Reverse blocking type IGBT and manufacturing method therefor
A reverse-resistance type and N-type technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of reducing device switching speed, poor reverse blocking ability of FS-IGBT structure, and short-circuit safe working area of devices. Bad question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
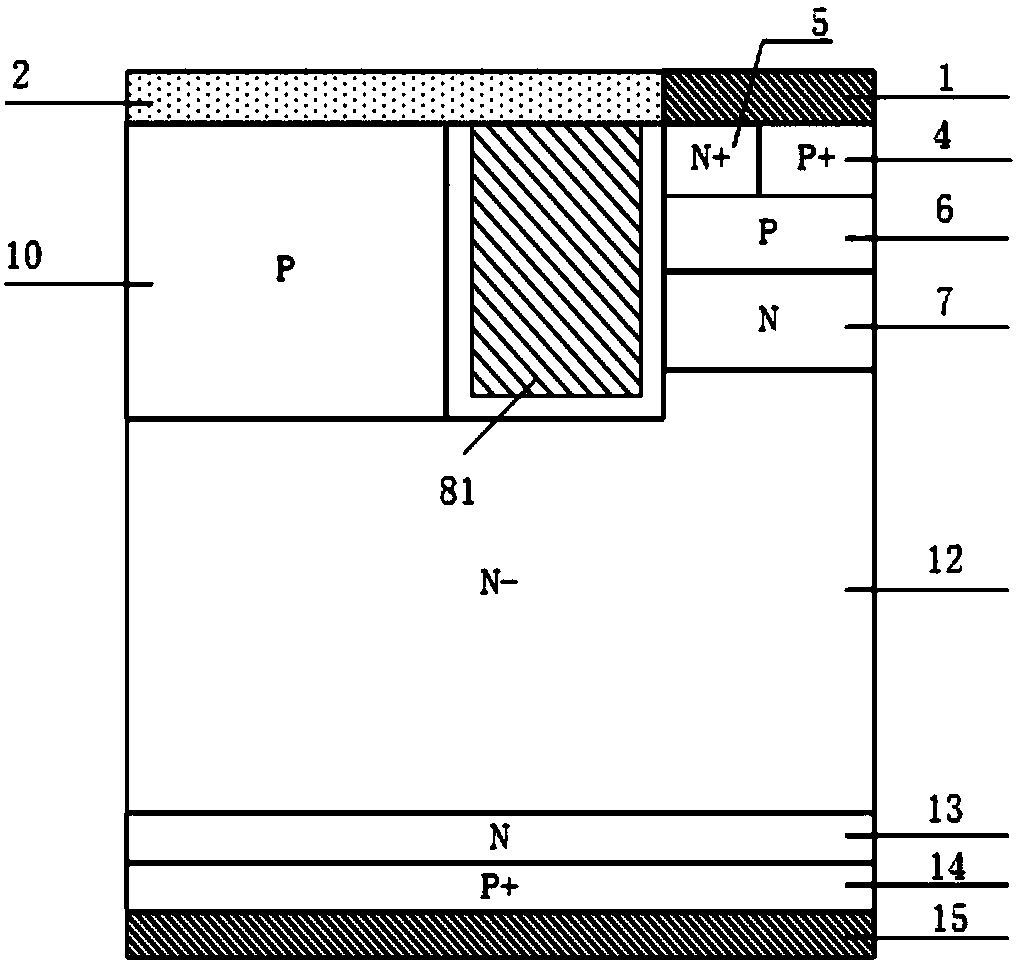
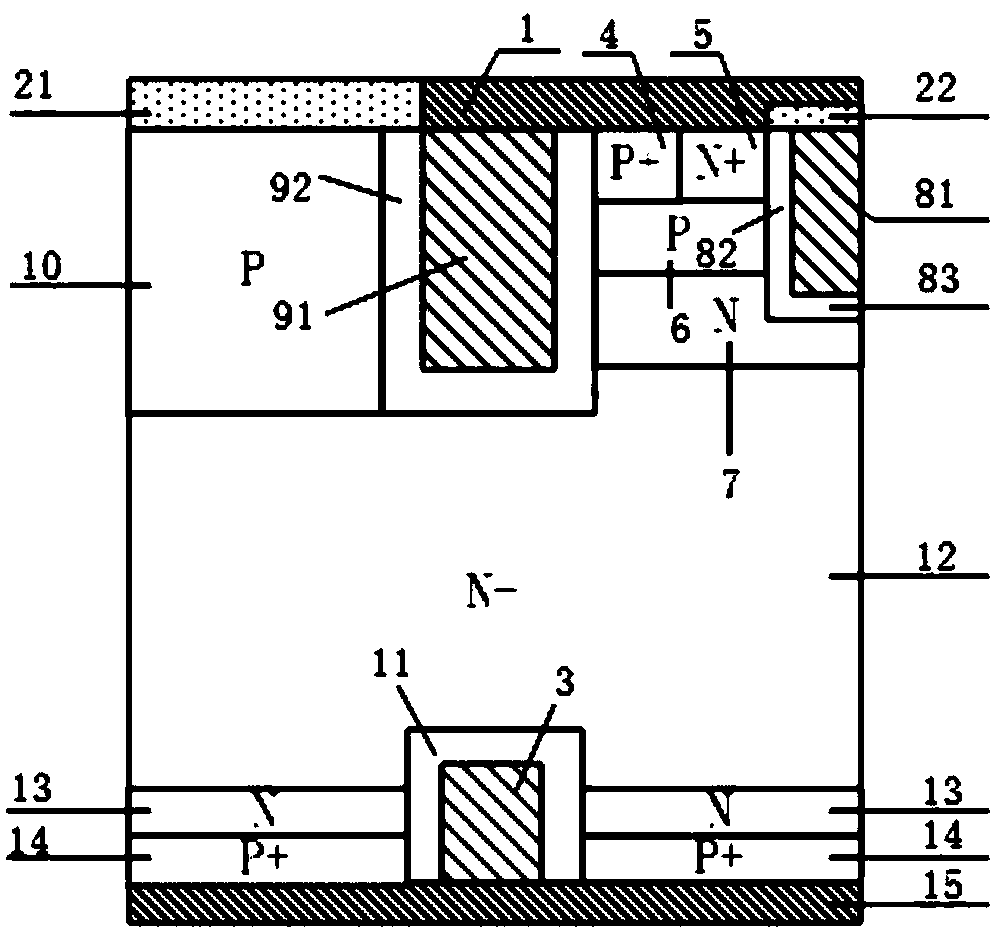
[0102] This embodiment provides a reverse resistance type IGBT, such as figure 2 Its cell structure shown includes: P-type collector region 14, collector metal 15 on the back of P-type collector region 14, N-type electric field stop layer 13 on the front of P-type collector region 14, and N-type electric field stopper layer 13 on the front of P-type collector region 14. The N-type drift region 12 above the layer 13; it is characterized in that: the N-type drift region 12 has a P+ emitter region 4, an N+ emitter region 5, a P-type base region 6, an N-type charge storage layer 7, a P-type body region 10, Trench gate structure, trench emitter structure and trench collector structure;
[0103] The trench emitter structure is located in the center of the top layer of the N-type drift region 12 and penetrates into it along the vertical direction of the device. The emitter dielectric layer 92 is composed of; the N-type drift region 12 on one side of the trench emitter structure has...
Embodiment 2
[0105] This embodiment provides a reverse resistance type IGBT, the cell structure of which is as follows image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, except that three identical and independent trench collector structures are arranged in the N-type field stop layer and the P-type collector region on the back of the device, the other structures are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0106] Compared with Embodiment 1, this embodiment further improves the reverse breakdown voltage of the device.
