Laser-induced photothermal expansion drive device
A driving device and thermal expansion technology, which is applied in the drive of manipulators, medical equipment and industrial mechanical devices, and in the field of robots, can solve the problems of inability to realize control, difficulty in miniaturization and integration, high energy consumption, etc., and achieve excellent photothermal and electric co-expansion drive function , easy integration and miniaturization, and the effect of improving work performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
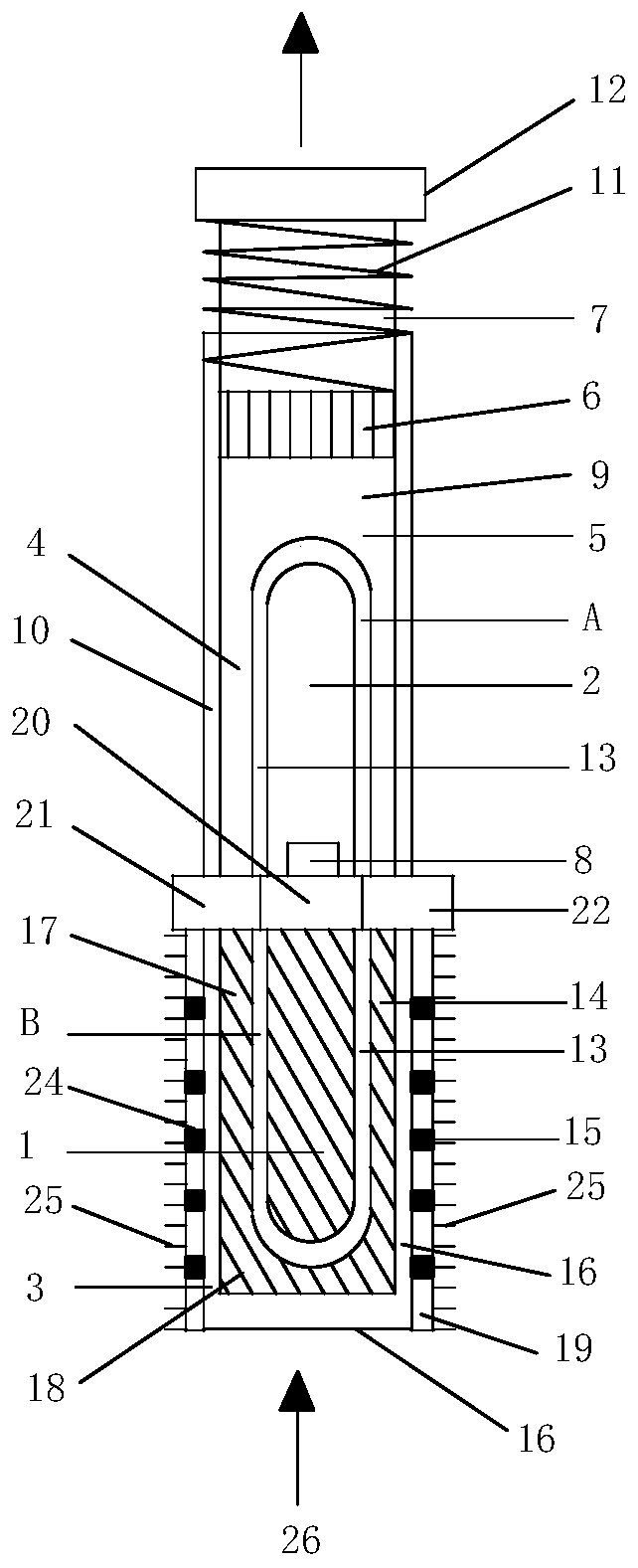
[0024] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a laser-induced photothermal expansion driver (see figure 1 ), including: including: laser heating and cooling two-way worker 1, photothermal expansion conversion driver 2; laser heating and cooling two-way worker 1, including: laser, graphene-type laser thermoelectric converter 3; photothermal expansion conversion driver 2 , including: photothermal phase change expansion driver 4; photothermal phase change expansion driver 4, including: photothermal phase change expansion material 5, liquid metal 13, liquid metal U-shaped tube A, photothermal expansion drive piston 6, light Thermal expansion drive rod 7, temperature sensor 8, cylinder body 9, heat insulation layer 10, ordinary spring 11, optical thermal expansion driving force output end 12; liquid metal 13 is assembled in liquid metal U-shaped tube A; liquid metal U-shaped tube A, optical The thermal phase change expansion material 5, the photothermal expansion driving pi...
