Mhp non-specific nuclease and coding gene and application thereof
A non-specific nuclease technology, applied in Mhp non-specific nuclease and its coding gene and application field, can solve the problems of high price, difficult renaturation, large-scale application limitations, etc., achieve low ion concentration, enhance infection and pathogenesis function, reducing the effect of trapping and killing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Acquisition and point mutation of Mhp non-specific nuclease nucleotide sequence
[0041] Primers were designed using the known Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (Mhp) nonspecific nuclease gene (gene accession number AAZ53943.1), Mhp597-F' (5'-ATGAAAATTAAAAAAATTATTTCTTTTT-3') and mhp597-R' (5'-TTAATTCTGACTGTTTTGGCCT- 3'), using the Mhp whole genome as a template, carry out PCR amplification, connect the obtained sequence to the cloning vector and send it to Meiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for sequencing. Use DNAStar software to translate the sequencing results into protein sequences, find the TGA stop codon inside the gene fragment of Mhp non-specific nuclease, and design mutation primers. The TGA inside the gene is mutated into TGG, that is, the nucleotide sequence of the Mhp non-specific nuclease is obtained. The result is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the corresponding amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2.
[0042] PCR amplification system and conditions are as f...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The construction of embodiment 2 expressing Mhp non-specific nuclease engineering strain
[0048] 1. Amplification of Mhp nonspecific nuclease gene
[0049] The primers were designed according to the sequence characteristics of the modified Mhp non-specific nuclease gene. The upstream primer Mhp597-F contains the NcoI site Mhp597-F (5'-CATGCCATGGGCACCGGAC TCGGAGC TTATTT-3'), and does not amplify the original signal peptide (1-18) Amino acid excision, total length is 54bp), downstream primer Mhp597-R contains XhoI site Mhp597-R (5'-CCGCTCGAGATTCTGACTGTTTTGG CCT-3'), Mhp non-specific nuclease gene (shown in SEQ ID NO: 1) is used as a template to carry out PCR amplification. The PCR amplification system and conditions were the same as in Example 1.
[0050] 2. Cloning of Mhp nonspecific nuclease gene
[0051] Step (1) PCR amplification product was recovered by using the ordinary agarose gel DNA recovery kit of Beijing Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., and connec...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Study on the enzymatic properties of Mhp non-specific nuclease
[0060] 1. Degradation of different nucleic acid substrates by Mhp nonspecific nucleases
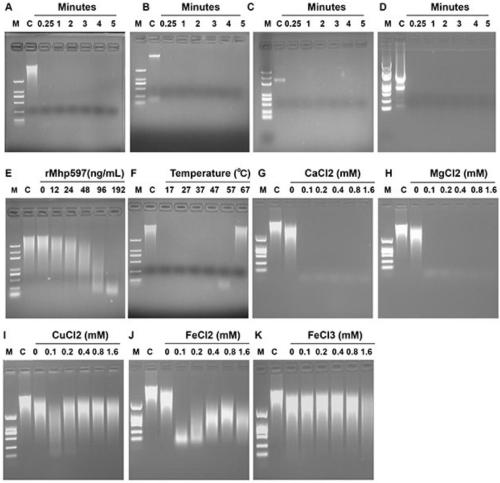
[0061] Using dsDNA (calf thymus DNA), ssDNA, plasma DNA, and RNA as substrates, 1 μg Mhp597 protein was added, and 10mM Ca 2+ , 100mM Mg 2+ In the buffer (Table 2), react for 0.25min, 1min, 2min, 3min, 4min, 5min respectively, and then run the reaction system by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The results showed that 1 μg Mhp nonspecific nuclease could completely degrade 1 μg double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), plasmid DNA and RNA, and the degradation reaction time was very short, and the degradation reaction could be completed by mixing ( figure 2 A, figure 2 B, figure 2 C, figure 2 D).
[0062] Table 2 Degradation of different nucleic acid substrates by Mhp nonspecific nucleases
[0063]
[0064] 2. The effect of protein concentration on the activity of Mhp non-specific nu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com