Embodiment 3
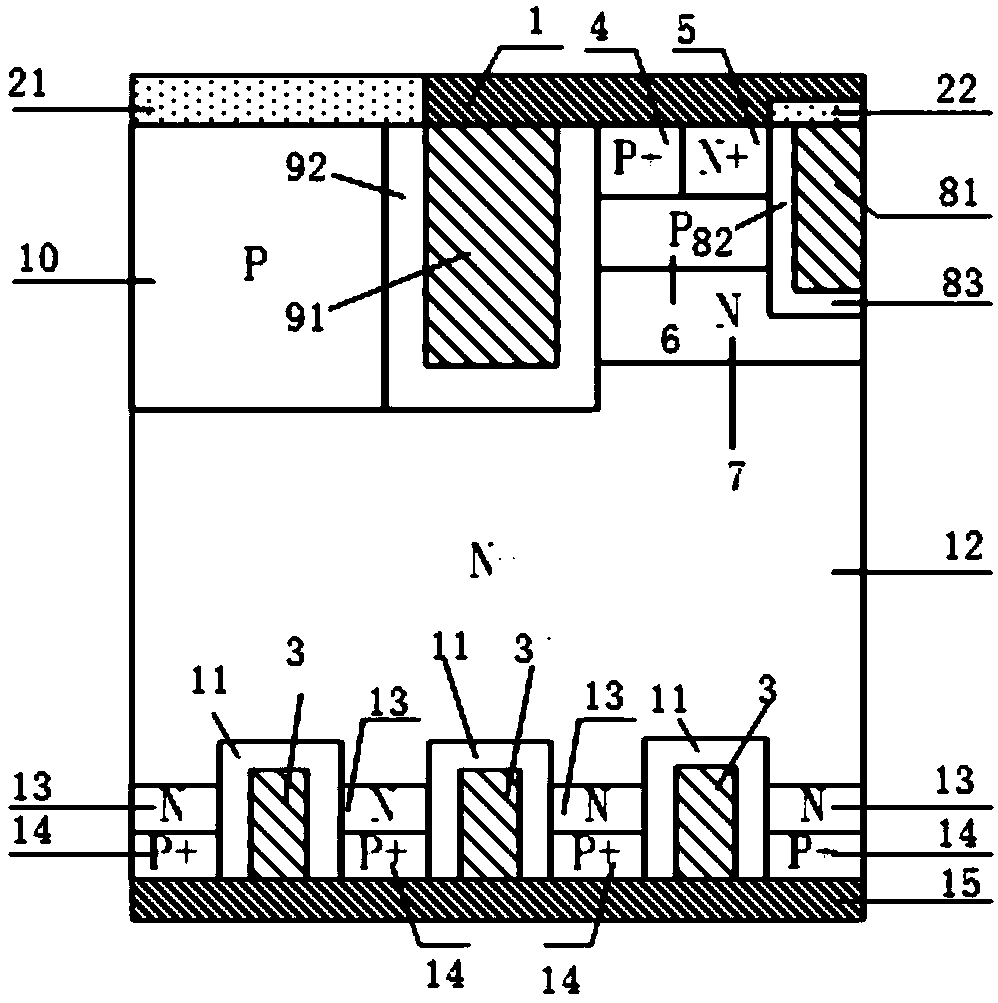
[0108] This embodiment provides a reverse resistance type IGBT, the cell structure of which is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1 except that the first P-type layer 16 connected thereto is disposed under the trench emitter structure.
[0109] In this embodiment, by introducing the first P-type layer 16 connected to the trench emitter electrode 91 through the emitter dielectric layer 92 on the bottom side, the first P-type layer 16 extends laterally to one side to the bottom of the N-type charge storage layer 7 In the N-type drift region 12, the breakdown voltage of the device is improved, and at the same time, the contradiction between the breakdown voltage caused by the concentration of the charge storage layer and the forward conduction voltage drop is improved.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com