Embodiment 2
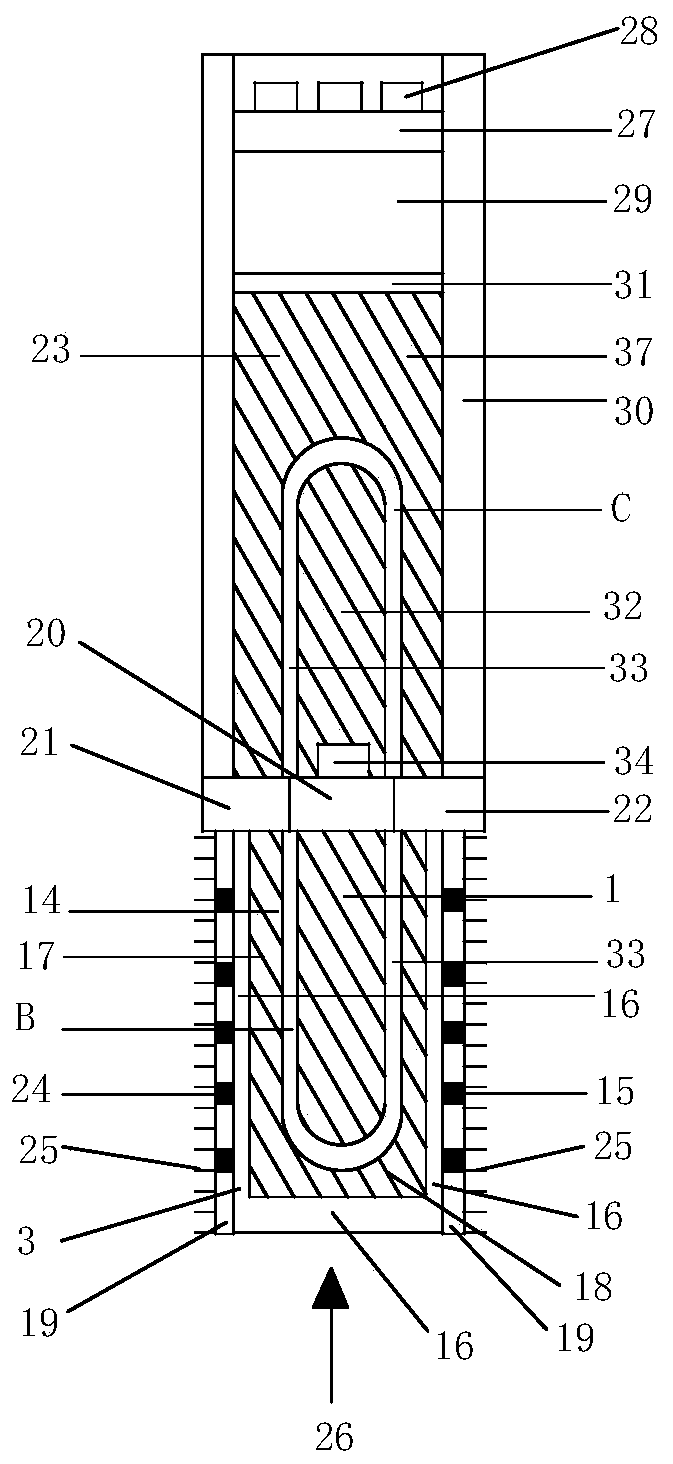
[0033] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a laser-induced photothermal expansion-driven microvalve (see figure 2 ), including: laser heating and cooling two-way worker 1, photothermal expansion-driven microvalve 23; said photothermal expansion-driven microvalve 23, including: graphene type liquid metal heater 37, polymer driving layer 27, micro Channel matrix 28, cavity 29, heat insulating layer 30; graphene-type liquid metal heater 37, including: second graphene layer 31, graphene heat conduction composite matrix 32, high-temperature liquid metal 33, liquid metal U-shaped tube C, Temperature sensor 34; high-temperature liquid metal 33 is assembled in liquid metal U-shaped tube C; liquid metal U-shaped tube C and temperature sensor 34 are assembled in graphene thermally conductive composite matrix 32; graphene thermally conductive composite matrix 32 passes through the second graphite The alkene layer 31 is closely connected with the cavity 29; the other end of th...
