Polyethyleneimine based chloramines type antibacterial cellulose membrane, preparation method and application
A polyethyleneimine-based chloramine-type, polyethyleneimine technology, applied in the field of polymer material preparation, to achieve the effects of environmental protection in the preparation process, mild reaction conditions, and simple process operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] A preparation method of polyethyleneimine chloramine type antibacterial cellulose film, comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step 1: preparing a cellulose solution with a mass concentration of 5wt%;
[0032] Step 2: After defoaming the cellulose solution prepared in step 1, casting a film on the substrate, washing after solidification to obtain a regenerated cellulose gel film;
[0033] Step 3: oxidizing the regenerated cellulose gel film obtained in step 2 with an aqueous solution of sodium periodate to obtain a dialdehyde cellulose gel film with an aldehyde group content of 1 to 3 mmol / g;
[0034] Step 4: immersing the dialdehyde cellulose gel film obtained in step 3 in a polyethyleneimine aqueous solution for grafting reaction to obtain a polyethyleneimine grafted cellulose film;
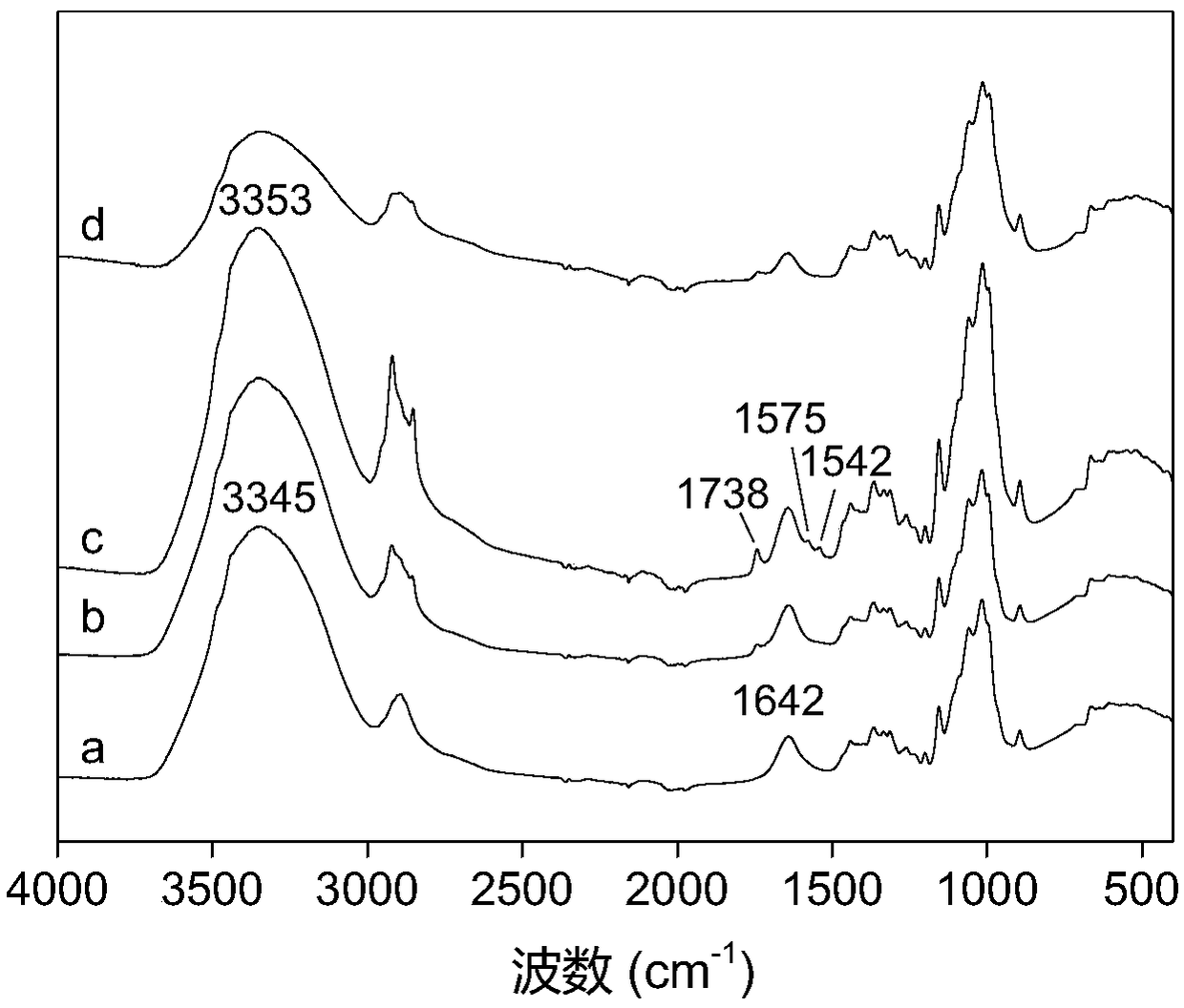
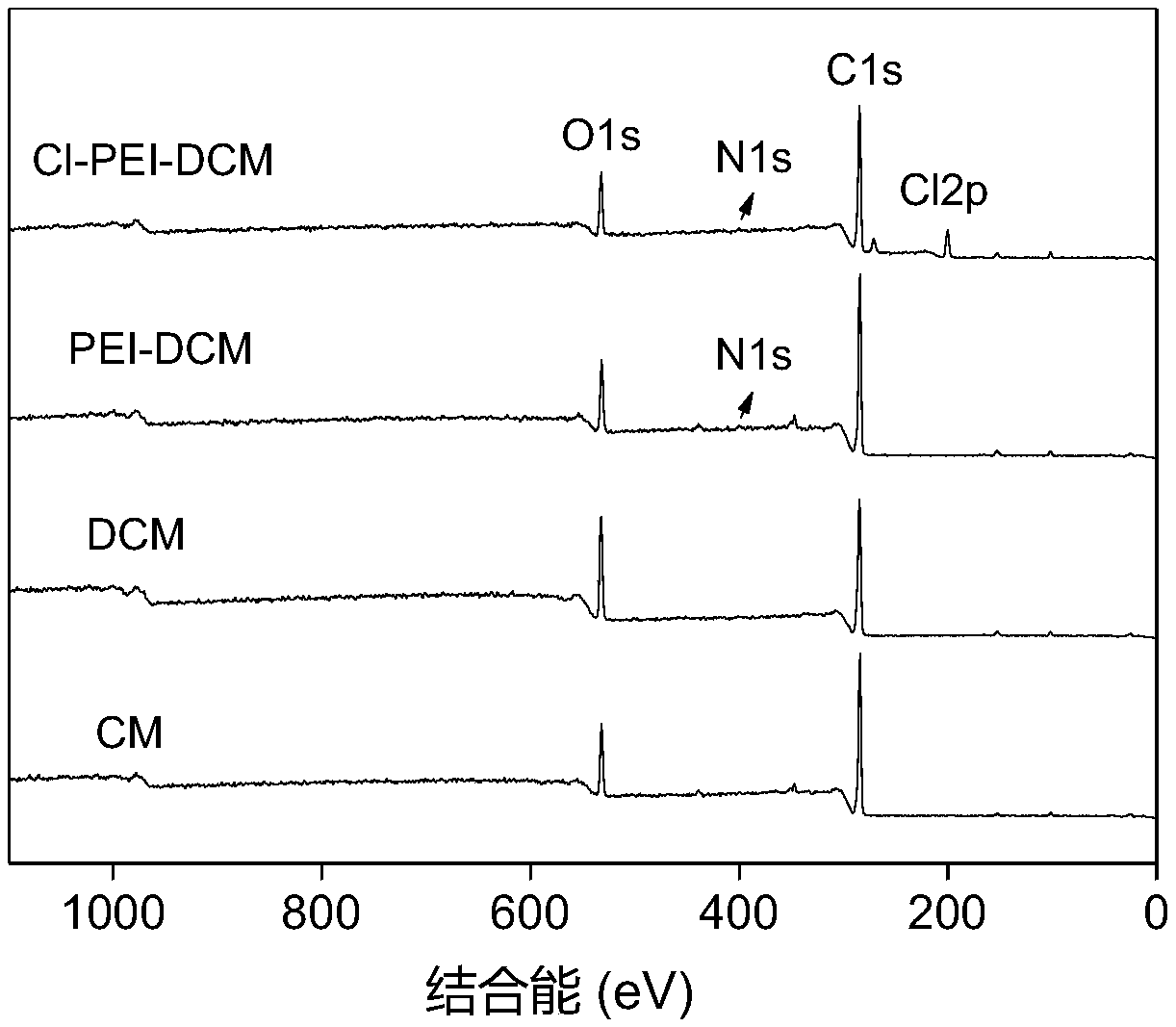
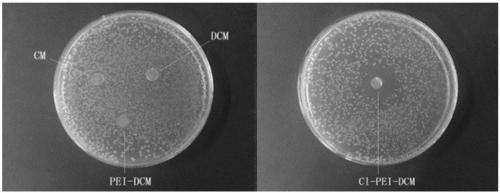
[0035] Step 5: After chlorinating the polyethyleneimine-grafted cellulose film obtained in step 4, a polyethyleneimine-based chloramine-type antibacterial cellulose film is obtained. ...
Embodiment 1
[0044] Prepare polyethyleneimine-based chloramine-type antibacterial cellulose membranes according to the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Add 5 g of cellulose to 95 g of TBAH / DMSO solvent, stir and dissolve to obtain a 5 wt % cellulose solution; the TBAH / DMSO solvent is a mixture of 50 wt % TBAH aqueous solution and DMSO in a mass ratio of 1:4 liquid;
