Thermoplastic cellulose and aliphatic copolyester blend 3D printed wire and preparation method
An aliphatic copolyester, 3D printing technology, applied in additive processing and other directions, can solve the problems of low melt viscosity and high melt viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
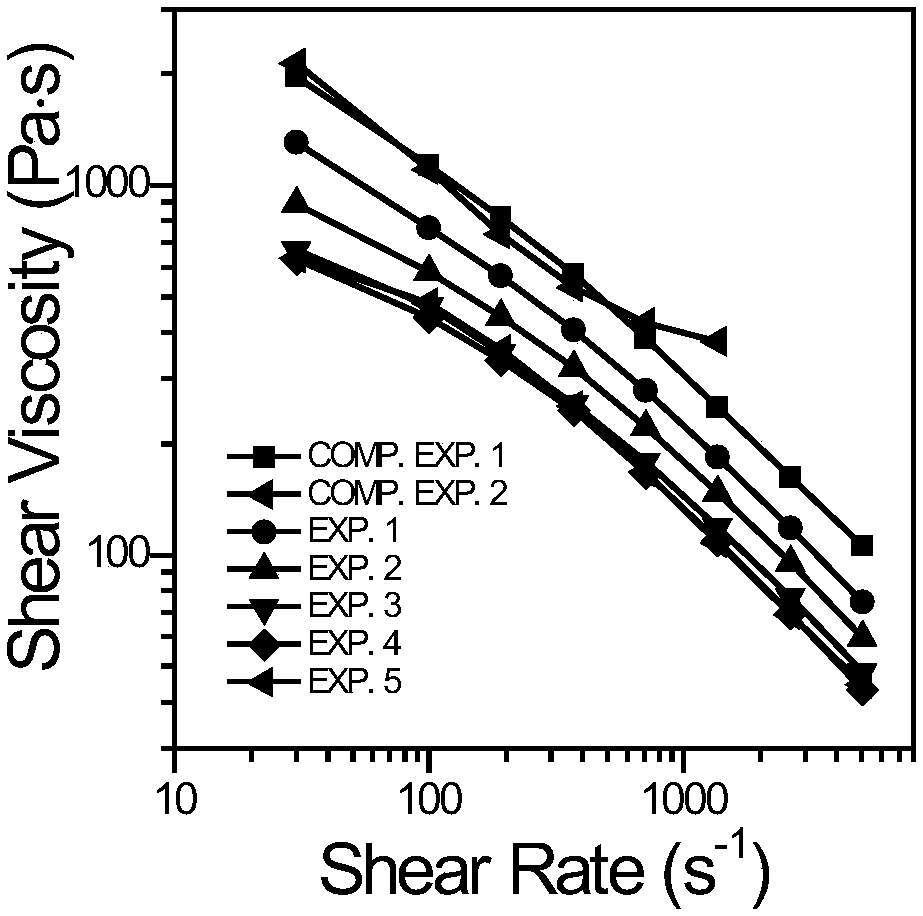
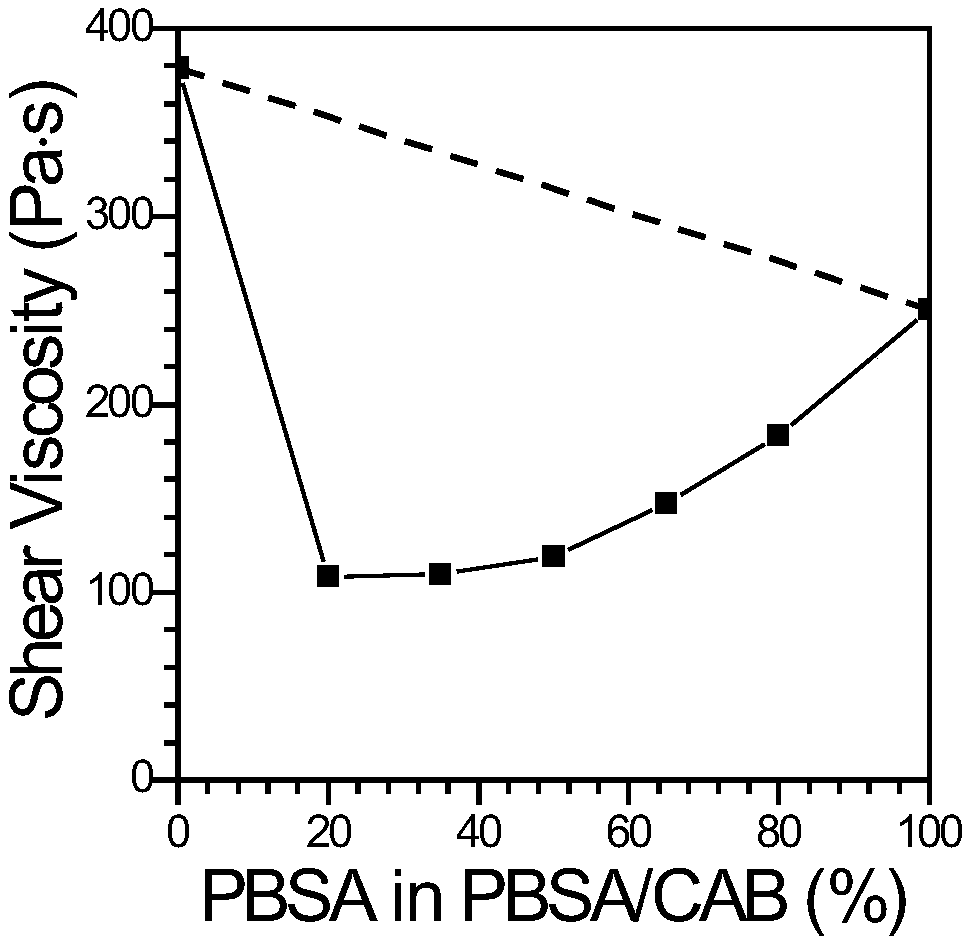
[0101] MD 3001PBSA and Eastman TM CAB-381-0.5 in the PolyLab HAAKE mentioned above TM Rheomex OS PTW16 co-rotating twin-screw extruder melt blend extrusion pelletizing. In the first stage of the extruder, the calibrated volumetric particle feeder is used for Feeding of MD 3001PBSA particles at a rate of 1680g / hr and a calibrated volumetric powder feeder was used for Eastman TM Feeding rate of CAB-381-0.5 powder: 420g / hr. The temperatures of the 2-11 sections of the extruder are: 140°C, 150°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C and 160°C, the screw speed is set at 200rpm, the torque at 48-52%. The extruder is equipped with a circular die with a diameter of 3 mm. After the splines are extruded from the die and cooled in a water bath, they are cut into cylindrical particles of about 3 mm by a pelletizer. The particles were collected, and after being pumped in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 4 hr, they were packaged for later use. The melt index of the part...
Embodiment 2
[0103] MD 3001PBSA and Eastman TM CAB-381-0.5 in the PolyLab HAAKE mentioned above TM Rheomex OS PTW16 co-rotating twin-screw extruder melt blend extrusion pelletizing. In the first stage of the extruder, the calibrated volumetric particle feeder is used for Feeding of MD 3001PBSA particles at a rate of 1365g / hr and a calibrated