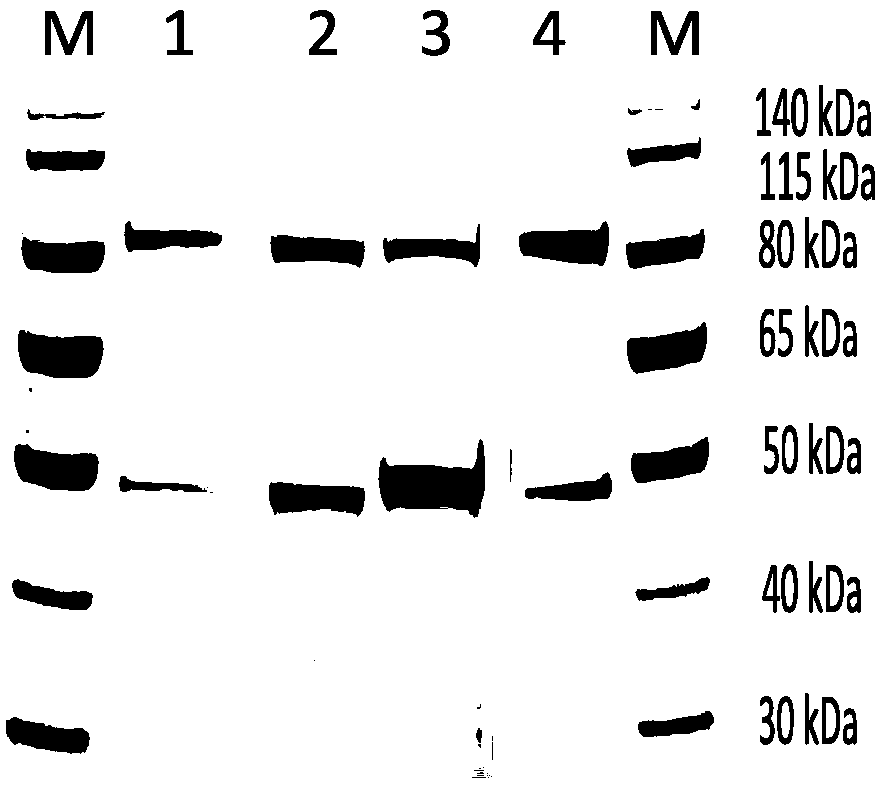
Mutant xanthine dehydrogenase and applications thereof
A technology of xanthine oxidase and xanthine, which is applied in the application field of variant xanthine dehydrogenase, degrading samples containing hypoxanthine and xanthine, and can solve problems such as XDH transformation of Rhodobacter capsularis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Embodiment 1, the preparation of variant xanthine dehydrogenase
[0079] 1. Construction of mutant xanthine dehydrogenase recombinant plasmid
[0080] 1. Selection of mutation sites and design of mutation primers
[0081] The fundamental difference between xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase lies in the difference in the structure of the electron acceptor region, resulting in different redox environments and thus different selectivities for NAD and oxygen. The present invention selects D358, F270, and S362 sites that contribute greatly to the oxidation-reduction potential of the electron acceptor region for site-directed mutation, and constructs a mutant xanthine dehydrogenase that utilizes oxygen as an electron acceptor to enhance activity.
[0082] The mutation method mediated by PCR primers was used to construct mutants using the recombinant plasmid pTRAN as a template. The sequences of the designed primers were as follows:
[0083] Primer pairs for constru...
Embodiment 2
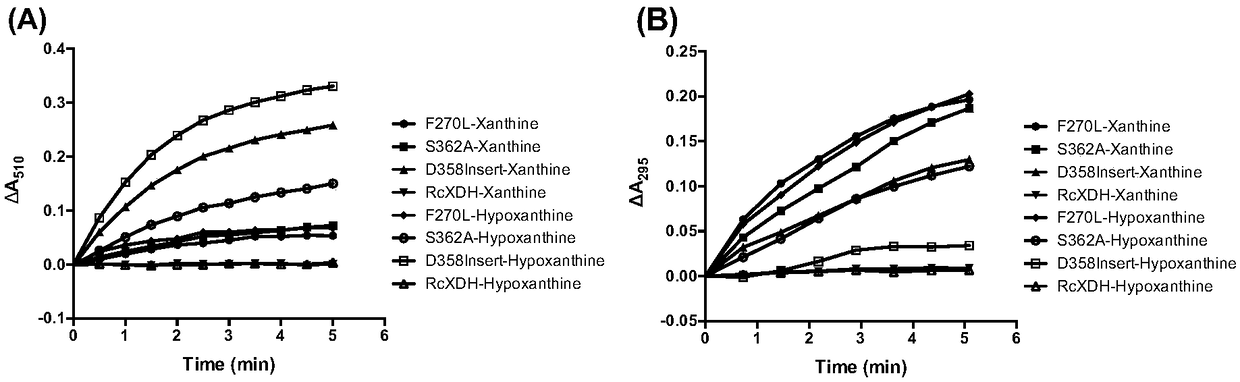
[0117] Embodiment 2, the characterization of variant xanthine dehydrogenase as xanthine oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase
[0118] 1. Determination of xanthine oxidase activity
[0119] The xanthine oxidase activity of variant xanthine dehydrogenases can be precisely characterized by two methods.
[0120] The first method is based on xanthine oxidase catalyzing the following reactions (reaction formulas 1 and 2). Uric acid has specific absorption at 295 nm, so the enzyme activity can be characterized by measuring the generation of product uric acid by spectrophotometry.
[0121]
[0122]
[0123] In the present invention, the reaction system for measuring xanthine oxidase enzyme activity is shown in Table 1.
[0124] The 2mL reaction system composition of table 1 xanthine oxidase activity assay
[0125] Numbering
sample name
Mother solution concentration (mM)
Amount added (μL)
Final concentration (mM)
1
Tris-HCl aqueous solution at p...
Embodiment 3
[0181] Example 3. Application of mutant xanthine dehydrogenase as xanthine oxidase in degrading xanthine and hypoxanthine and processing materials containing such substrates
[0182] 1. Method 1
[0183] With reference to the construction method of the xanthine oxidase reaction system in Table 2, construct the following a) to j) 8 groups of reaction systems:
[0184] a) 50mM Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH 8.5), respectively containing EDTA with a final concentration of 1mM, 0.1mM potassium oxonate, 0.1mM xanthine, 0.0033% 4-AAP, 0.2% phenol, 2.68U The variant xanthine dehydrogenase F270L prepared by / ml horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and 1.56mg / L embodiment 1;
[0185] b) 50mM Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH 9.5), respectively containing final concentration of 1mM EDTA, 0.1mM potassium oxonate, 0.1mM xanthine, 0.0033% 4-AAP, 0.2% phenol, 2.68U The variant xanthine dehydrogenase D358Insert prepared by / ml horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and 1.23mg / L embodiment 1;
[0186] c) 50mM Tris-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com