Environment-friendly flower fertilizer and fermentation process thereof
An environment-friendly, flower fertilizer technology, applied in the direction of nitrogen fertilizer, potassium fertilizer, magnesium fertilizer, etc., can solve the problems that are not conducive to the growth and development of flowers, the color of flowers is dim, and waste of resources, so as to promote the division of flower and grass cells, brighten the color and reduce environmental load. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
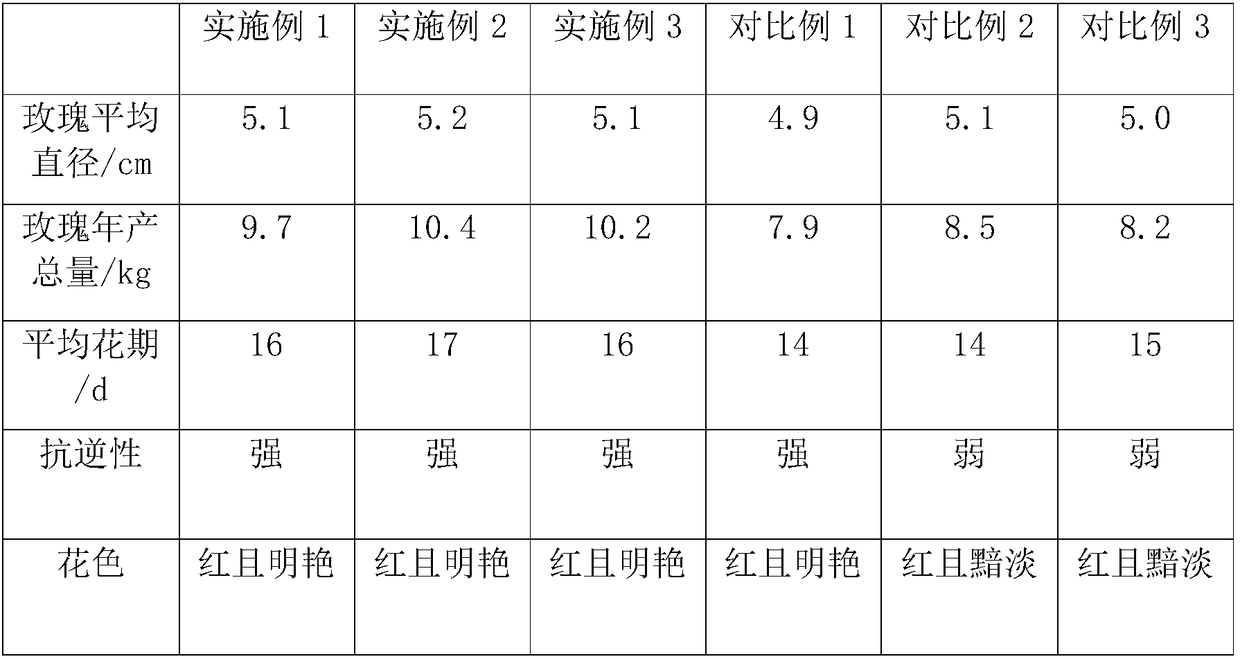
[0022] An environmentally friendly flower fertilizer, including the following raw materials by weight: 40 parts of agricultural and forestry waste, 30 parts of agricultural products, 25 parts of animal manure, 15 parts of plant ash, 2 parts of plant growth regulators, 8 parts of total nutrients, 1 part of decomposing bacteria, 3 parts of fermenting bacteria.
[0023] The present invention also provides the above-mentioned environmental protection type flower fertilizer fermentation process, which includes the following steps:
[0024] Step 1: Crush agricultural and forestry waste, agricultural product scraps, and animal manure to 40 meshes. The agricultural and forestry waste is crop stalks, and the agricultural product scraps are sugar residues. The water content is controlled to 50%, and the decomposing bacteria are inoculated. It is made by mixing Cellulomonas, Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma reesei in a weight ratio of 1:2.8:1.6. At 37°C, it is agitated with oxygen at a rate ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] 50 parts of agricultural and forestry waste, 35 parts of agricultural waste, 30 parts of animal manure, 19 parts of plant ash, 3 parts of plant growth regulators, 10 parts of total nutrients, 1.5 parts of decomposing bacteria, 3.5 parts of fermenting bacteria.
[0030] The fermentation process is the same as that in Example 1. The difference is: Step 1: The agricultural and forestry waste is sawdust, the agricultural products are waste residue from oil pressing, the water content is 53%, and the weight ratio of the components of the decomposing bacteria is 1:3.4:2.3. The fermentation temperature is 41℃, the oxygenation rate is 11L / min, and the final pH value is 4.5; Step 2: PH is 5.7, the weight ratio of each component of the fermentation bacteria is 1:3:1.7:0.7, and the first stage fermentation temperature is 34℃, the second stage fermentation temperature and days are 50℃ and 4 days respectively; Step 3: The concentration of each component of the plant growth regulator is ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] 60 parts of agricultural and forestry waste, 40 parts of agricultural products, 35 parts of animal manure, 23 parts of plant ash, 4 parts of plant growth regulators, 12 parts of total nutrients, 2 parts of decomposing bacteria, 4 parts of fermenting bacteria.
[0033] The fermentation process is the same as in Example 1. The difference is: Step 1: The agricultural and forestry waste is dead leaves, and the agricultural products are leftovers of wine and furfural. The weight ratio of the two is 1:1, the water content is 55%, and the decomposition bacteria are each group. The bacterial weight ratio is 1:4:3, the fermentation temperature is 45°C, the oxygenation rate is 14L / min, and the final pH value is 5; Step 2: The pH is 6, and the weight ratio of each component of the fermentation bacteria is 1:3.5 :2:0.8, the fermentation temperature in the first stage is 38℃, the fermentation temperature and days in the second stage are 55℃ and 5 days respectively; Step 3: the concentra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com