Double-immobilized enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
An immobilized enzyme, dual technology, applied in the direction of immobilization on or in an inorganic carrier, can solve the problems of large difference in immobilization effect, unsatisfactory immobilized enzyme activity, etc., and achieve high environmental stability and repeatability. Use performance, high enzyme activity, high activity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
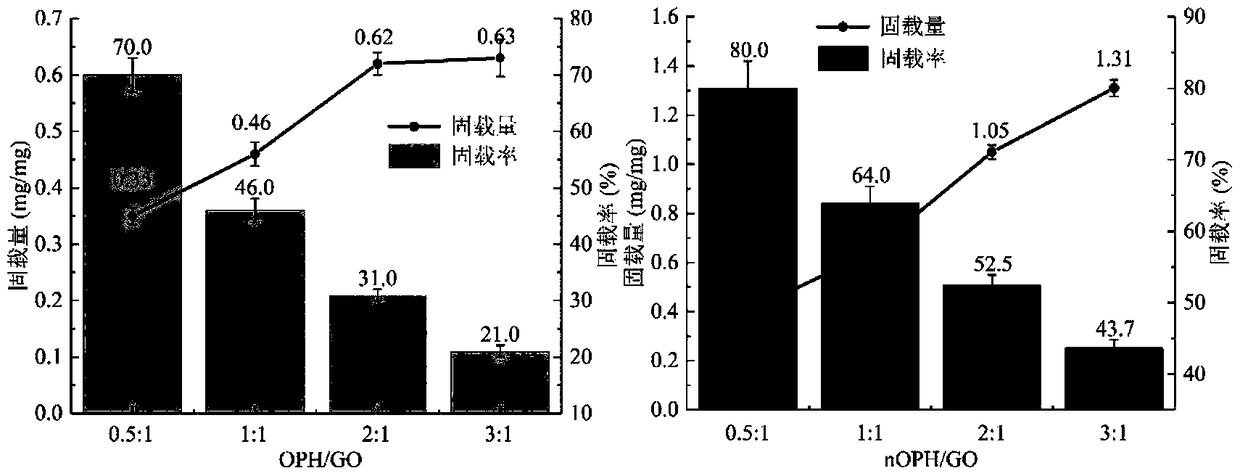
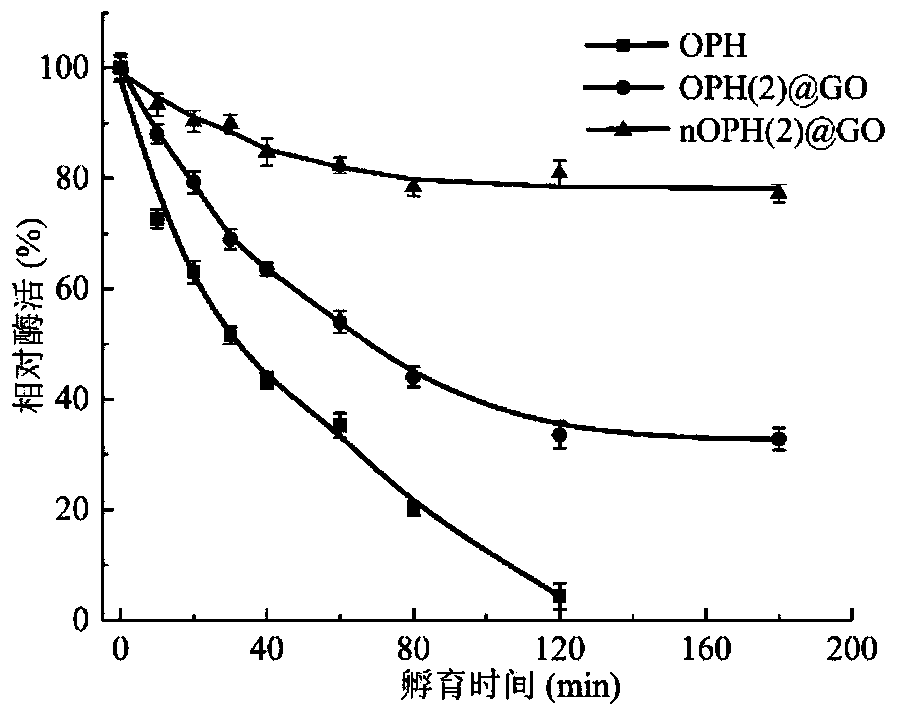
[0048](1) Accurately weigh a certain amount of graphene oxide (GO), use 50mmol / L, pH=6.0 phosphate buffer solution to prepare a dispersion solution with a concentration of 10mg / mL, mechanical stirring (1000r / min) combined with ultrasonic ( 100W) for 1h;
[0049] (2) Prepare an organophosphate hydrolase (OPH) solution with a concentration of 10 mg / mL in 50 mmol / L, pH=6 phosphate buffer solution, and add modifier: N-acryloyloxysuccinimide to the enzyme solution (NAS), after mixing, react the solution at 4°C for 10h, then add monomers to the enzyme solution in sequence: acrylamide (AAM) and N-(3-aminopropyl)-methacrylamide hydrochloride (APM), cross-linking agent: N-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS), after passing through nitrogen for 3 minutes, add initiator: ammonium persulfate (APS) and catalyst: tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED), initiate In-situ free radical polymerization in water phase, the addition ratio (mass ratio) of the above-mentioned components is OPH:NAS:AAM:APM:BIS:A...
Embodiment 2
[0058] (1) Accurately weigh a certain amount of graphene (GN), use 50mmol / L, pH=9.0 phosphate buffer solution to configure a dispersion solution with a concentration of 5mg / mL, mechanical stirring (100r / min) combined with ultrasonic (200W ) for 2.5 hours;
[0059] (2) Prepare an organophosphate hydrolase (OPH) solution with a concentration of 5 mg / mL in 50 mmol / L, pH=9.0 phosphate buffer solution, and add modifier: N-acryloyloxysuccinimide to the enzyme solution (NAS), after mixing, react the solution at 4°C for 5h, then add monomers to the enzyme solution in sequence: acrylamide (AAM) and N-(3-aminopropyl)-methacrylamide hydrochloride (APM), cross-linking agent: N-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS), after passing nitrogen for 3 minutes, add initiator: ammonium persulfate (APS) and catalyst: tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED), trigger water Phase in-situ radical polymerization, the addition ratio (mass ratio) of the above-mentioned components is OPH:NAS:AAM:APM:BIS:APS:TEMED=1:0.02...
Embodiment 3
[0064] (1) Accurately weigh a certain amount of single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs), use 50mmol / L, pH=7.0 phosphate buffer solution to prepare a dispersion solution with a concentration of 2mg / mL, and mechanically stir (600r / min) to combine Ultrasonic (150W) treatment for 2 hours;
[0065] (2) Prepare an organophosphate hydrolase (OPH) solution with a concentration of 2 mg / mL in a phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.0, and add a modifier: N-acryloyloxysuccinimide (NAS) to the enzyme solution, After mixing, react the solution at 4°C for 2.5 hours, then add monomers to the enzyme solution in sequence: acrylamide (AAM) and N-(3-aminopropyl)-methacrylamide hydrochloride (APM) , Cross-linking agent: N-methylene bisacrylamide (BIS) After passing nitrogen gas for 3 minutes, add initiator: ammonium persulfate (APS) and catalyst: tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED), trigger the in-situ free Based polymerization reaction, the addition ratio (mass ratio) of the above-mentioned componen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com