Method for preparing copper nanoparticles from modified polysaccharide
A copper nano-modification technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology and other directions for materials and surface science, can solve the problems of high environmental hazards, high price, easy oxidation of copper nanoparticles in reaction time, etc. Low cost, mild reaction, good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Modification of starch
[0025] Take a 250 ml round bottom flask, add 10 g of starch, 5 g of sodium periodate and 100 ml of deionized water in sequence, and stir for 12 hours in an oil bath at 37°C. Filter and wash with water 4 times, then place in a vacuum freeze dryer for 72 hours to obtain dry dialdehyde starch powder.
[0026] (2) Dissolution of dialdehyde starch
[0027] Get 2 grams of dialdehyde starch prepared in step (1) and place it in a beaker, add 90 milliliters of sodium hydroxide-urea solutions with mass fractions of 6% and 4%, respectively. After stirring at room temperature for 1 hour, freeze in a -20°C refrigerator for 12 hours, and then slowly thaw at room temperature to obtain a dialdehyde starch solution.
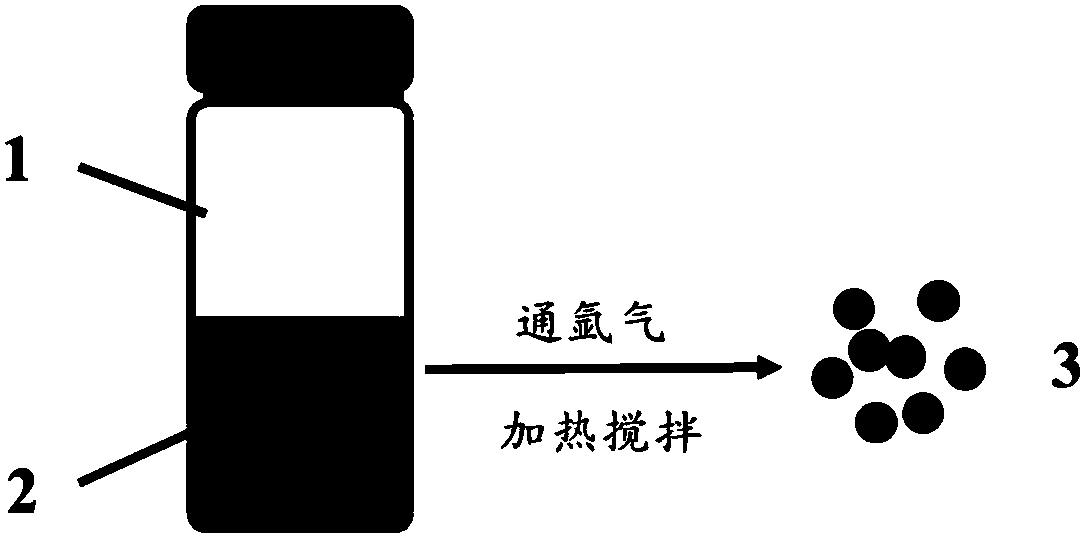
[0028] (3) Preparation of copper nanoparticles
[0029] The dialdehyde starch solution that 5 milliliters of steps (2) process obtains is added in the glass vial, then add 1 milliliter of 1 mg / ml polyethyleneimine solution, 1 milliliter conc...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Modification of cellulose
[0032] Take a 250 ml round bottom flask, add 10 g of cellulose, 5 g of sodium periodate and 100 ml of deionized water in sequence, and stir for 12 hours in an oil bath at 37°C. Filter and wash 4 times with water, then place in a vacuum freeze dryer for 72 hours to obtain dry dialdehyde cellulose powder.
[0033] (2) Dissolution of dialdehyde cellulose
[0034] Take 1 gram of dialdehyde cellulose prepared in step (1) and place it in a beaker, and add 90 milliliters of sodium hydroxide-urea solutions with mass fractions of 7% and 12%, respectively. After stirring at room temperature for 1 hour, freeze in a -20°C refrigerator for 12 hours, and then slowly thaw at room temperature to obtain a dialdehyde starch solution.
[0035] (3) Preparation of copper nanoparticles
[0036] Add the dialdehyde cellulose solution obtained in milliliter step (2) into the glass vial, then add 1 milliliter of 5 mg / ml polyethyleneimine solution, 1 milliliter ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Modification of starch
[0039] Take a 250 ml round bottom flask, add 10 g of starch, 5 g of sodium periodate and 100 ml of deionized water in sequence, and stir for 12 hours in an oil bath at 37°C. Filter and wash with water 4 times, then place in a vacuum freeze dryer for 72 hours to obtain dry dialdehyde starch powder.
[0040] (2) Dissolution of dialdehyde starch
[0041] Get 3 grams of dialdehyde starch prepared in step (1) and place it in a beaker, add 90 milliliters of sodium hydroxide-urea solutions with mass fractions of 6% and 4%, respectively. After stirring at room temperature for 1 hour, freeze in a -20°C refrigerator for 12 hours, and then slowly thaw at room temperature to obtain a dialdehyde starch solution.
[0042] (3) Preparation of copper nanoparticles
[0043] The dialdehyde starch solution that 5 milliliters of steps (2) process obtains is added in the glass vial, then add the polyethylenimine solution of 1 milliliter 5 mg / ml, 1 milliliter c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com