[0046] Step 2: After defoaming the cellulose solution prepared in step 1, casting the film on the substrate, placing it in the air to gel, and eluting the solvent with water to obtain a regenerated cellulose gel film (CM);
[0047] Step 3: Put 2 g of the regenerated cellulose gel film obtained in Step 2 into a sodium periodate solution with a concentration of 1 g / L and pH=5, oxidize it at 25°C for 6 hours, and then wash it with water to obtain dialdehyde fibers plain gel membrane (DCM);
[0048] Step 4: Immerse the dialdehyde cellulose gel film obtained in step 3 in the PEI solution with a concentration of 0.05% and pH=10, ca...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Prepare polyethyleneimine-based chloramine-type antibacterial cellulose membranes according to the following steps:
[0057] Step 1: Add 5 g of cellulose to 95 g of TBAH / DMSO solvent, stir and dissolve to obtain a 5 wt % cellulose solution; the TBAH / DMSO solvent is a mixture of 50 wt % TBAH aqueous solution and DMSO in a mass ratio of 1:4 liquid;
[0058] Step 2: after degassing the cellulose solution prepared in step 1, casting a film on the substrate, placing it in the air to gel, and eluting the solvent with water to obtain a regenerated cellulose gel film;
[0059] Step 3: Put 2 g of the regenerated cellulose gel film obtained in Step 2 into a sodium periodate solution with a concentration of 1 g / L and pH=5, oxidize it at 25°C for 6 hours, and then wash it with water to obtain dialdehyde fibers plain gel film;
[0060] Step 4: Immerse the dialdehyde cellulose gel film obtained in step 3 into the PEI solution with a concentration of 1% and pH=9, carry out grafting ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com