Method for improving dehydration performance of citric acid wastewater sludge by using penicillium oxalicum
A technology of citric acid wastewater and Penicillium oxalicum, which is applied in dehydration/drying/concentrated sludge treatment, biological sludge treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of biological conditioning that have not been reported, the source of the bacteria is not specified, and the cultivation period is long. Achieve the effect of short separation and purification cycle, easy operation, and improved dehydration performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Test sludge sample
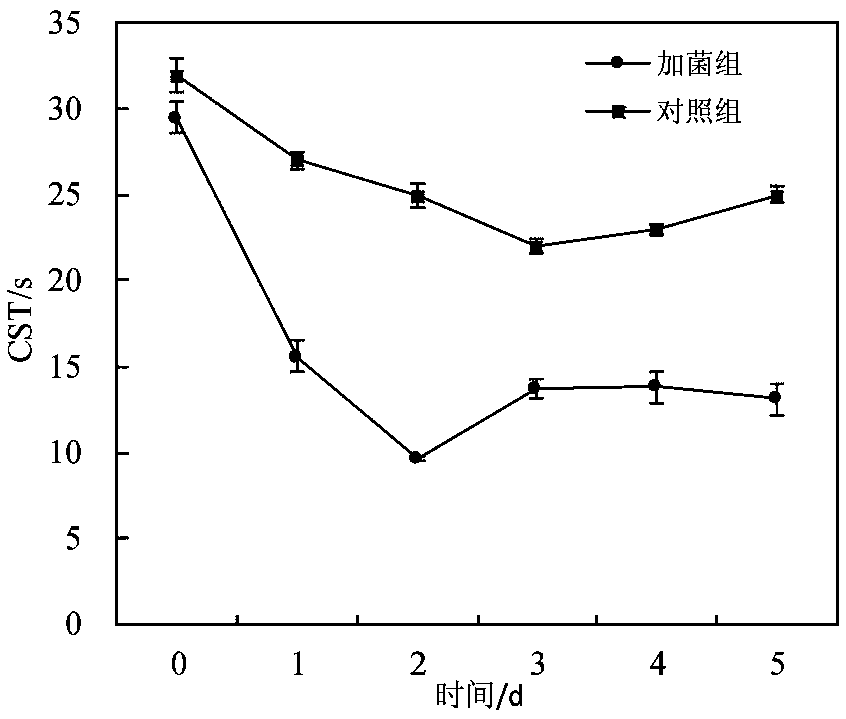
[0038] The method of the present invention uses Penicillium oxalicum to improve the dewatering performance of citric acid sludge. During specific implementation, the test sludge sample is taken from the secondary sedimentation process of the oxidation ditch treatment process of a sewage treatment workshop of a citric acid production enterprise in Shandong The pond returns sludge. The company produces 60t of absolutely dry sludge every day. The sludge treatment method is to add PAM coagulation after concentration. The dosage is 6kg / t of absolute dry sludge. Finally, it is dehydrated by plate and frame filter press or belt filter press. The basic characteristics of the tested sludge are shown in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1 Basic characteristics of the tested sludge samples
[0040] Water content (%)
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Separation and purification of sludge filamentous fungi
[0042] Dilute the citric acid wastewater sludge sample by 10~10 5 After the different concentration gradients, they were inoculated into Sabouraud medium by the spreading plate method, and cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 25~30℃ for 2~3 days. Various fungal colonies were isolated and picked using the three-point inoculation method. The colony was expanded and cultivated in a petri dish. Repeat the inoculation 3 to 5 times to obtain fungi with different colony morphology after separation and purification. Fungi with different colony characteristics are respectively inoculated on the slant medium and stored in the refrigerator at 4°C.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Screening and identification of filamentous fungi
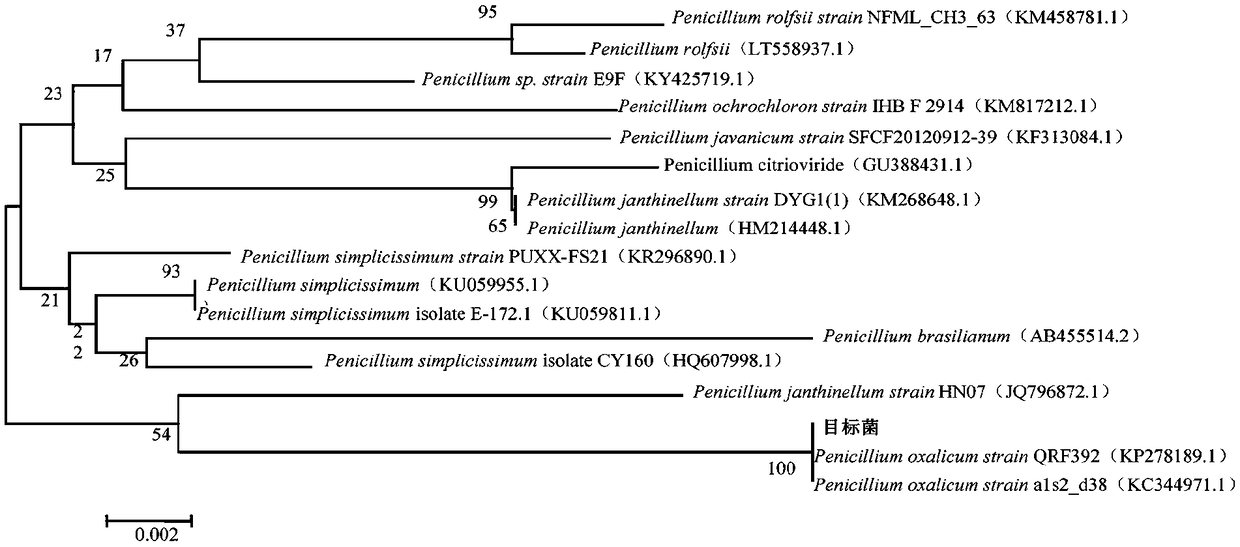
[0044] The purified fungi were analyzed for morphology and growth characteristics, and the filamentous fungi with fast growth rate and developed mycelium were screened out, and then organic matter degradation experiments were performed on them, including gelatin liquefaction, cellulose hydrolysis, starch hydrolysis, and the characteristics were screened out. Obvious filamentous fungus, after 18SrDNA gene sequence and morphological identification, the morphology under microscope looks like figure 1 As shown, it was identified as Penicillium oxalicum.
[0045] (1) Gelatin liquefaction experiment
[0046] Medium configuration: 20 g of glucose, 5.0 g of peptone, 200 g of gelatin, dissolved in 1000 mL of distilled water for sterilization, and 10 mL of the sterilized medium solution was placed in a test tube. The fungus was inoculated on the culture medium and cultured at 25°C and 180 rpm for several days. The blank con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com