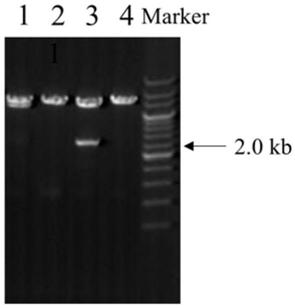
Application of long chain non-coded RNA-NKILA in bone tissue damage repair
A long-chain non-coding, damage repair technology, applied in the field of stem cell bioengineering, can solve problems such as many complications, immune rejection, iatrogenic infection, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting calcium ion deposition and enhancing alkaline phosphatase activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Acquisition of NKILA gene fragments
[0030] According to the RNA nucleotide sequence of the long-chain non-coding RNA-NKILA in the NCBI database (RefSeq sequence number: NR_131157.1, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence listing) and BamH I and Xba I on the lentiviral vector pLV Specific enzyme cutting sites, using DNA chem192 synthesizer, according to the principle of solid-phase phosphoramidite triester method, double-strand synthesis of NKILA gene fragments, and adding two specific enzyme cutting sites on the 5' end and 3' end respectively site BamH I (GGATCC) and Xba I (TCTAGA) to obtain a NKILA gene fragment containing a specific restriction site, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence listing.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Construction of lentiviral expression vector pLV-NKILA
[0032] Restriction endonucleases BamH I and Xba I were used to double-enzyme the lentiviral empty vector pLV (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 in the sequence listing) and the NKILA gene fragment obtained in Example 1, respectively. The T4 DNA ligase system was used to carry out ligation reaction between the digested NKILA gene fragment and the linear lentiviral empty vector pLV, then transform competent cells, screen positive colonies, and extract the plasmids of positive colonies to obtain the lentiviral expression vector pLV- NKILA.
[0033] 1. Enzyme digestion of lentiviral empty vector pLV
[0034] The enzyme digestion reaction system is as follows (20 μL):
[0035]
[0036] Reaction conditions for enzyme cleavage: react at 37°C for 4 hours.
[0037] 2. Enzyme digestion of NKILA gene fragment
[0038] The enzyme digestion reaction system is as follows (20 μL):
[0039]
...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3: Lentiviral Packaging
[0055] HEK293T cells were seeded in six-well culture plates for culture, and cultured in a cell culture incubator at 37°C with DMEM complete medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). When the cell density reached about 70%, the Lipofectamine 3000 liposome transfection reagent (purchased from Thermo Fisher, model L3000015), respectively transfected lentiviral expression vector pLV-NKILA and lentiviral empty vector pLV into HEK293T cells for lentiviral packaging. Specific steps are as follows:
[0056] 1) Take two 1.5mL EP tubes and add 150μL serum-free DMEM medium to each;
[0057] 2) Add 1 μg lentiviral expression vector pLV-NKILA, 0.5 μg lentiviral packaging plasmid pSPAX2, and 0.5 μg lentiviral packaging plasmid pMD2G into one of the EP tubes, and mix well;
[0058] 3) Add Lipofectamine 3000 liposome transfection reagent into another EP tube and mix well;
[0059] 4) Quickly add the plasmid solution obtained in step 2) to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com