Iron-carbon micro-electrolysis process for introducing ozone and treating waste water
A technology of iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and wastewater treatment, which is applied in water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment equipment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of increased electromotive force, color change, and high treatment cost, and achieve a reduction Comprehensive cost, lower pH value, and ensure the effect of no color return
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The waste water with COD=30000 mg / L is treated by adopting the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis process of the present invention.
[0035] S1, with the sulfuric acid solution of 4.5mol / L and the sodium hydroxide solution that the mass fraction is 15%, the pH of waste water is adjusted to 4;
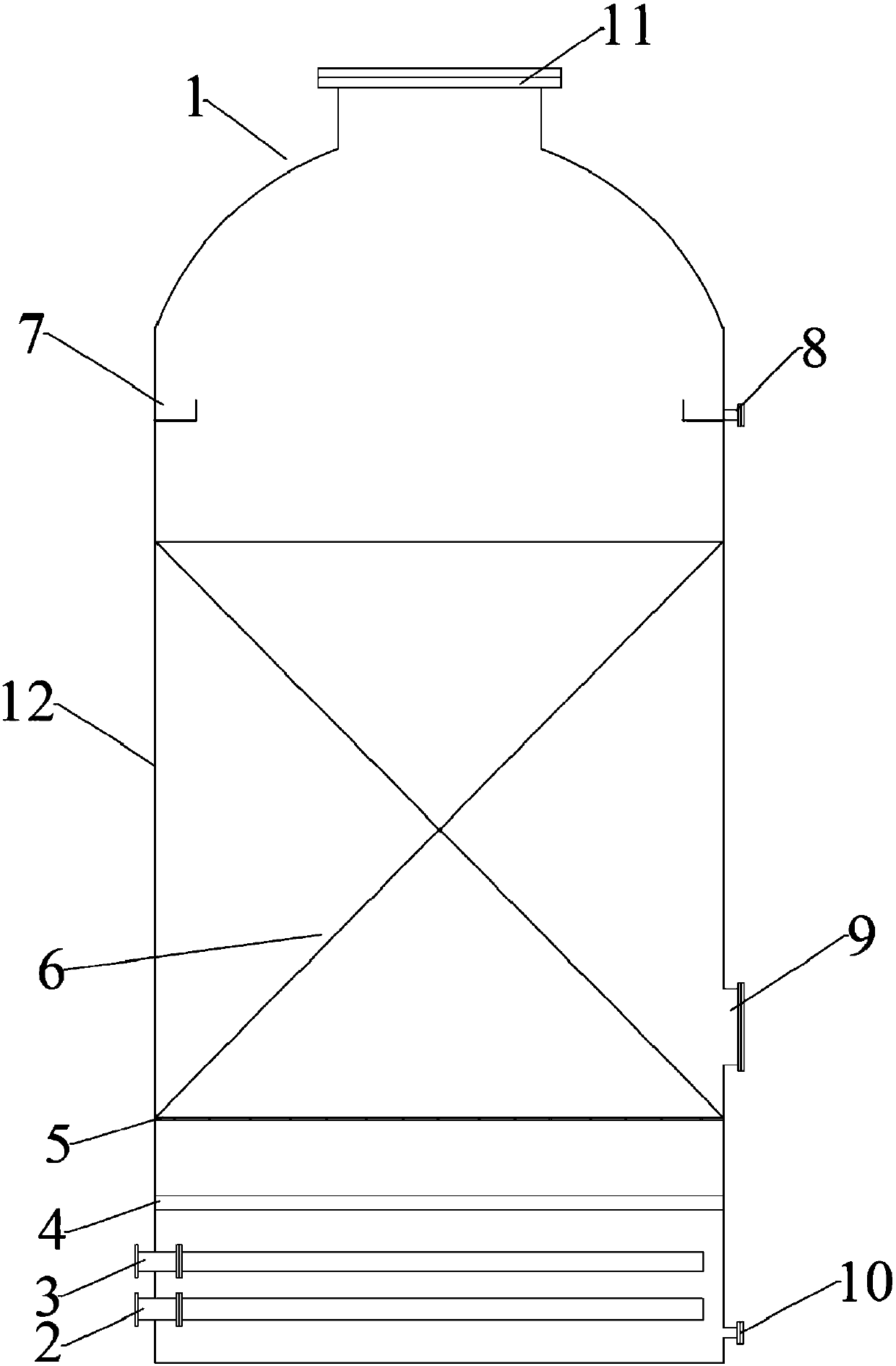
[0036] S2, after filtering the waste water with a pH of 4 in S1, transport it from the water inlet pipe 2 to the reaction tank 1, wherein the iron-carbon filler layer 6 is filled in the reaction chamber 12, and the mass ratio of iron filings and carbon particles in the iron-carbon filler layer 6 It is 1:2. After the waste water submerges the iron-carbon packing layer 6, the ozone is transported from the air inlet pipe 3 to the reaction tank 1. The ozone input amount per cubic meter of waste water is 10g. After 2 hours of reaction, the treated waste water is discharged from the overflow tank 7 and outlet pipe 8 discharge the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor;
[0037] S3, transp...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The waste water with COD=18000mg / L is treated by adopting the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis process in the present invention.
[0041] S1, the pH of waste water is adjusted to 5 with the sulfuric acid solution of 9.2mol / L and the sodium hydroxide solution of 30% by mass fraction;
[0042] S2, after filtering the waste water with a pH of 5 in S1, transport it from the water inlet pipe 2 to the reaction tank 1, wherein the iron-carbon filler layer 6 is filled in the reaction chamber 12, and the mass ratio of iron filings and carbon particles in the iron-carbon filler layer 6 1:3, after the waste water submerges the iron-carbon filler layer 6, the ozone is transported from the air inlet pipe 3 to the reaction tank 1, and the input amount of ozone per cubic meter of waste water is 8g. The water tank 7 and the water outlet pipe 8 discharge the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor;
[0043] S3, transporting the wastewater output from the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis react...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The waste water with COD=13000mg / L is treated by adopting the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis process in the present invention.
[0047] S1, the pH of waste water is adjusted to 2 with the sulfuric acid solution of 6.5mol / L and the sodium hydroxide solution of 20% by mass fraction;
[0048] S2, after filtering the waste water with a pH of 2 in S1, transport it from the water inlet pipe 2 to the reaction tank 1, wherein the iron-carbon filler layer 6 is filled in the reaction chamber 12, and the mass ratio of iron filings and carbon particles in the iron-carbon filler layer 6 It is 1:2.5, after the waste water submerges the iron-carbon filler layer 6, the ozone is transported from the air inlet pipe 3 to the reaction tank 1, and the input amount of ozone per cubic meter of waste water is 9g. 7 and outlet pipe 8 discharge the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor;
[0049] S3, transporting the wastewater output from the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor in S2 to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com