Low-temperature preparation method for lightweight heat-insulation ceramics
A lightweight thermal insulation and ceramic technology, applied in ceramic products, ceramic material production, clay products and other directions, can solve the problems of complex preparation process of modified clay, cumbersome firing process, high energy consumption, etc., to improve the effect of building energy saving , The effect of reducing raw material consumption and reducing production energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
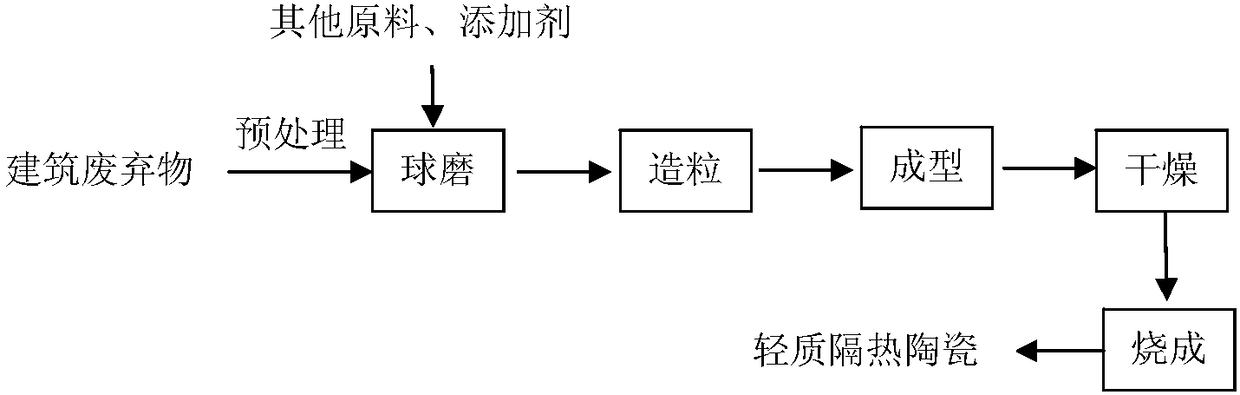
[0032] A preparation method of lightweight heat-insulating ceramics, the preparation flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0033] (1) Pass the construction waste through a 30-mesh sieve after ball milling, then weigh 67g of construction waste, 23g of albite, 9.3g of ball soil, and 0.7g of SiC, and use a ball mill to mix the materials for 1 hour at a speed of 600r / min;
[0034] (2) Grind the mixture after ball milling with water, pass through a 30-mesh sieve, and put it into an oven to dry at 60°C for 5 minutes;
[0035] (3) Pour the granulated powder in step (2) into a mold, press to form at 200MPa, and then dry;
[0036] (4) Put the ceramic body obtained in step (3) into a high-temperature furnace for firing at a firing temperature of 1200°C, a heating rate of 50°C / min, and a holding time of 0.1 hour to obtain lightweight heat-insulating ceramics.
[0037] The cross-sectional morphology of the lightweight heat-insulating ceramics obtained...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A preparation method of lightweight heat-insulating ceramics, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) Take by weighing 10g ball soil, 90g ceramic polishing slag, with ball mill with the rotating speed of 400r / min, ball mill mixing 2 hours;
[0042] (2) Grind the ball-milled mixture with water, pass through a 300-mesh sieve, and bake in an oven at 80°C for 6 minutes;
[0043] (3) Pour the granulated powder in step (2) into a mold, press to form under 10MPa, and then dry;
[0044] (4) Put the ceramic body obtained in step (3) into a high-temperature furnace for firing at a firing temperature of 1150°C, a heating rate of 2°C / min, and a holding time of 1.5 hours to obtain lightweight heat-insulating ceramics.
[0045] The lightweight heat-insulating ceramics prepared in this example have a density of 0.37g / cm 3 , the water absorption rate is 3.29%, the compressive strength is 2.58MPa, the average pore diameter is 1.36mm, and the thermal conductivity is 0.10W / m·K.
Embodiment 3
[0047] A preparation method of lightweight heat-insulating ceramics, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) Put the construction waste through a 200-mesh sieve after ball milling, then weigh 30g of construction waste, 30g of ceramic polishing slag, 30g of fly ash, and 10g of ball soil, and use a ball mill to mix the materials for 24 hours at a speed of 200r / min ;
[0049] (2) Grind the ball-milled mixture with water, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, and bake in an oven at 100°C for 5 minutes;
[0050] (3) Pour the granulated powder in step (2) into a mold, press to form at 1000MPa, and then dry;
[0051](4) Put the ceramic body obtained in step (3) into a high-temperature furnace for firing at a firing temperature of 1100°C, a heating rate of 30°C / min, and a holding time of 12 hours to obtain lightweight heat-insulating ceramics.
[0052] The lightweight heat-insulating ceramics prepared in this example have a density of 0.76g / cm 3 , the water absorption rate is 1.03%, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com