Methods for the synthesis of ethylfumarates and their use as intermediates
A kind of technology of monoethyl fumarate, monoethyl fumarate acid chloride
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
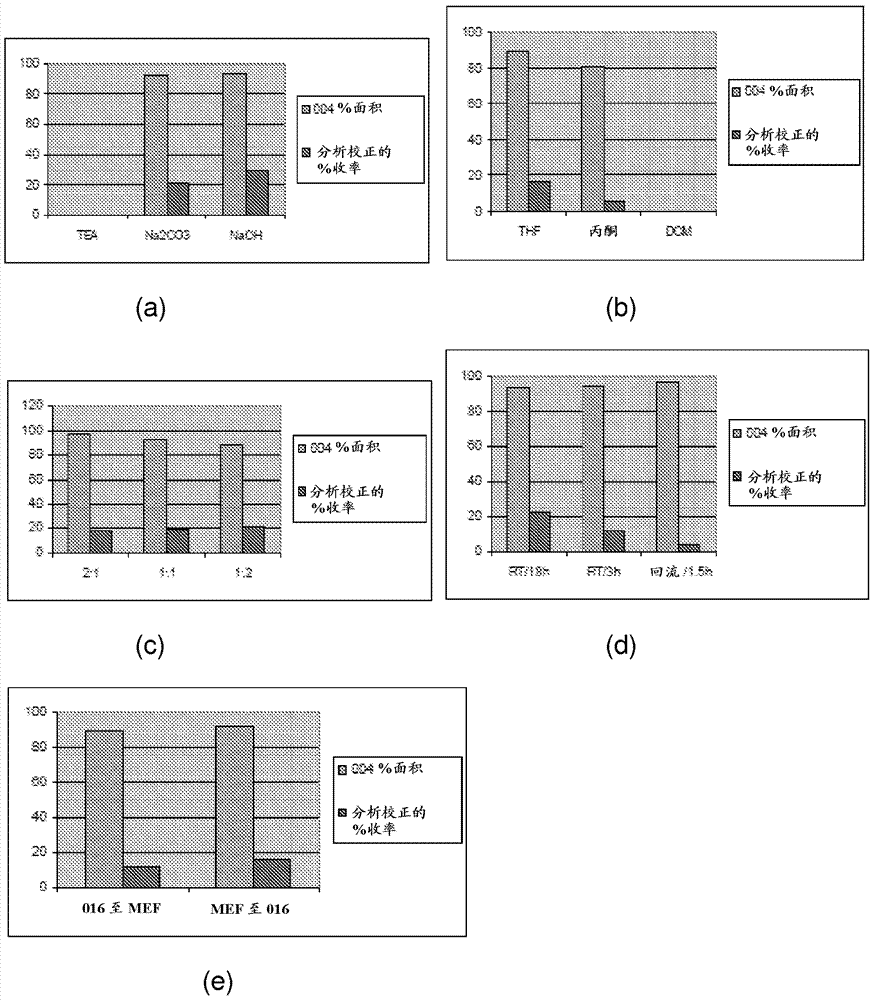
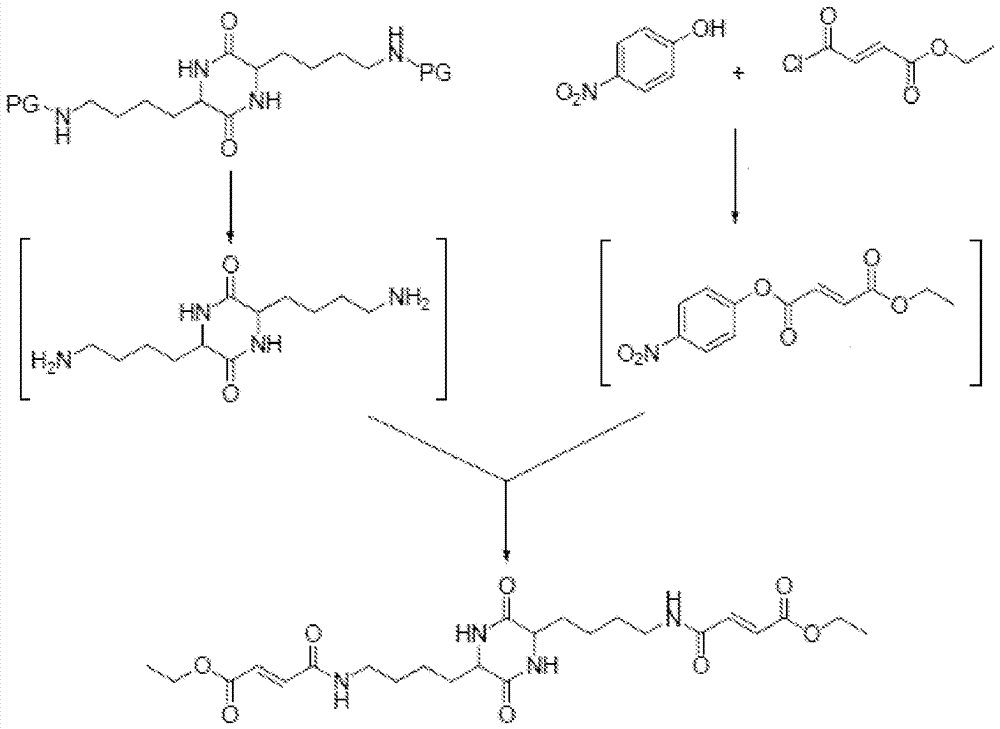
[0059] Coupling of ethyl fumarate acid chloride and 4-nitrophenol: To a 1 L 4-neck round bottom flask was added 11.20 g (80.51 mmol) of 4-nitrophenol, 90 mL of water and 69 mL of acetone. While stirring under nitrogen, a solution of 12.80 g (120.8 mmol) of sodium carbonate in 90 mL of deionized water was added to the reaction. 21 mL of ethyl fumarate chloride (EFC) (17.0 mL, d=1.16 g / mL, 121 mmol) in acetone was added to the mixture using an addition funnel. A 25-33°C exotherm was observed during the EFC addition. The reaction mixture faded from yellow to colorless as the EFC addition proceeded. At the end of the EFC addition, the reaction pH was 7-7.5. Approximately 15 minutes after the EFC addition was complete, the reaction was diluted with 450 mL of deionized water. A precipitate formed at 27°C. The mixture was kept for 15 minutes, then the solid was separated, washed with deionized water (3x220 mL), and dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C for 1 hour. The product was anal...