Embodiment 3
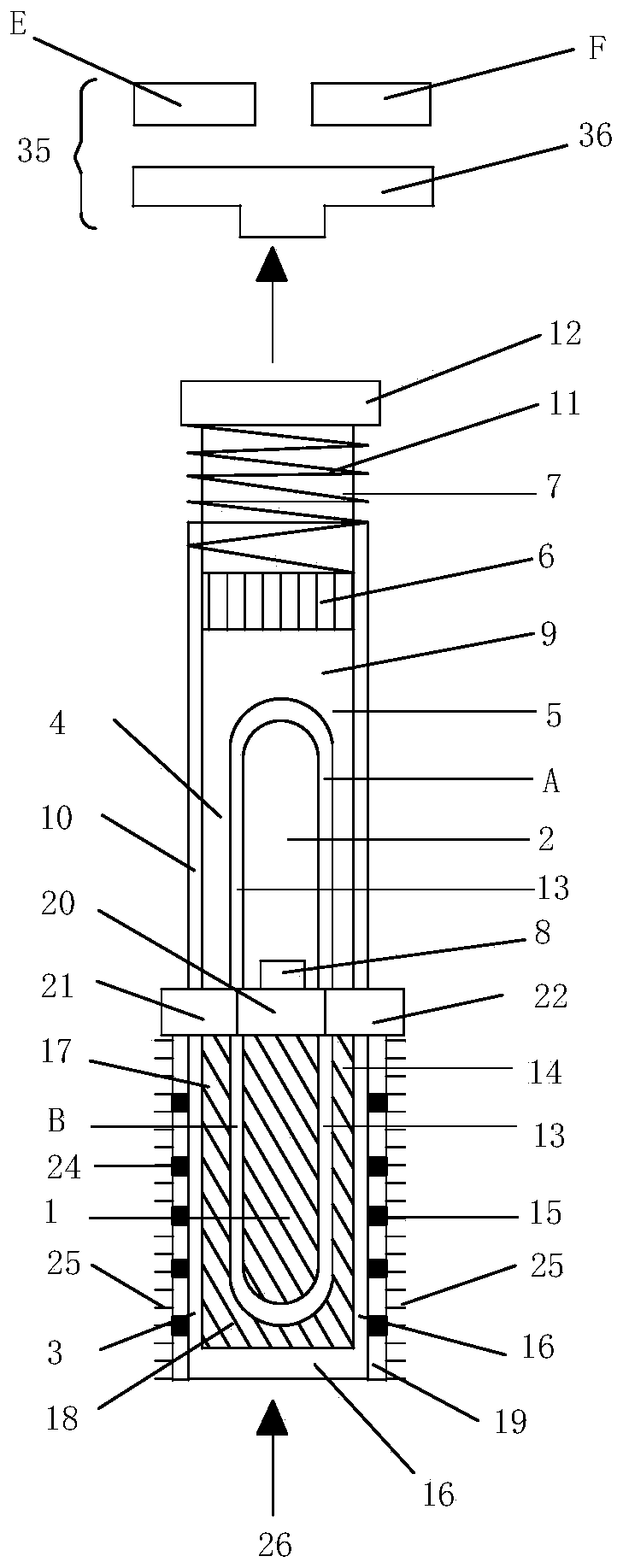
[0040] Embodiment three of the present invention provides a laser-induced photothermal expansion driven relay (see image 3 ), including: laser-induced thermal expansion drivers (see figure 1 , image 3 ), photothermal expansion driven relay 35 (see image 3 ); the photothermal expansion driven relay 35 includes: photothermal expansion driven linear moving piece 36, contact E, contact F; photothermal expansion driven linear moving piece 36 is close to the photothermal expansion driving force output end 12 of the laser-induced photothermal expansion driver. The laser-induced photothermal expansion driver (the working principle and process are the same as those in Embodiment 1) and the photothermal expansion-driven relay jointly constitute the laser-induced photothermal expansion-driven relay. Driven by the photothermal expansion driving force output end 12 of the laser-induced photothermal expansion driver, the photothermal expansion driven linear moving piece 36 can move lin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com