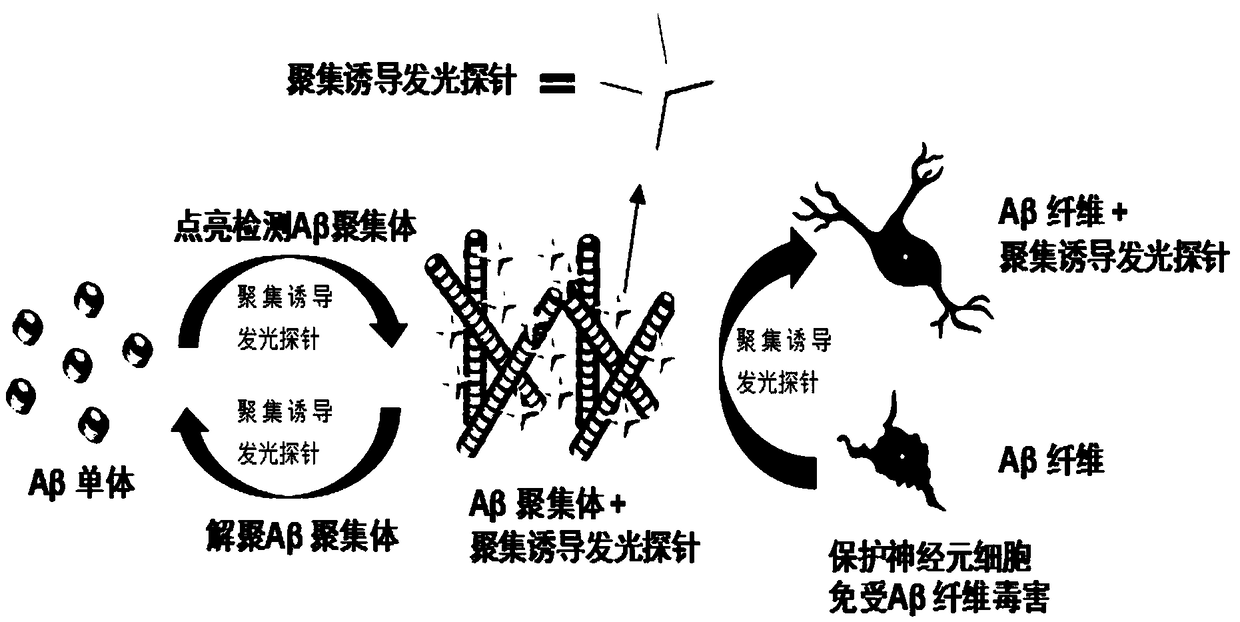
Compound, aggregation-induced emission probe and preparation method and application thereof
A compound and reaction technology, applied in the field of fluorescent probes, can solve the problems of small Stokes shift, poor photostability, and limited application of fluorescent reagents, and achieve high luminescence efficiency in aggregated states, large Stokes shifts, and biocompatibility good sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] Example 1: Synthesis of aggregation-induced luminescent probe compound III-1
[0101] The synthetic route is:
[0102]
[0103] (1) Synthesis of Compound II-1:
[0104] The compound of formula I-1 (1.1g, 3.0mmol) and ammonium formate (1.16g, 15mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solvent of ethanol (30 mL) and N,N-dimethylformamide (5mL), followed by nitrogen protection Heated to reflux for 12 h; after the reaction was completed, cooled to room temperature and rotary evaporated under reduced pressure, the residue was extracted with dichloromethane (50mL×3), the combined dichloromethane layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and then Rotary evaporation under reduced pressure, the residue was separated by silica gel column chromatography, and the eluent was dichloromethane to obtain the compound of formula II-1 (yield 53%, 587 mg); the relevant structural characterization data of the compound of formula II-1 are as follows: 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ,500MHz): δ9.84(br...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of compound IV-1
[0109] The synthetic route is:
[0110]
[0111] Boron trifluoride diethyl ether (227mg, 1.6mmol) was added to a THF (10mL) solution of the compound of formula I (184mg, 0.5mmol), heated to reflux for 12h under nitrogen protection; after the reaction was completed, cool to room temperature and Rotary evaporation was performed under reduced pressure, and 10 mL of n-hexane was added to the residue to precipitate a red solid precipitate, which was filtered and dried under vacuum to obtain the compound of aggregation-induced luminescent probe formula IV-1 (yield 79%, 164 mg). The relevant structural characterization data are as follows: 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ,500MHz):δ10.12(br s,2H), 7.94(s,1H),7.91(s,1H),7.48(d,J=2.0Hz,2H),7.35(dd,J 1 =8.5Hz,J 2 =1.5Hz, 2H), 7.04(s, 1H), 7.01(s, 1H), 6.88(d, J=8.0Hz, 2H), 6.46(s, 1H), 3.86(s, 6H); 13 C NMR (DMSO-d 6 ,125MHz):178.7,151.3,148.2,147.0,126.0,125.3,117.9,116.0,112.4,101.1,55.8...
