Passivation contact electrode structure and applicable solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
A solar cell and contact electrode technology, applied in circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing carrier Auger recombination loss, difficulty in mass production, irradiation loss, etc., and reduce surface recombination efficiency. , strong electrical conductivity, the effect of reducing radiation loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
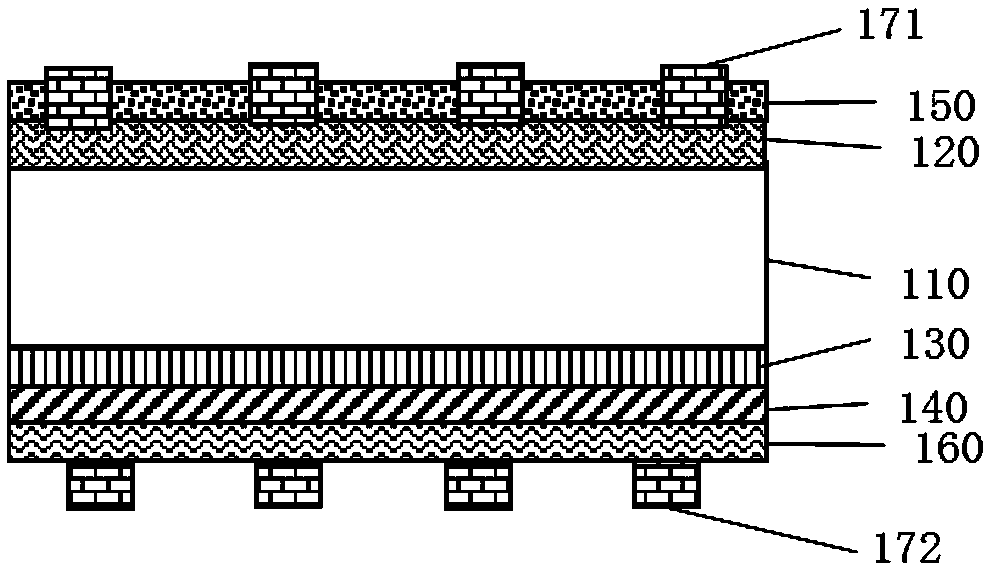
[0034] figure 1 An exemplary diagram illustrating fabrication of a solar cell according to an embodiment of the present invention is illustrated.
[0035] The crystalline silicon substrate 110 may be an n-type or p-type crystalline silicon wafer with a thickness of 70-250 μm. In this embodiment, the crystalline silicon substrate 110 is preferably a p-type crystalline silicon wafer, which may be a single crystal or polycrystalline silicon wafer. The p-type crystalline silicon substrate 110 is cleaned and textured. Phosphorus is diffused on the front side of the textured p-type crystalline silicon substrate to form an n-type doped crystalline silicon layer 120 emitter.
[0036] Fabricate passivated contact electrode structures on the back of the cell. The passivation contact electrode structure includes a doped semiconductor layer 140 deposited on the crystalline silicon substrate 110 as one of doped polysilicon, microcrystalline silicon or microcrystalline silicon-carbon all...
Embodiment 2
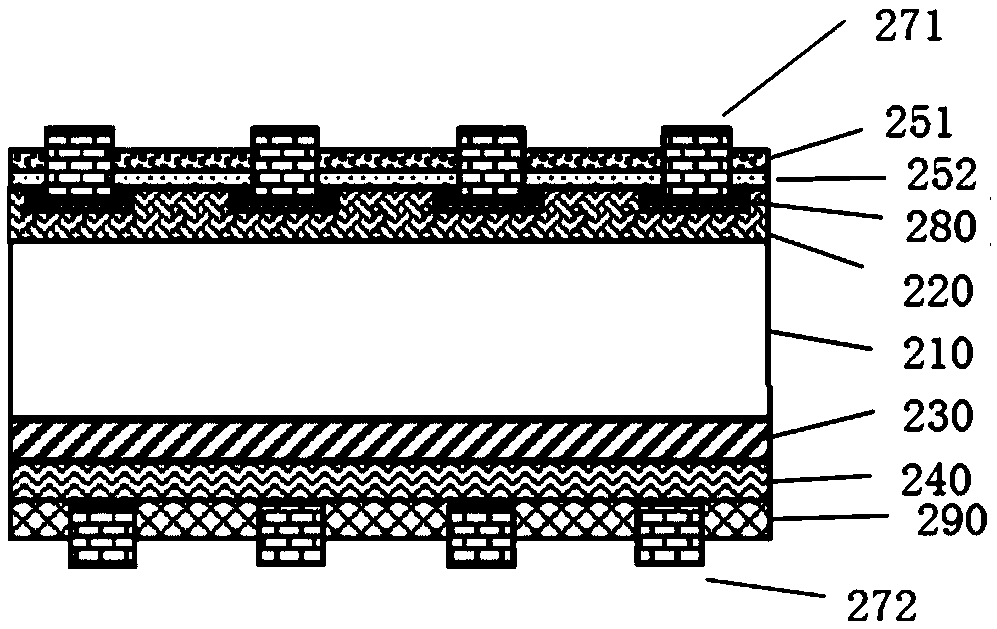
[0045] figure 2 A diagram illustrating an example of manufacturing a solar cell according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0046] In this embodiment, the crystalline silicon substrate 210 is an n-type crystalline silicon wafer, which may be a single crystal or polycrystalline silicon wafer. The n-type crystalline silicon substrate 210 is cleaned and textured. Boron diffusion is performed on the front surface of the textured n-type crystalline silicon substrate 210 to form a p-type crystalline silicon layer 220 emitter.