volumetric powder feeder was used for Eastman TM Feeding rate of CAB-381-0.5 powder: 735g / hr. The temperatures of the 2-11 sections of the extruder are: 140°C, 150°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C and 160°C, the screw speed is set at 200rpm, the torque at 43-47%. The extruder is equipped with a circular die with a diameter of 3 mm. After the splines are extruded from the die and cooled in a water bath, they are cut into cylindrical particles of about 3 mm by a pelletizer. The particles were collected, and after being pumped in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 4 hr, they were packaged for later use. The melt index of the part...
Embodiment 3
[0105] MD 3001PBSA and Eastman TM CAB-381-0.5 in the PolyLabHAAKE mentioned above TM Rheomex OS PTW16 co-rotating twin-screw extruder melt blend extrusion pelletizing. In the first stage of the extruder, the calibrated volumetric particle feeder is used for Feeding of MD 3001PBSA particles at a rate of 1050g / hr, while a calibrated volumetric powder feeder was used for Eastman TM Feeding rate of CAB-381-0.5 powder: 1050g / hr. The temperatures of the 2-11 sections of the extruder are: 140°C, 150°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C, 160°C and 160°C, the screw speed is set at 200rpm, the torque at 41-43%. The extruder is equipped with a circular die with a diameter of 3 mm. After the splines are extruded from the die and cooled in a water bath, they are cut into cylindrical particles of about 3 mm by a pelletizer. The particles were collected, and after being pumped in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 4 hr, they were packaged for later use. The melt index of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com