Two-step method for preparing instant high molecular weight polyacrylamide
A polyacrylamide and high molecular weight technology is applied in the field of two-step preparation of instant high molecular weight polyacrylamide. easy clumping effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
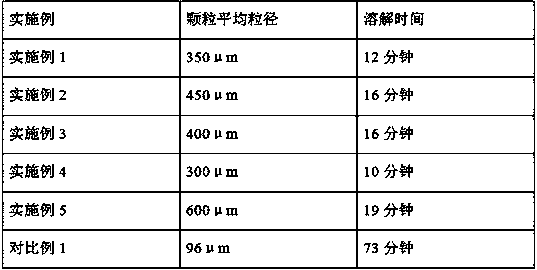
[0028] Add 300 g of cyclohexane into a 1 L four-neck flask, add 1.15 g of sorbitan monostearate and 1 g of sucrose fatty acid ester with an HLB value of 3, and heat until dissolved. Dissolve 95g of acrylamide and 0.8g of potassium persulfate in 200g of water in a beaker, and put them into a four-necked flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. Rotate at 400 rpm, blow nitrogen, stir for 30 minutes, and keep the temperature at 40°C. Heat to 70°C, react for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 75°C and keep for 1 hour. In another flask, add 20g of ethanol and 100g of water to form a mixed solution. The alcohol-water mixed solution was added dropwise into the four-neck flask, and the dropwise addition was completed within half an hour, and the stirring was continued for half an hour. Azeotropic removal of water yielded white solid particles with an average particle size of 350 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Add 300g of n-hexane into a 1L four-necked flask, add 2g of hydrophobic nano-silica and 1g of diethylene glycol fatty acid ester, and heat until dissolved. Dissolve 95g of acrylamide and 0.8g of sodium persulfate in 200g of water in a beaker, and add them into a four-necked flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. Rotate at 400 rpm, blow nitrogen, stir for 30 minutes, and keep the temperature at 40°C. Heat to 70°C, react for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 75°C and keep for 1 hour. In another flask, add 6g of ethanol and 50g of water to form a mixed solution. The alcohol-water mixed solution was added dropwise into the four-neck flask, and the dropwise addition was completed within half an hour, and the stirring was continued for half an hour. Azeotropic removal of water yielded white solid particles with an average particle size of 450 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Add 300 g of toluene into a 1 L four-neck flask, add 3 g of glyceryl monostearate, and heat until dissolved. Dissolve 95g of acrylamide and 0.8g of azobisisobutylimidazoline hydrochloride in 200g of water in a beaker, and add them into a four-necked flask under a nitrogen atmosphere. Rotate at 400 rpm, blow nitrogen, stir for 30 minutes, and keep the temperature at 40°C. Heat to 60°C, react for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 75°C and keep for 1 hour. In another flask, add 10g of isopropanol and 100g of water to form a mixed solution. The alcohol-water mixed solution was added dropwise into the four-neck flask, and the dropwise addition was completed within half an hour, and the stirring was continued for half an hour. Azeotropic removal of water yielded white solid particles with an average particle size of 400 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com