Tundish steel strip feeding device and method
A tundish and steel belt technology, applied in the field of tundish feeding steel belt devices, can solve the problems of floating and removing unfavorable inclusions, high equipment maintenance cost, inconvenient installation and maintenance, etc., and achieves a simple structure, improved quality, and convenient operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
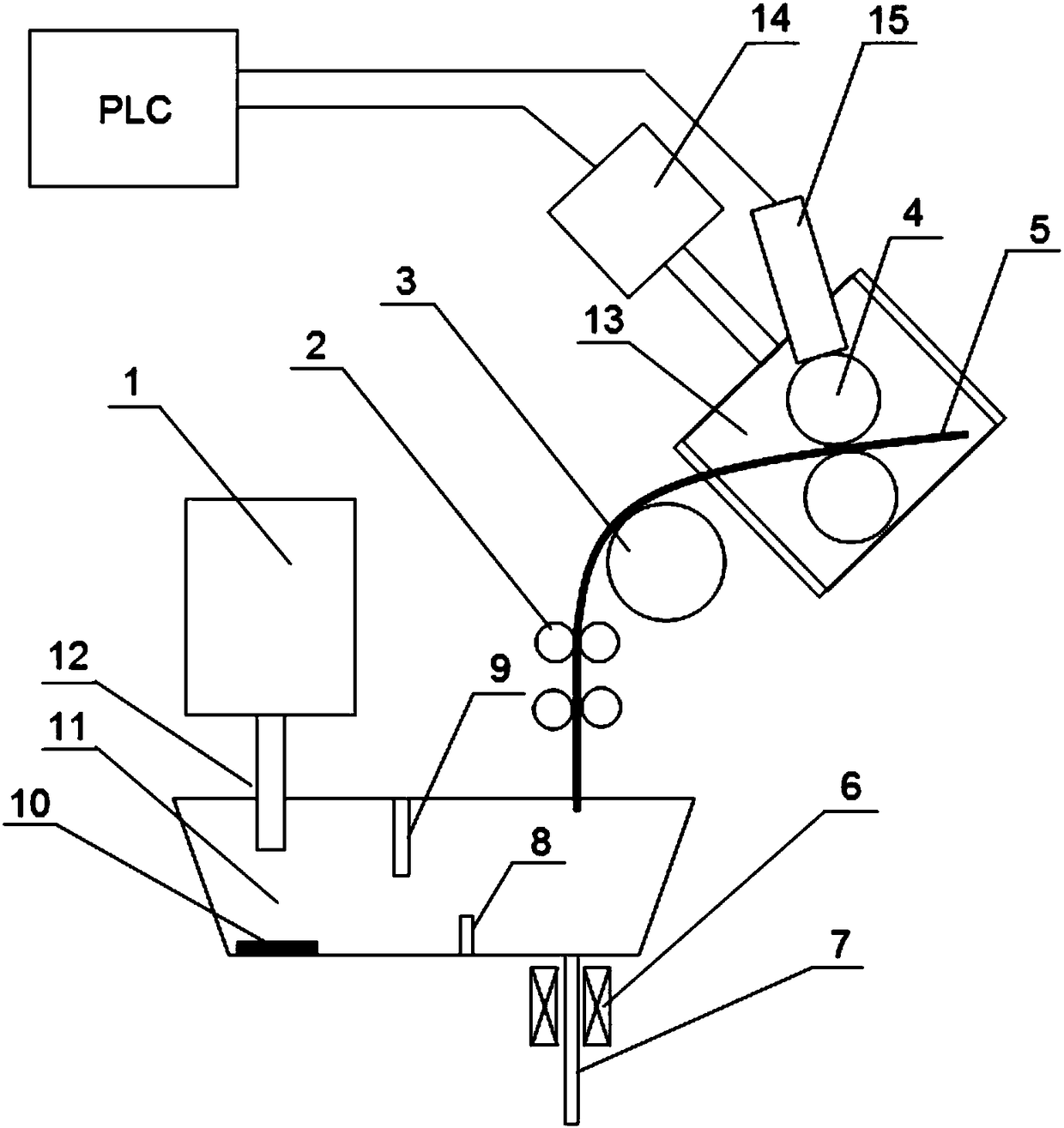
[0026] When casting aluminum-killed steel, the superheat of molten steel in ladle 1 is controlled at 25°C; the steel strip 5 to be fed is installed on the belt feeding device; when the amount of molten steel in tundish 11 reaches the required range, the immersion Measure the temperature of the molten steel above the nozzle 7, and know the superheat value of the molten steel in this area according to the temperature measurement; calculate the feeding rate based on the current superheat value of the molten steel in this area and the superheat value that needs to be controlled by the target. The amount of steel strip 5. Since aluminum-killed steel is prone to flocculation, the target superheat is controlled at 10°C. During the belt feeding operation, the operator of the continuous casting machine should observe the change of the liquid steel level in the mold. Once the flocculation phenomenon occurs at the submerged nozzle, the electromagnetic induction heater 6 around the submer...
Embodiment 2
[0028] When casting non-aluminum killed steel, the superheat of molten steel in ladle 1 is controlled at 20°C; the steel strip 5 to be fed is installed on the belt feeding device; when the amount of molten steel in tundish 11 reaches the required range, the Measure the temperature of the molten steel above the submerged nozzle 7, know the superheat value of the molten steel in this area according to the temperature measurement, and calculate the feeding Enter the amount of steel strip 5. Since non-aluminum killed steel is not prone to flocculation, the target superheat is controlled at 5 °C. During the belt feeding operation, the operator of the continuous casting machine should observe the change of the liquid steel level in the mold. Once the submerged nozzle 7 is found to have frozen flocculation, the electromagnetic induction heating around the submerged nozzle 7 should be started immediately. 6, and adjust its heating power frequency to 10000Hz. After the flocculation p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com