System and method for detecting plant diseases
A plant and disease technology, applied in the direction of testing plants/trees, neural learning methods, material inspection items, etc., can solve the problems of being less reliable, not proposing the global existence of diseases, not allowing lighting and/or photography to change and adapt, To achieve the effect of reducing the amount of data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
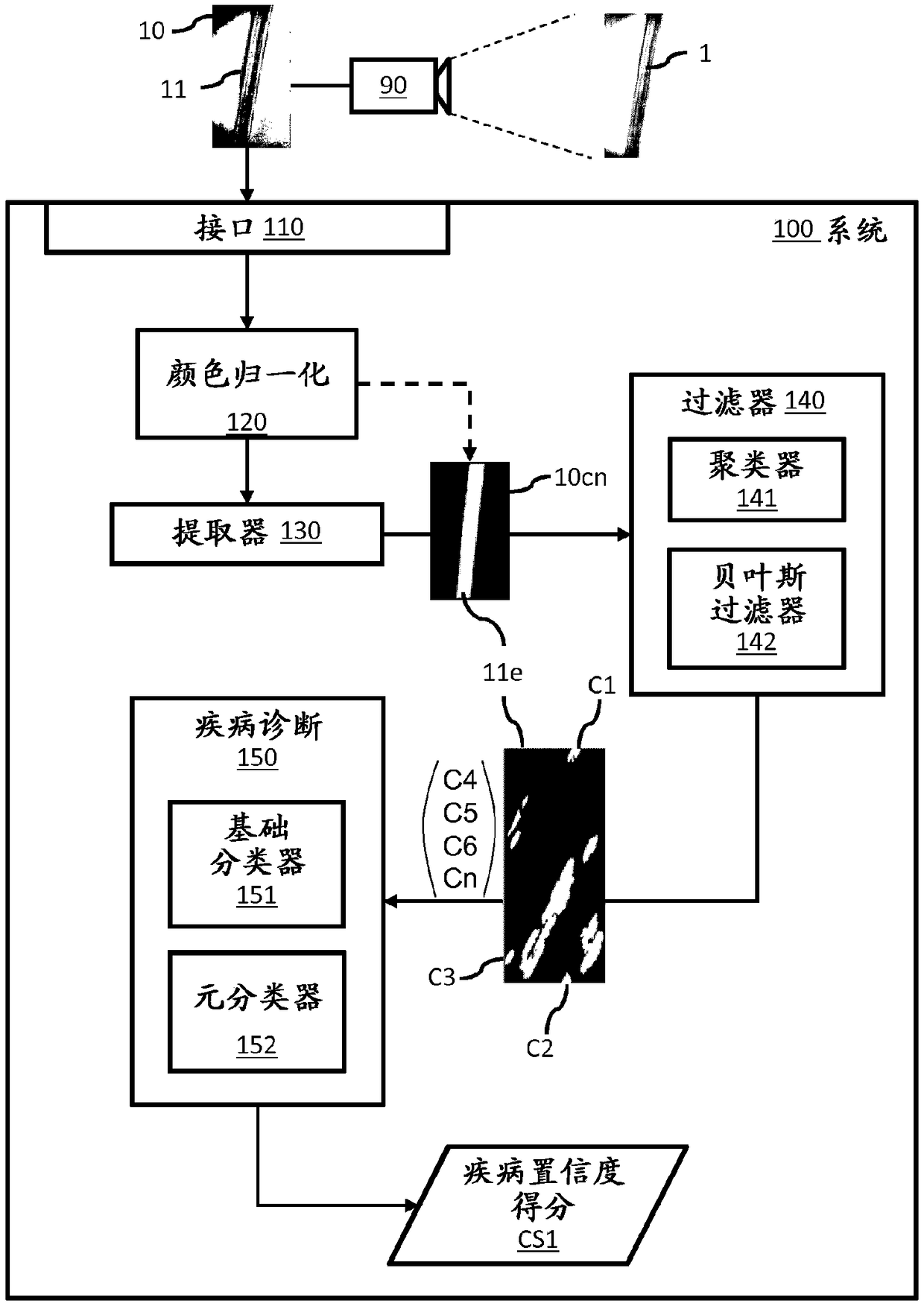
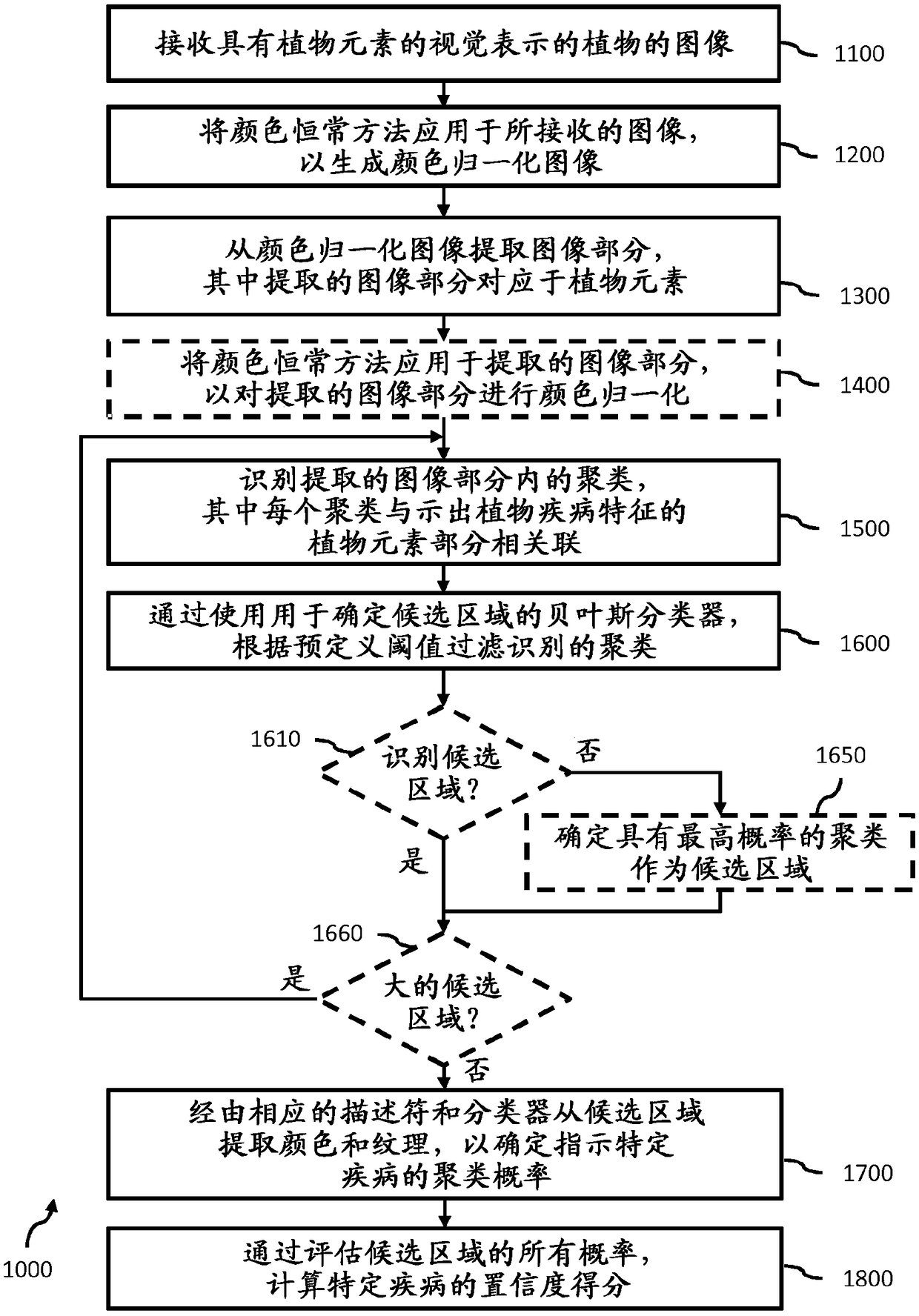
[0135] Embodiment 1 relates to a system for plant disease detection comprising: an interface module configured to receive an image of a plant comprising a visual representation of at least one plant element; a color normalization module configured to a color constancy method applied to the received image to generate a color normalized image; an extractor module configured to extract one or more image portions from the color normalized image, wherein the extracted image portion is associated with at least one plant element a filtering module configured to: identify one or more clusters from one or more visual features within the extracted image portion, wherein each cluster is associated with a portion of a plant element showing a plant disease signature; and, One or more candidate regions are filtered from the one or more clusters identified according to a predefined threshold by using a Naive Bayes classifier that is always present in patients indicative of a particular diseas...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Embodiment 2 relates to the system of embodiment 1, wherein the color normalization module is further configured to apply one or more color constancy methods to the extracted one or more image portions to Color normalization of image parts.
