Preparation method of a natural polymer-based 3D porous composite scaffold with controllable pore size
A technology of natural macromolecules and composite scaffolds, applied in the field of preparation of natural macromolecular-based 3D porous composite scaffolds, can solve the problems of limited amino group content of active groups, etc., and achieves the enhancement of hydrophobicity, the expansion of emulsion concentration range, and the saving of raw materials. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
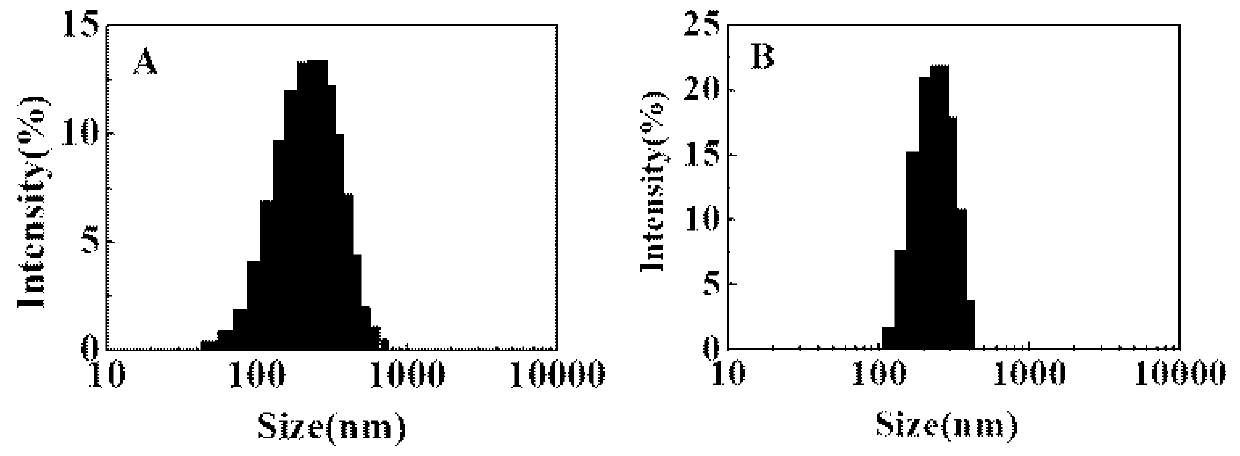
[0034] (1) Preparation of aminated gelatin: Dissolve 2 g of B-type gelatin in 50 ml, pH5.0, 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution, then add 6.4 g of ethylenediamine and 1.222 g of EDC, and adjust the pH to 5.0 and dilute to 100 ml with phosphate buffer solution, stir and react at 37°C for 1 h, then pour it into a dialysis bag for dialysis for 3 days, change the water 2 to 3 times a day, and finally freeze-dry in a low-temperature refrigerator to obtain a white product;
[0035] (2) Preparation of aminated gelatin nanoparticles: Dissolve 1.25 g of modified gelatin in 25 ml of distilled water, then add 25 ml of desolvating reagent acetone, redissolve the upper white suspension in 25 ml of distilled water and adjust the pH When the value is 3, add acetone dropwise until a white precipitate is formed, then add 150 μl glutaraldehyde for cross-linking reaction for 3 h. Finally, use a centrifuge to centrifuge the reacted mixed solution at 12500 g for 30 min, redissolve the centrifuged lowe...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Preparation of aminated gelatin: Dissolve 5 g of type B gelatin in 125 ml, pH 5.0, 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution, then add 16 g of ethylenediamine and 3.055 g of EDC, and adjust the pH to 5.0 and dilute to 250 ml with phosphate buffer solution, stir and react at 37°C for 1 h, then pour it into a dialysis bag for dialysis for 3 days, change the water 2 to 3 times a day, and finally freeze-dry in a low-temperature refrigerator to obtain a white product;
[0040] (2) Preparation of aminated gelatin nanoparticles: Dissolve 2.5 g of aminated gelatin in 50 ml of distilled water, then add 50 ml of desolvating reagent acetone, redissolve the upper white suspension in 50 ml of distilled water and adjust the pH When the value is 3, add acetone dropwise until a white precipitate is formed, and then add 300 μl glutaraldehyde for cross-linking reaction for 3 h. Finally, use a centrifuge to centrifuge the reacted mixed solution at 12500 g for 30 min, redissolve the centrifuged ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Preparation of aminated gelatin: Dissolve 10 g of type B gelatin in 250 ml, pH5.0, 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution, then add 32 g of ethylenediamine and 6.11 g of EDC, and adjust the pH to 5.0 and dilute to 500 ml with phosphate buffer solution, stir and react at 37°C for 1 h, then pour into a dialysis bag for dialysis for 3 days, change the water 2 to 3 times a day, and finally freeze-dry in a low-temperature refrigerator to obtain a white product;
[0045] (2) Preparation of aminated gelatin nanoparticles: Dissolve 2.5 g of aminated gelatin in 50 ml of distilled water, then add 50 ml of desolvating reagent acetone, redissolve the upper white suspension in 50 ml of distilled water and adjust the pH When the value is 3, add acetone dropwise until a white precipitate is formed, and then add 300 μl glutaraldehyde for cross-linking reaction for 3 h. Finally, use a centrifuge to centrifuge the reacted mixed solution at 12500 g for 30 min, redissolve the centrifuged lowe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com