SSR molecular marker in linkage with radish clubroot-resisting QTL and applications of SSR molecular marker
A molecular marker and anti-clubroot technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of low throughput, high development cost, and limited application of SNP markers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
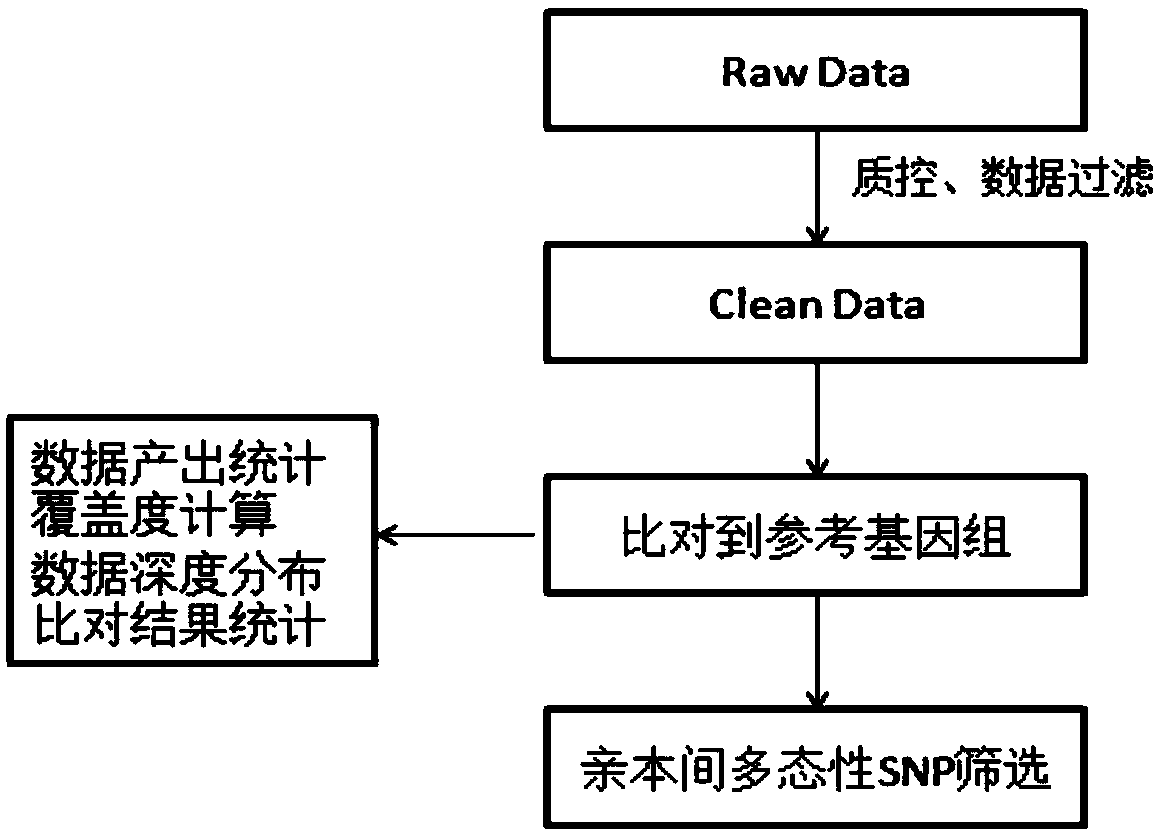
[0032] Example 1: Simplified Genome Sequencing
[0033] Take 130 F 2 Genomic DNA of radish was extracted by CTAB method from the young leaves of individual plants and parents. Genomic DNA was digested with restriction endonuclease EcorI and digested at 37°C for 15 minutes. After digestion and random interruption, 300bp-500bp DNA was recovered after electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel, and A was added after the end was repaired: Add Solexa Adapter P2Adapter (the P2 adapter is a bifurcated Y-shaped adapter, which can prevent the amplification of fragments not connected to the P1 adapter), and purify it, take 5 μL for PCR amplification, purify and recover 350-550bp DNA on 1% agarose gel, and then carry out the library Detection and sequencing on the machine, the sequencing instrument is Illumina Hiseq 4000, F 2The average information collection depth of offspring is 0.5X, and the average information collection volume is not less than 0.25G. The parental resequencing depth is 30X,...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: Obtaining of SNP genetic markers
[0038] SNP markers ( figure 1 ).
[0039] All the filtered data of each sample obtained after filtering were compared with the BGI assembly reference genome sequence R.sativus.sequence.v130428.chr.fa (394M) using SOAP2 software, and the comparison information was calculated.
[0040] Using the consensus sequence, the polymorphic sites compared with the reference sequence are screened out and filtered to obtain the SNP site information of each sample. SNPs and consensus sequences are obtained from parents and offspring, and all individual SNPs are integrated to obtain high-quality genotype markers for the entire population. When performing SNP integration, if the quality value of the genotype is less than 20, the copy number is greater than 1.5, the depth of the parental genotype is less than 5 or greater than 300, and the depth of the offspring's genotype is less than 3 or greater than 300, record such a genotype For m...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: Radish F 3 Phenotypic Identification of Clubroot Resistance in Families
[0052] Will F 2:3 The seeds of each numbered phenotype were sown in 50-hole trays. 3 days after the emergence of the seedlings, the root irrigation method was adopted (the concentration of the clubroot spores was 1 × 10 7 ·mL -1 ), the resistance identification of 25 plants was carried out with No. 4 physiological race respectively. The soil should be kept moist and the temperature should not be lower than 10°C. After 6 weeks of inoculation, wash the root soil, and investigate the incidence of individual plants according to the 0-3 standard. The grading criteria are: grade 0, no tumor in the root; grade 1, small tumor in the lateral root; grade 2, large tumor in the lateral root or nodular tumor in the main root; grade 3, obvious tumor in the main lateral root. Level 0 is disease-resistant, and others are susceptible. The identification of disease resistance was carried out in Hu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com