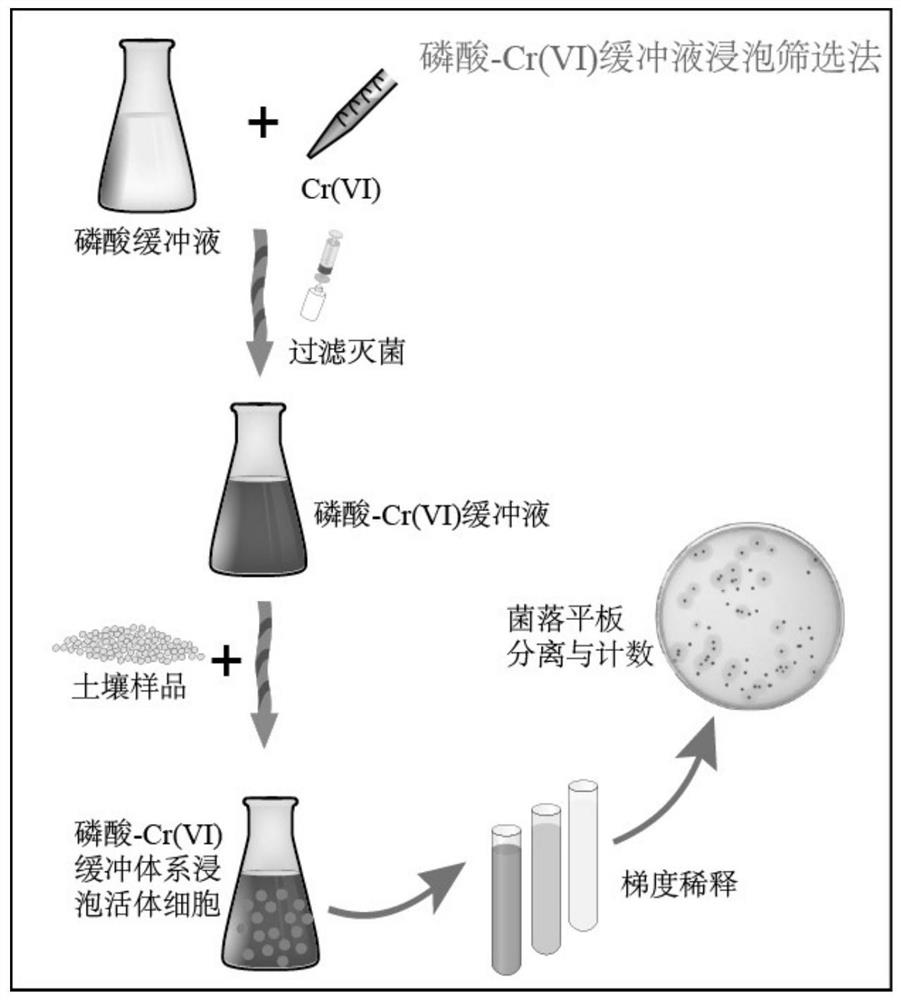
[0031] 1. The method of screening Cr(VI)-resistant microorganisms by soaking in phosphate-Cr(VI) buffer solution (hereinafter referred to as PCB method)
[0032] Prepare pH 7.4 disodium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution, weigh 8 g NaCl, 0.2 g KCl, 1.42 g NaCl into a 1 L beaker 2 HPO 4 and 0.27 g KH 2 PO 4 , then add about 800 mL of deionized water into the beaker, stir well to dissolve, adjust the pH to 7.4 with concentrated hydrochloric acid, and dilute the solution to 1 L with deionized water. Configuration 20 g K 2 Cr 2 o 7 L -1 Mother liquor, weighed 20 g and dried to constant weight K 2 Cr 2 o 7 To a 1 L beaker, add about 800 mL of deionized water, fully dissolve and dilute to 1 L. pH 7.4 phosphate buffer with 20 g K 2 Cr 2 o 7 L -1The mother liquor was mixed according to a certain volume, and filtered and sterilized with a 0.22 μm filt...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: a kind of screening method of resistant Fe(Ⅲ) microorganism
[0046] Ferric ions are important trace elements for microorganisms, but high concentrations of ferric iron can also be toxic to microorganisms. At the same time, ferric iron is oxidizing, and it is easy to produce redox reactions with reducing sugars in the medium, such as glucose. The method can be implemented through the following steps, so as to avoid the reduction reaction and improve the microorganism screening efficiency.
[0047] Step (1). Configure an inorganic buffer solution system containing ferric iron. In this example, disodium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution is used to weigh 8 g of NaCl, 0.2 g of KCl, and 0.2 g of NaCl into the beaker. 2 HPO 4 1.42 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.27 g, and about 800 ml of deionized water was added to the beaker, and stirred thoroughly to dissolve. Concentrated hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to adjust the pH to 7.4, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com