A high-efficiency preparation method for multiple member mutants of the same gene family of kale at the same time
A gene family and mutant technology, applied in the field of plant molecular biology, can solve the problems of labor-intensive, low mutation efficiency, large workload, etc., to save costs, improve mutation efficiency, and reduce experimental difficulty and intensity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
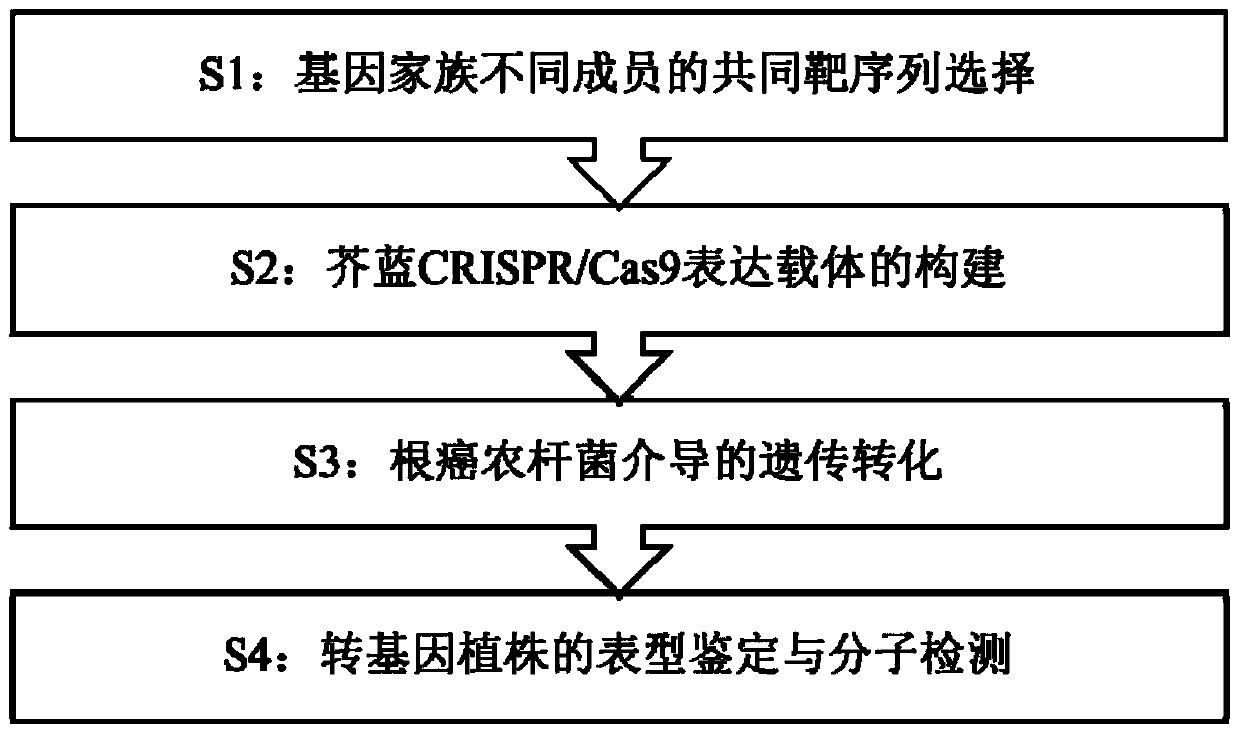
[0035] A method for efficiently preparing mutants of multiple members of the same kale gene family at the same time, comprising: selecting common target sequences of different members of the same kale gene family, and synthesizing a pair of complementary Oligo sequences according to the selected target sequences, Then carry out the ligation and transformation reaction to obtain the recombinant plasmid, which is then digested with the pCC plasmid to recover the target band, and then connect the two target bands to construct the CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector, and finally use the root Genetic transformation method mediated by Agrobacterium carcinoma to obtain transgenic mutant plants. , see the flow chart figure 1 .
