A fusion protein and its preparation method and its application in the preparation of ophthalmic diseases, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor drugs
A fusion protein and ophthalmic disease technology, applied in the direction of anti-tumor drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, metabolic diseases, etc., can solve the problems of single target, short half-life of polypeptides, etc., to reduce the frequency of medication, prolong the half-life, and increase drug compliance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
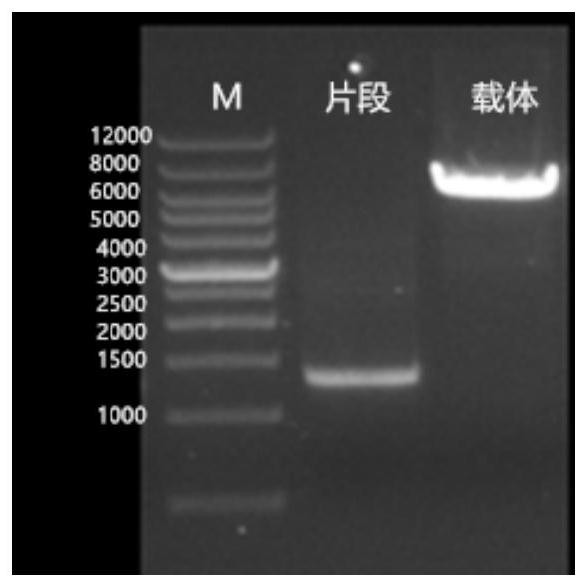
[0044] (1) Acquisition of fusion protein gene and construction of expression vector
[0045] The sequence of angiostatic polypeptide HM-3 is shown in SEQ ID NO.5, the sequence of interleukin 4 is shown in SEQ ID NO.6, and the human immunoglobulin IgG1-Fc region (SEQ ID NO.7) is passed through different connecting peptides Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser flexible (F) linker, AlaGluAlaAlaAlaAlaLysGluAlaAlaAlaAlaLysGluAlaAla AlaLysGluAlaAlaAlaLysAla rigid (R) linker, connected with IL4DM-HM3 protein, designed two new Fc fusion proteins Fc-IL4DM-HM3, with flexible (F) The amino acid sequence of protein one constructed by linker is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of protein two constructed by rigid (R) linker is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. According to CHO cell codon preference, for 2 The coding sequence of a novel Fc fusion protein Fc-IL4DM-HM3 was optimized, and NheI restriction site, Kozak sequence and signal peptide were all introduce...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Inhibitory effect of fusion protein on proliferation of various tumor cells
[0098] MTT assay was used to detect the inhibitory effect of the integrin blocker fusion protein obtained in Example 1 on the proliferation of various tumor cells, including melanoma cells B16F10, gastric cancer cells MGC-803, lung cancer cells A549, liver cancer cells Hep-G2, Breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231, colon cancer cells HCT-116, human glioma U87, cervical cancer cells Hela.
[0099] Tumor cells were incubated at 37°C, 5% CO. 2 When the density was above 90%, the cells were collected by trypsin digestion. The cells were resuspended in the culture medium and counted under a microscope. The cell concentration was adjusted to 3.0×104 cells / mL, and the cell suspension was inoculated into a 96-well plate. medium, 100 μL per well, and incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 Incubate overnight in an incubator. The fusion protein 1, fusion protein 2 and positive drug Taxol were diluted with culture medium...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Three-dimensional transwell assay to detect the activity of fusion protein 1 and protein 2 in inhibiting the migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells
[0144] Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were cultured in endothelial cell culture medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum and 1×ECGS at 37°C, 5% CO 2 When the incubator was cultured to a confluency of more than 90%, the transwell method was used to detect the activity of fusion protein 1 and protein 2 to inhibit endothelial cell migration. Only the second to eighth passages of endothelial cell HUVEC were used. The specific operations are as follows:
[0145] (1) Dilute 1:4 with 10 mg / mL Matrigel in DMEM medium, spread on transwell membrane, and air dry at room temperature;
[0146] (2) The HUVEC cells cultured to the logarithmic growth phase were digested with 0.2% EDTA, collected, washed twice with PBS, resuspended in endothelial cell culture medium containing 0.1% BSA, counted under a microscop...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com