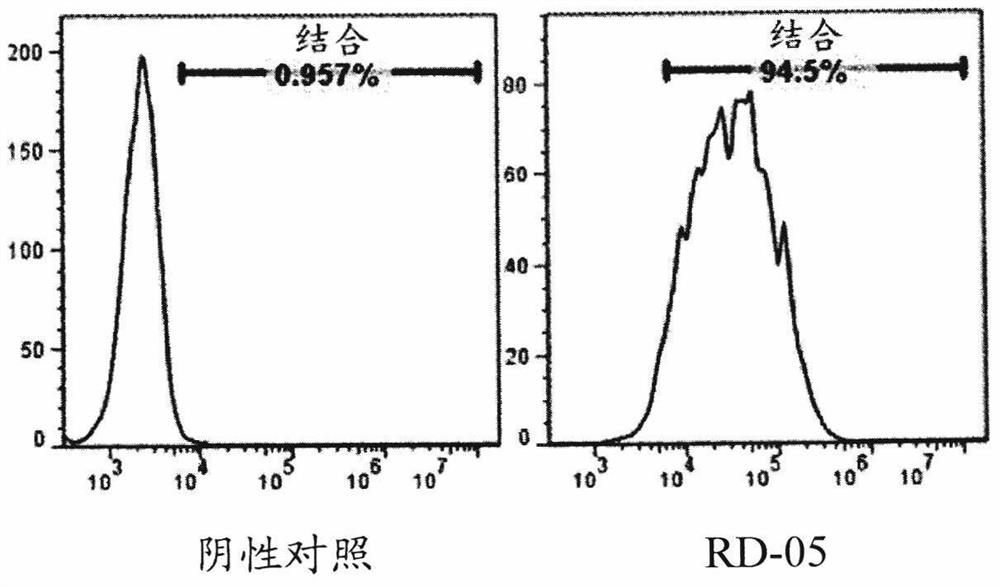
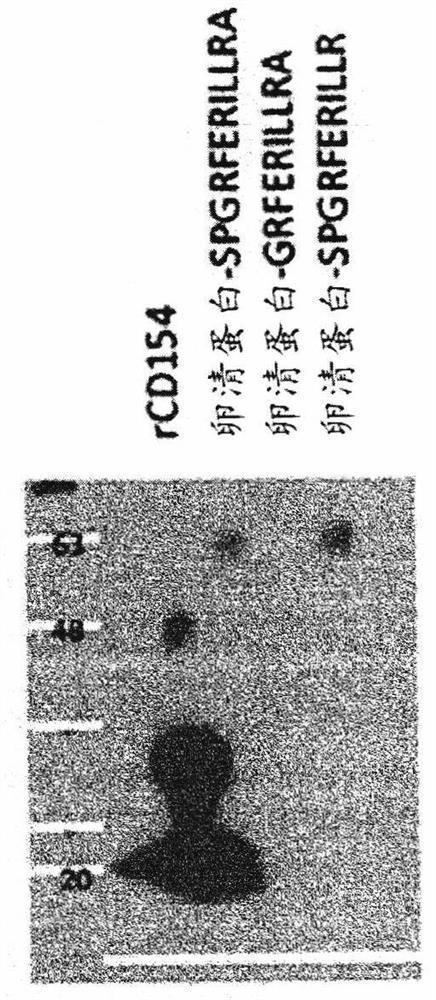
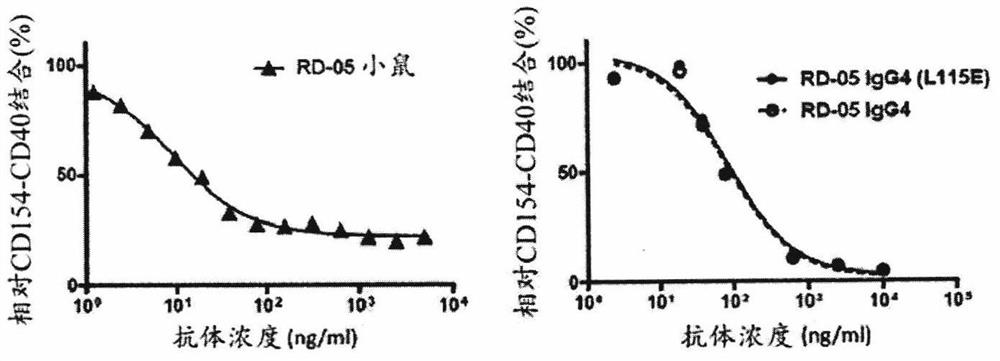
CD154 binding polypeptides and uses thereof
A technology that binds peptides and fragments. It is applied in the field of disease treatment and can solve problems such as thrombosis and antibodies that do not use clinical practice.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Embodiment 1: animal test
[0117] Cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis) were maintained at the Nonhuman Primate Center of Seoul National University Hospital (Seoul, Korea) or the Korean Institute of Toxicology (Jeongeup, Jeollabuk-do, Korea). The monkeys used in the experiments were 30 to 40 months old and weighed 2.5 to 3.5 kg. A part of the study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Seoul National University Hospital, and a part of the study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health proposed by the Korea Institute of Toxicology at the request of Seoul National University. guide.
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2: Production of anti-human CD154 antibodies
[0119] To generate anti-human CD154 antibodies, recombinant human soluble CD154 protein (sCD40L, catalog number: 310-02, Peprotech, NJ, USA) was immunized into BALAB / c mice. Female Balb / c mice (6-8 Week-old, 17-25 g; KOATECH, Pyeongtaek, Gyeonggi-do, Korea), intraperitoneally administered 3 times at 2-week intervals. Two weeks after the final immunization, 100 μg of CD154 protein was intraperitoneally injected into the immunized mouse, and 3 days later, the spleen was extracted from the mouse, and splenocytes were isolated therefrom.
[0120] For the production of monoclonal antibodies, 10 8 10 splenocytes with resistance to 9-azaguanine 7 A SP2 / 0-Ag14 mouse myeloma cell ( CRL-1581; American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) fusion (Koeler and Milstein, Nature 1975; 256:495-497).
[0121] After fusion, the cells were washed once with PBS, and then resuspended in DMEM (Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medi...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Example 3: Sequencing of the variable region of the anti-human CD154 antibody
[0125] In order to determine the heavy chain and light chain of the above-mentioned RD-05 antibody (including the heavy chain variable region (V H ) and the light chain variable region (V L )) The sequence of the CDRs of the gene was cloned as follows.
[0126] For gene cloning, RNA was extracted from RD-05 hybridoma cells using the RNA MiniPrep kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions, and PCR was performed (Novagen Mouse Ig Primer Set #69831, MuIgV H 5'-F, MuIgGV H 3'-2 and MuIgκV L S'-B, MuIgκV L 3'-1), thereby synthesizing cDNA.
[0127] The primers and PCR conditions for the synthesis of the heavy chain cDNA used were as follows: Forward primer MuIgV H 5'-F: 5'-ACTAGTCGACATGAACTTYGGGYTSAGMTTGRTTT-3' (Y: C or T; S: C or G; M: A or C; and R: A or G); reverse primer MuIgGV H 3'-2: 5'-CCCAAGCTTCCAGGGRCCARKGGATARACIGRTGG-3' (R: A or G; K: G or T; and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com