Method for analyzing tiny particles in drinking water
An analysis method and drinking water technology, which are applied in the direction of material analysis, analysis material, and measuring device using wave/particle radiation, which can solve problems such as human injury, and achieve the effects of easy sampling, accurate analysis results, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] step 1:
[0053] Dissolve Nile Red in acetone;
[0054] Step 2:
[0055] Divide bottled water of three different brands of X, Y, Z into three parts: each part is dyed with Nile Red;
[0056] Step 3:
[0057] Filter the three types of bottled water after Nile Red dyeing;
[0058] Step 4:
[0059] Micro-infrared analysis of the filtered particles, scanning electron microscope + X-ray energy spectrometer analysis;
[0060] Step 5:
[0061] Perform component analysis and classification of the particulate matter after component analysis, and analyze possible sources.
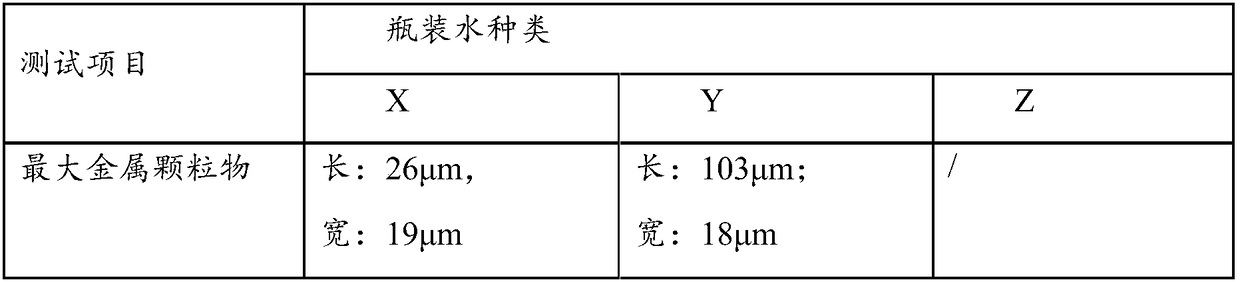
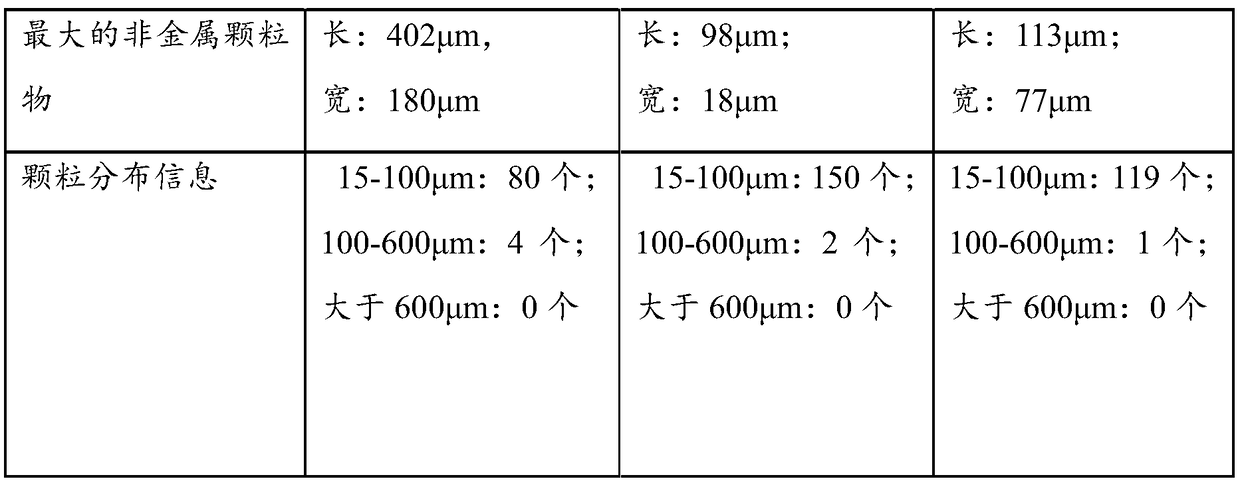
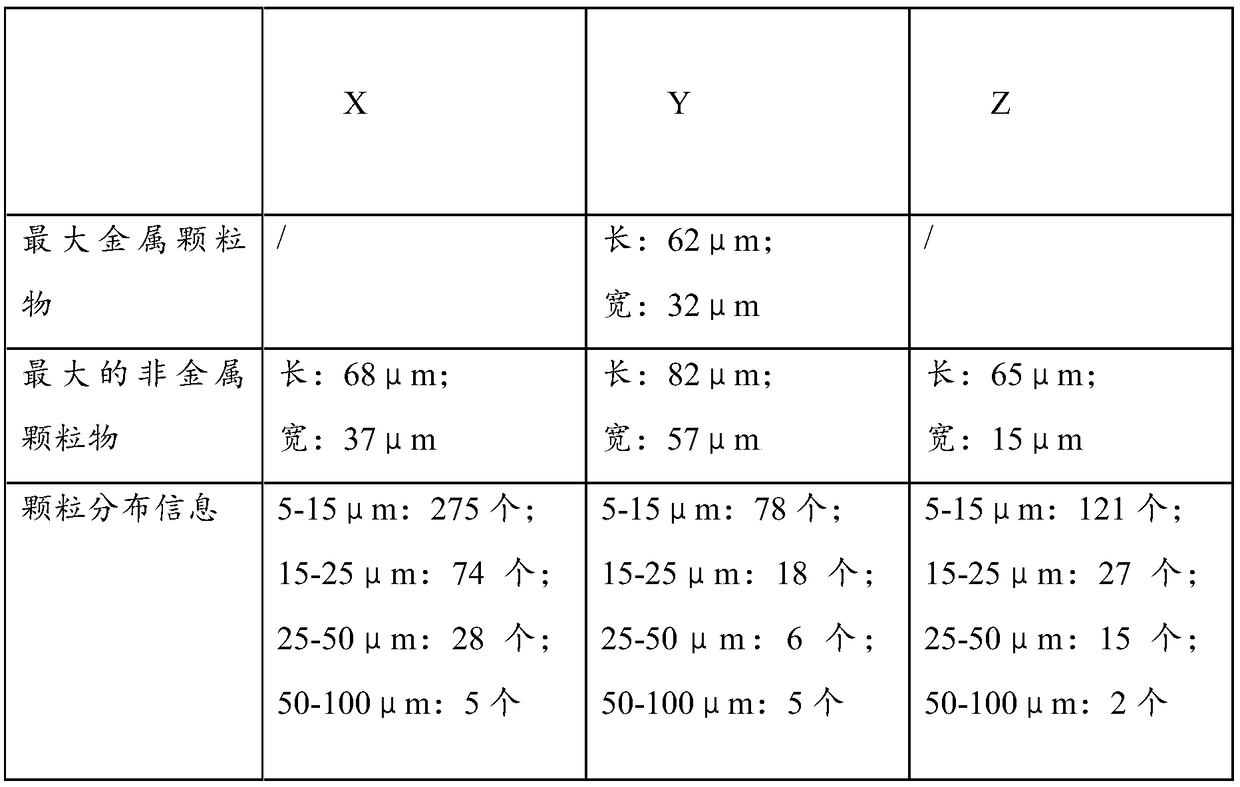
[0062] The analysis results are shown in Table 1.
[0063] Table 1 Particle size analysis
[0064]
[0065]
[0066] The micro-infrared test results of the samples are shown in Table 2.
[0067] Table 2 Micro-infrared analysis results
[0068] X
Polyester fiber, carbon black, metal oxide, polyisoprene
Y
Inorganic salt, acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer ABS, protein
Z
Cellulose, protein, carbon black
[0069] Result a...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Step 1: Pour Nile Red powder into acetone to dissolve it to prepare a solution with a concentration of Nile Red of 0.1 mg / mL; prepare the filter membrane, clean it and analyze it under the microscope. If there are particles that affect the analysis results, continue to clean and clean. The filter membrane is placed in a clean petri dish.
[0092] Step 2: Filter 10 mL of acetone solution and 10 mL of Nile Red solution on a 1 μm filter membrane, respectively, and analyze particles and components.
[0093] Step 3: Pour the Nile Red solution into the pressure tank of the spray gun, filter through the built-in 0.45μm filter membrane of the filter gun, collect 10mL filtrate and filter it on the 1μm filter membrane, analyze the particles and components; (blank test)
[0094] Step 4: Prepare water samples a, b, c, d, e, 1.5L / bottle, 2 bottles each; clean the outer wall of the bottle with deionized water filtered by a 0.45μm filter membrane before testing to avoid introducing impuritie...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com