[0047] A polysilicon layer 230 is deposited on the back of the crystalline silicon substrate 210 by LPCVD or PECVD, preferably with a thickness of 5-50 nm, and then the polysilicon layer 230 is heavily doped with n-type by ion implantation.
[0048] On the p-type crystalline silicon layer 220 on the front side of the battery, use PECVD or atomic layer deposition (ALD) to make Al with a thickness of about 2-20nm. 2 o 3 Layer 251 and use P...
Embodiment 3
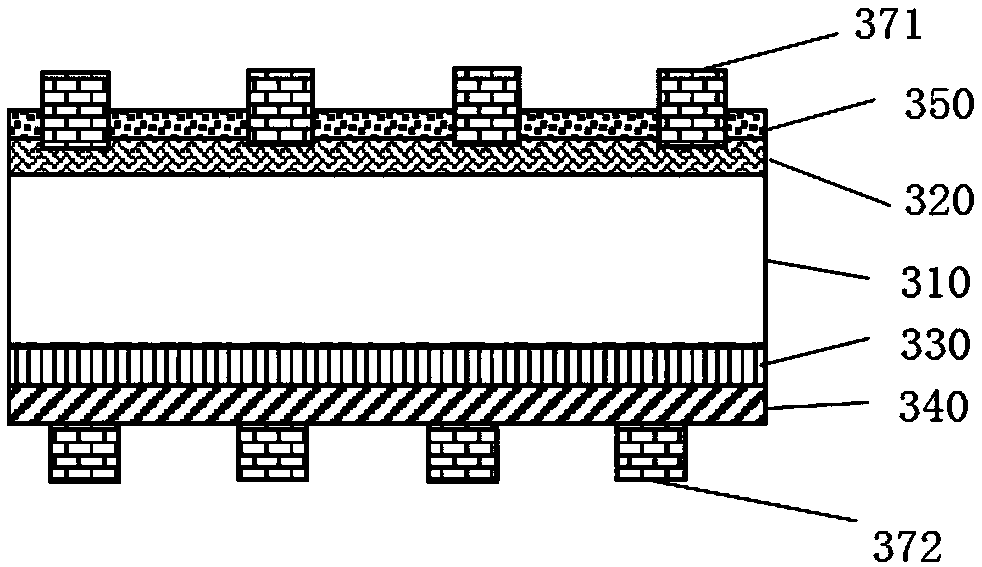
[0054] image 3 Another example diagram illustrating the fabrication of a solar cell according to an embodiment of the present invention.
[0055] In this embodiment, the crystalline silicon substrate 310 is an n-type crystalline silicon wafer, which may be a single crystal or polycrystalline silicon wafer. The n-type crystalline silicon substrate 310 is cleaned and textured. Phosphorus is diffused on the front side of the textured n-type crystalline silicon substrate 310 to form an n-type heavily doped crystalline silicon layer 320 .
[0056] Formation of SiN on the back of the cell using PECVD x The thickness of the tunneling thin film layer 330 is preferably 1-5 nm.
[0057] In SiO 2 The microcrystalline silicon layer 340 is deposited on the tunneling film layer 330 by PECVD or HWCVD, with a thickness of preferably 5-50 nm, and then the microcrystalline silicon layer 340 is doped with p-type by ion implantation.
[0058] Deposit 80-150nm SiN on the n-type heavily doped...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com