Bacterial cellulose film/nano-iron composite material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose membrane and composite materials, which is applied in the field of bacterial cellulose/nano-iron composite materials and its preparation, can solve problems such as easy agglomeration and activity decline, and achieve the goals of protecting the water environment, improving removal capacity, and facilitating recycling Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1, preparation bacterial cellulose film / nanometer iron composite material
[0038] 1) First cut the bacterial cellulose membrane into a disc with a diameter of about 3 cm, place the obtained disc in 100 ml of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 20 g / L and activate it for 12 hours to obtain activated-bacteria Cellulose film.
[0039] 2) Place the activated-bacterial cellulose membrane in a beaker containing 100 milliliters of ethanol / water solution with a volume ratio of 7 / 3, control the stirring speed to 15 rpm, and continue stirring for 1 hour; then take out the membrane and absorb it with filter paper After drying, put it into 100% ethanol again and continue stirring and extracting for 1 hour, and then dry it with filter paper again to obtain a semi-dehydrated-activated-bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0040] 3) Place the prepared semi-dehydration-activated-bacterial cellulose membrane in a four-necked flask, and add 100 milliliters of 0....
Embodiment 2
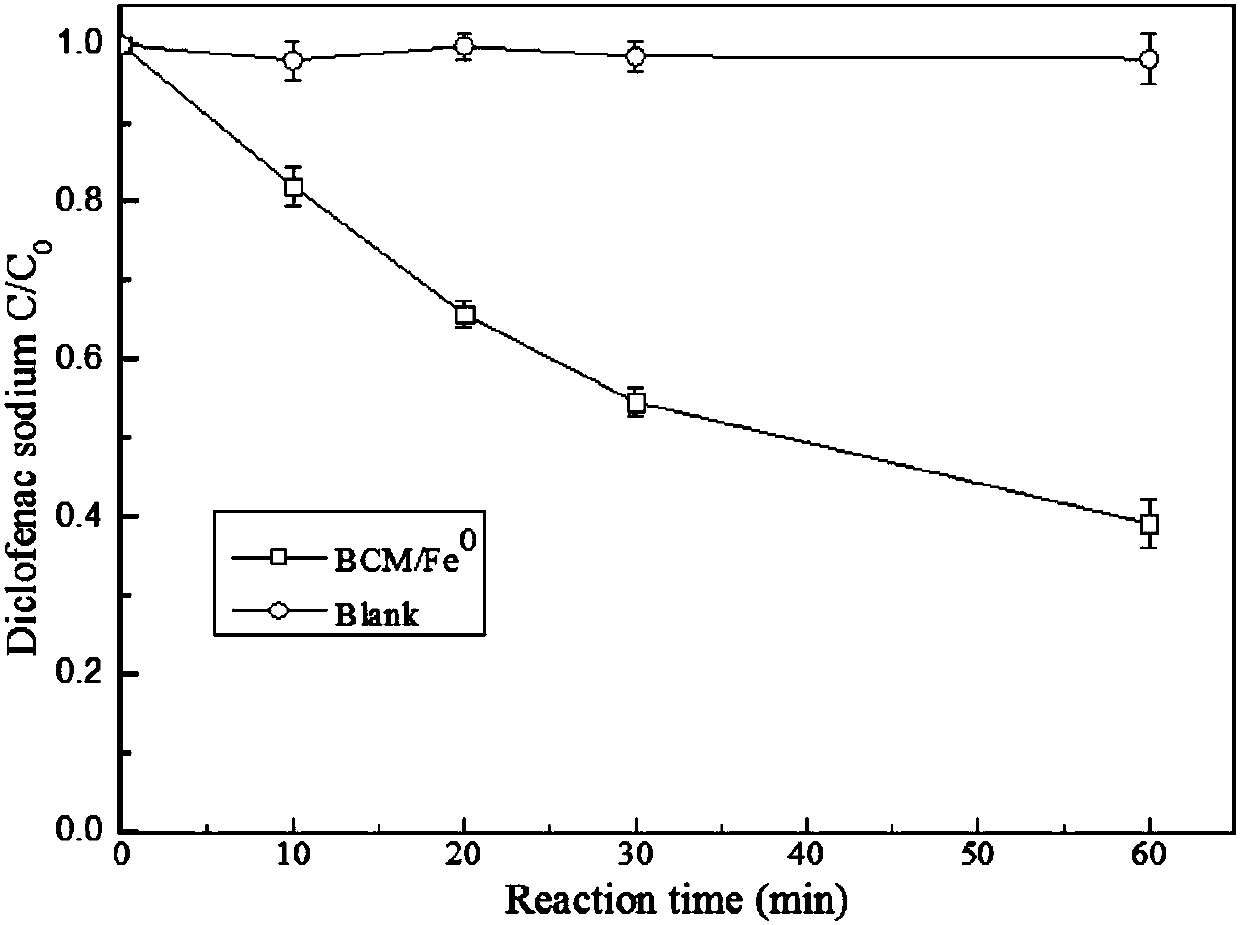
[0041] Example 2: Bacterial cellulose membrane / nanometer iron composite material removes diclofenac sodium in water
[0042] The selected model pollutant is diclofenac sodium with the following structural formula:
[0043]
[0044] Accurately measure 50 milliliters of diclofenac sodium solution with a concentration of 20 mg / L in a glass bottle, set the temperature at 20° C., and then place the bacterial cellulose membrane / nano-iron composite material prepared in Example 1 in the above solution as an experimental group (BCM / Fe 0 ). In addition, accurately measure 50 ml of diclofenac sodium solution with a concentration of 20 mg / L in a glass bottle, set the temperature at 20°C, and then place a pure bacterial cellulose film of the same specification in the above solution as a blank control group (Blank) .
[0045]Sampling was carried out at 10,20,30,60min respectively, and the concentration of diclofenac sodium was measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Bacterial cellulose membrane / nanometer iron composite material removes virus MS2 in water
[0048] The selected model virus is MS2 phage, and its capsid structure is as follows: image 3 shown.
[0049] The bacterial cellulose membrane / nanometer iron composite material that adopts embodiment 1 to prepare is to MS The initial concentration is 10 6 The pfu / mL solution was used for the removal experiment, and the pure bacterial cellulose membrane of the same specification was used as the blank control (Blank), and the results were as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0050] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that with the increase of reaction time, BCM / Fe 0 The removal of MS2 gradually increased, and after 4 hours of reaction, the MS2 in the water was basically completely removed, and the effect was good. But pure bacterial cellulose membrane has no removal effect on MS2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com