Embodiment 3
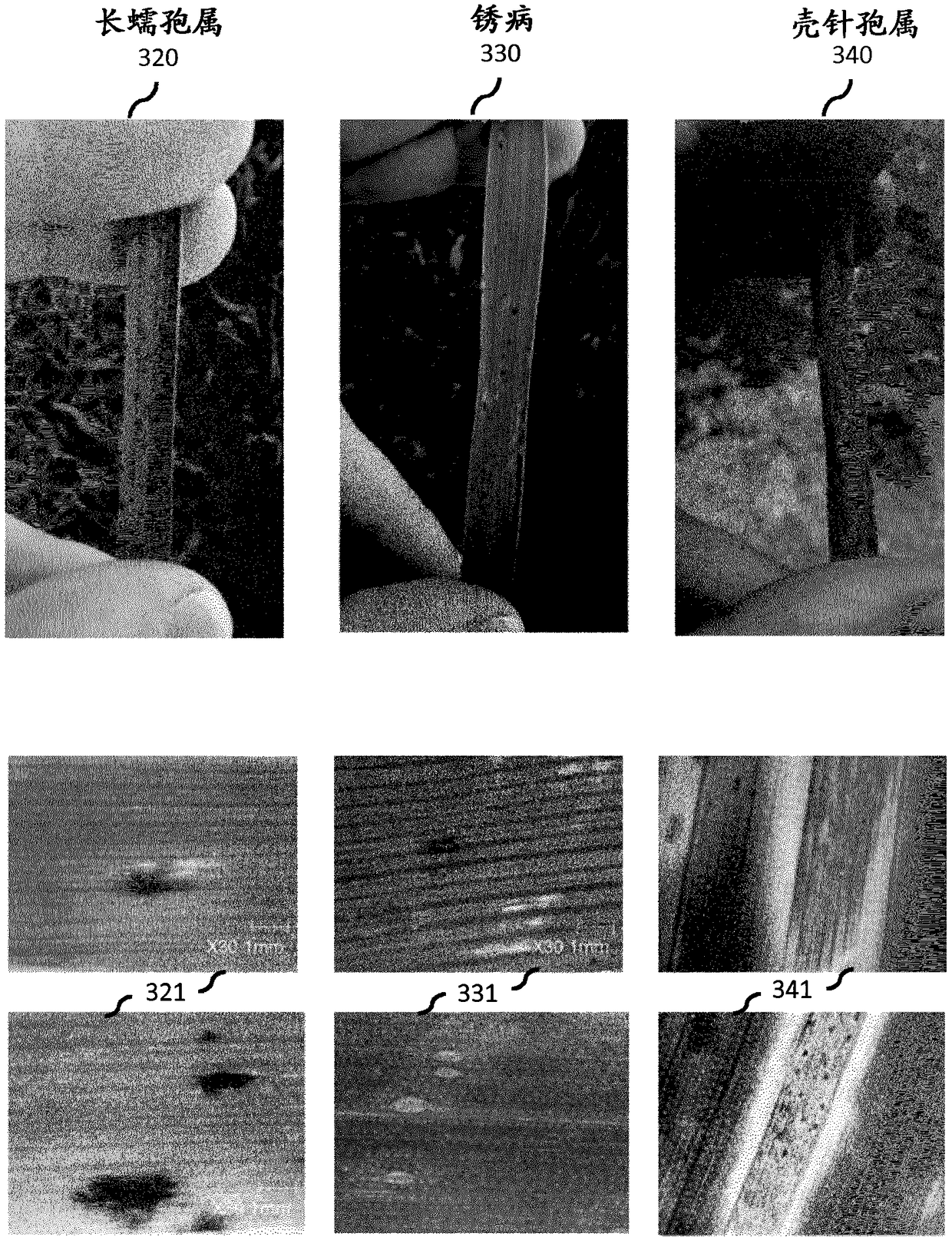
[0137] Embodiment 3 relates to the system of embodiment 1 or 2, wherein different plant diseases are associated with different image-disease-features, wherein the filtering module is further configured to extract from the plant disease pairs based on the identified image-disease-features Image parts are clustered.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com