Embodiment 3
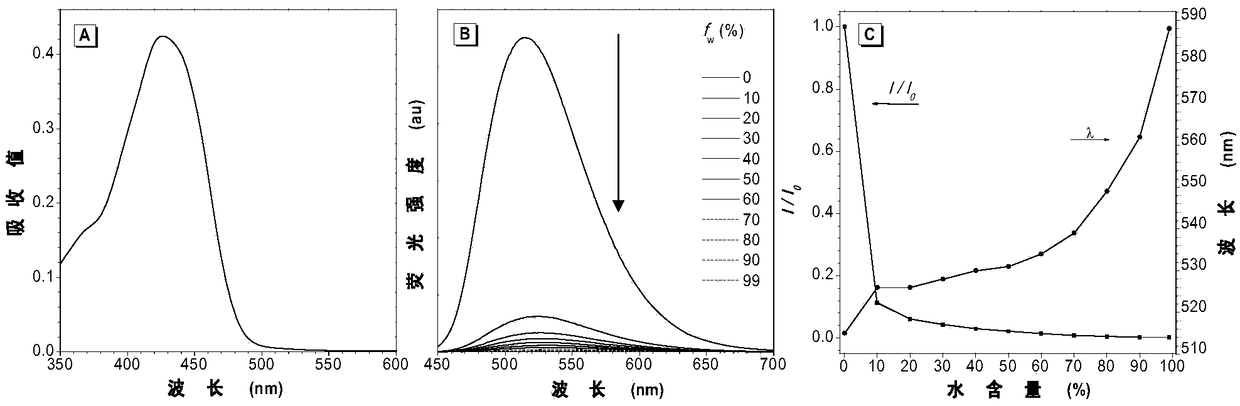
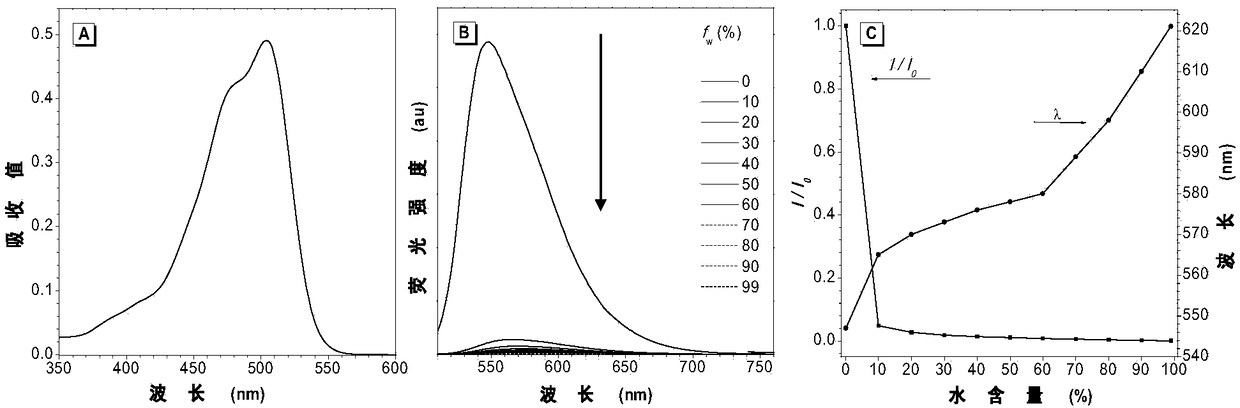
[0112] Embodiment 3: the photophysical property characterization of compound III-1 and IV-1 ( Figure 2 to Figure 7 )
[0113] The ultraviolet-visible absorption test result of compound III-1 and IV-1 is as follows Figure 2-4 shown. figure 2 The ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission spectrograms of the aggregation-induced luminescent probe compound III-1 prepared for Example 1; (A) the normalized ultraviolet absorption spectrogram of compound III-1 in tetrahydrofuran (10 -5 mol L -1 ); (B) Fluorescence emission spectrum of compound III-1 in the mixed solution of tetrahydrofuran and water with increasing water content; (C) change of maximum emission wavelength and maximum emission fluorescence of compound III-1 in the mixed solution of tetrahydrofuran and water Ratio change graph of intensity. image 3 The ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission spectrograms of the aggregation-induced luminescence probe compound IV-1 prepared for Example 2; (A) the nor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com