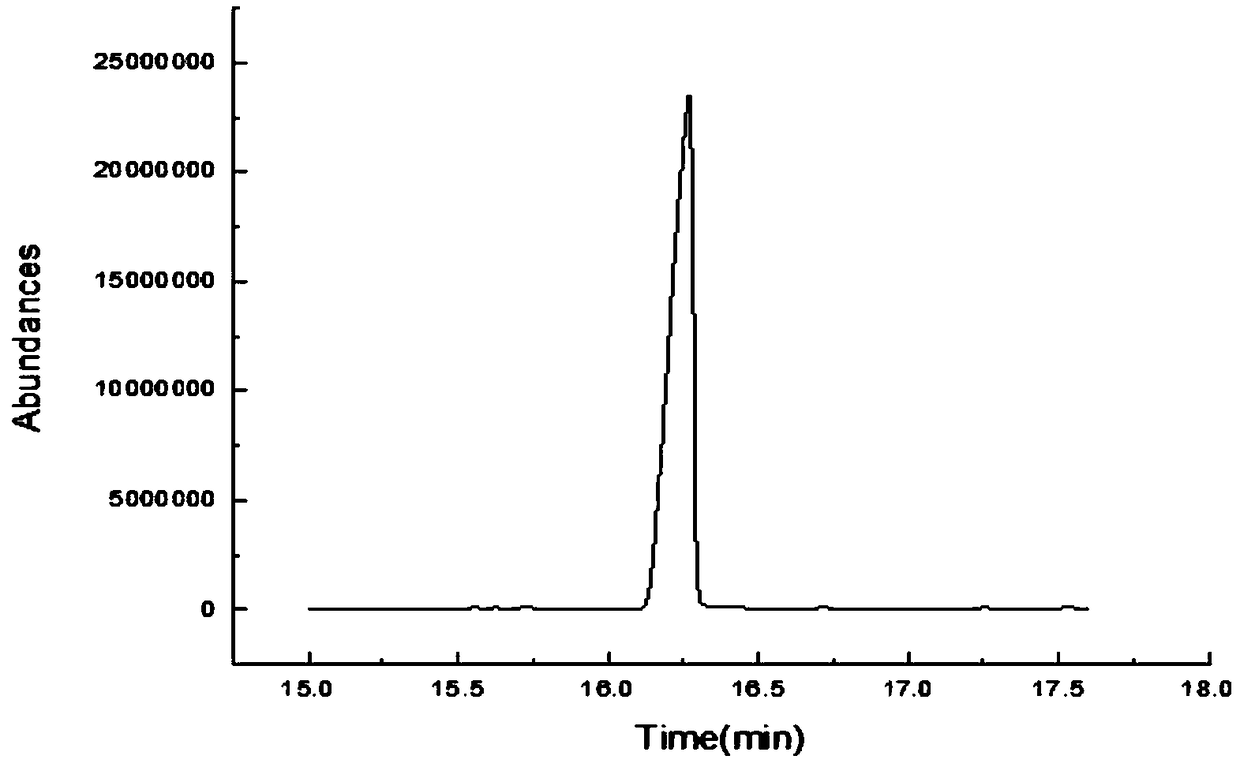
Strain and method for producing beta-phenethyl alcohol
A technology of phenylethyl alcohol and bacterial strains, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low concentration of β-phenylethyl alcohol products and less selection of production strains, and achieve the effects of easy control of fermentation conditions, good industrial application value, and low raw material cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Screening of Enterobacter sp.strain MF024 Strain
[0038] Collect root soil samples of roses, roses, lilies, etc. in forest parks around Shanghai, weigh 0.5-1.5g and dissolve them in sterile water, add an appropriate amount of glass beads and mix well, then add them to the liquid bacterial screening medium. Under the condition of 28-37 ℃, 200-300rpm shaker shakes and cultivates for 48h, then transfers to fresh liquid bacterial selection medium with 5% inoculum size (V / V) and cultivates for 24-48h, repeats this process 3- 5 times. Dilute the cultured bacteria by 10 -7 Double-coated on the solid bacterial screening medium, and cultured in an incubator at 30°C for 24-72h.
[0039] The morphology of the bacteria was observed under a microscope, and single colonies of different shapes were selected to be streaked on the solid bacterial screening medium, and cultured in an incubator at 30°C for 24-48h. Repeat 3-6 times until the morphology of the bacteria observed under th...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Strain 16S rDNA identification:
[0046] Enterobacteriaceae (MF024) obtained in the present invention were sent to Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd. for detection of 16S rDNA sequence. The obtained 16S rDNA sequence of the strain is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:1.
[0047] Among them, the general primers for PCR of 16S rDNA are:
[0048] 27F (5'→3'):agagtttgatcctggctcag;
[0049] 1492R (5'→3'): ggttacccttgttacgactt.
[0050] The 16S rDNA sequence (GenBank No. MG554655) of the strain of the present invention (MF024) was homologously compared with the 16S rDNA sequence in GenBank, and it was found that the highest similarity with Enterobacter strains was 99%, but not completely identical.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Physiological and biochemical identification:
[0053] Pick a single colony (MF024) of the bacterial strain of the present invention, inoculate it in LB liquid medium with a pH of 7.0, cultivate it at 30° C. and 200 rpm for 24 hours, and insert it into the biochemical identification strip of Enterobacteriaceae of Qingdao High-tech Industrial Park Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , to detect its physiological and biochemical properties. The results of the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain are as follows:
[0054] Table 1: Results of physiological and biochemical characteristics of Enterobacter sp.strain MF024
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] Symbols: +, 90%-100% of the strains are positive; -, 90%-100% of the strains are negative; D40%-60% of the strains are positive.
[0058] Physiological and biochemical characteristics indicated that this strain conformed to the relevant properties of the genus Enterobacter.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com