[0036] For the preparation of mutants of multiple members of all gene families in kale, the method of the present invention can be used to prepare. Below we will describe the kale PDS gene family as an example. The specific process is as follows:
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Selection of Brassica oleracea PDSs gene target sequence
[0038] Because in the prior art, the method of knocking out multiple genes in kale plants by using the CRISPR / Cas9 system is mostly to select several different target sites to knock out one by one, which is time-consuming, laborious and costly. However, the present invention provides prerequisites for simultaneously knocking out multiple genes in plants in a subsequent transformation by screening the common target sequences of different members of the same gene family. Therefore, the screening of common target sequences of different members of the same gene family is very important.
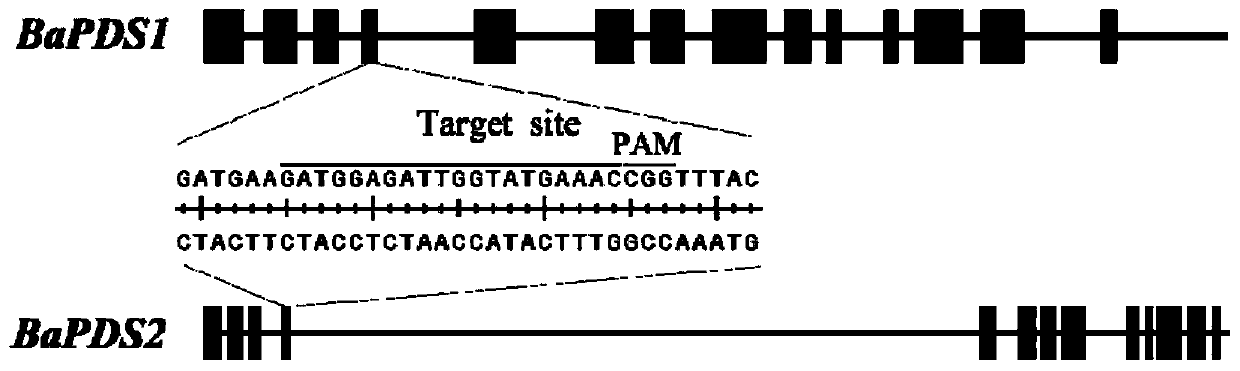
[0039] The Kale PDS gene family has two members, BaPDS1 and BaPDS2. Through cloning, the full-length CDS of the two genes, BaPDS1 and BaPDS2, were obtained. Using CRISPR-P (http: / / crispr.hzau.edu.cn / cgi-bin / CRISPR2 / CRISPR) online software to analyze the target sites of these two genes and screen the common target sequen...
Embodiment 2
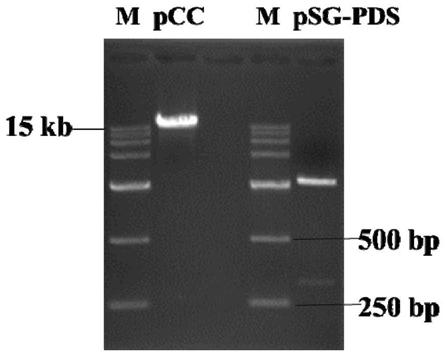
[0042] Example 2 Construction of Kale CRISPR / Cas9 Expression Vector
[0043] The construction process of the kale CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector specifically includes the following steps:
[0044] 1. Target sequence annealing and annealing: According to the selected target sequence, synthesize a pair of complementary Oligo DNA sequences, and add enzyme cutting sites CACC and AAAC to their 5' ends, and then anneal and anneal to obtain Oligo DNA with sticky ends. DNA double-stranded sequence. Among them, the reaction procedure of annealing and renaturation is: denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes, 30s at 1°C, cooling to 25°C, and storage at 4°C.
[0045] 2. Digestion of the pSG vector: the restriction endonuclease BbsI was used to digest the pSG vector. The digestion process was 37° C. for overnight reaction, followed by 65° C. for 20 minutes, and then the digested product was recovered.
[0046] 3. Ligation and transformation: Ligate the recovered enzyme-digested product with th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| conversion efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com