Embodiment 4
[0080] Example 4: For coupling Figure 11 Experimental Preparation 4 from MEF, TFAA and p-NP, NaOH: Part A: Assemble a 250 mL 3-neck round bottom flask with a magnetic stirrer, temperature readout / controller and addition funnel with nitrogen adapter. The vent gas is vented to an alkaline scrubber. Add p-nitrophenol (p-NP, 10 g) and trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA, 16.61 g, 11 mL) to the flask, and start stirring. The resulting yellow slurry was treated with triethylamine (TEA, 600 µL). A ~12 °C exotherm was observed after TEA addition. The solution was stirred for about 30 minutes (until clear, indicating complete formation).
[0081] Part B (In situ generation of 4-nitrophenyl ethyl fumarate): Assemble a 250 mL 4-neck round bottom flask with a magnetic stirrer, temperature readout / controller, addition funnel with nitrogen adapter, and reflux condenser . Monoethyl fumarate (MEF, 10.36 g) and acetone (9 mL) were added to the flask. TEA (16.33 mL) was added to the flask an...
Embodiment 5
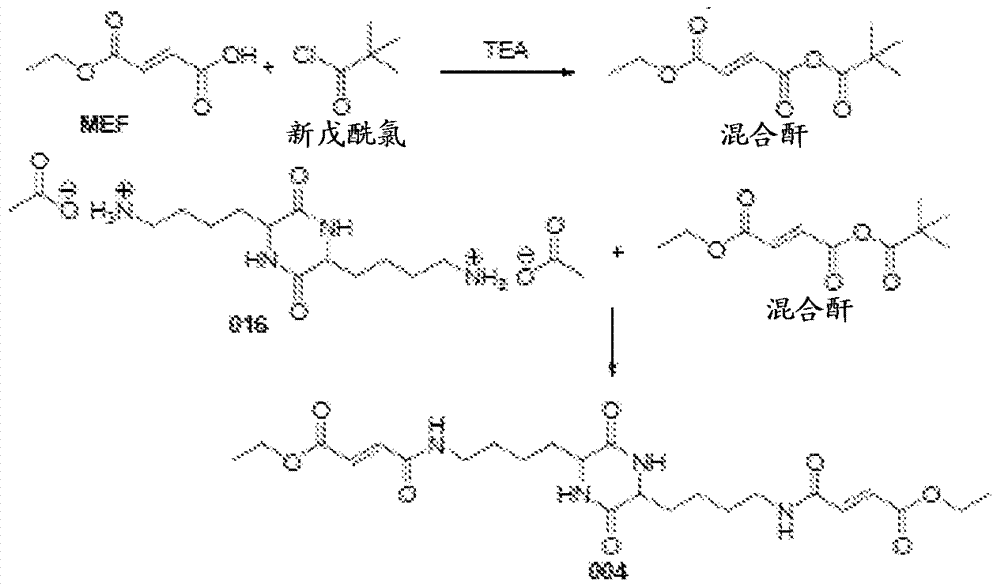
[0088] A 500 mL 3-neck round bottom flask was fitted with a magnetic stirrer, temperature reader / controller, and addition funnel with nitrogen inlet. The vent gas is vented to an alkaline scrubber. Monoethyl fumarate (MEF, 5 g), anhydrous dichloromethane or THF (10 mL) and triethylamine (TEA, 12 mL) were added to the flask. An exotherm was observed during TEA addition. The clear reaction mixture was cooled to 5°C in an ice bath. A solution of chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (CSI, 4.96 g) in 10 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane was added over 20-30 minutes. After the addition was complete, the reaction mixture was kept below 10 °C for 3 hours. For reactions with DCM, crude MEF anhydride was isolated by removal of solvent in vacuo. For reactions with THF as solvent, MEF anhydride was used without further manipulation.
[0089] A 500 mL 3-neck round bottom flask was assembled with a magnetic stirrer, temperature reader / controller, and addition funnel with nitrogen adapter. The vent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com