Semiconductor material wet surface process passivation method
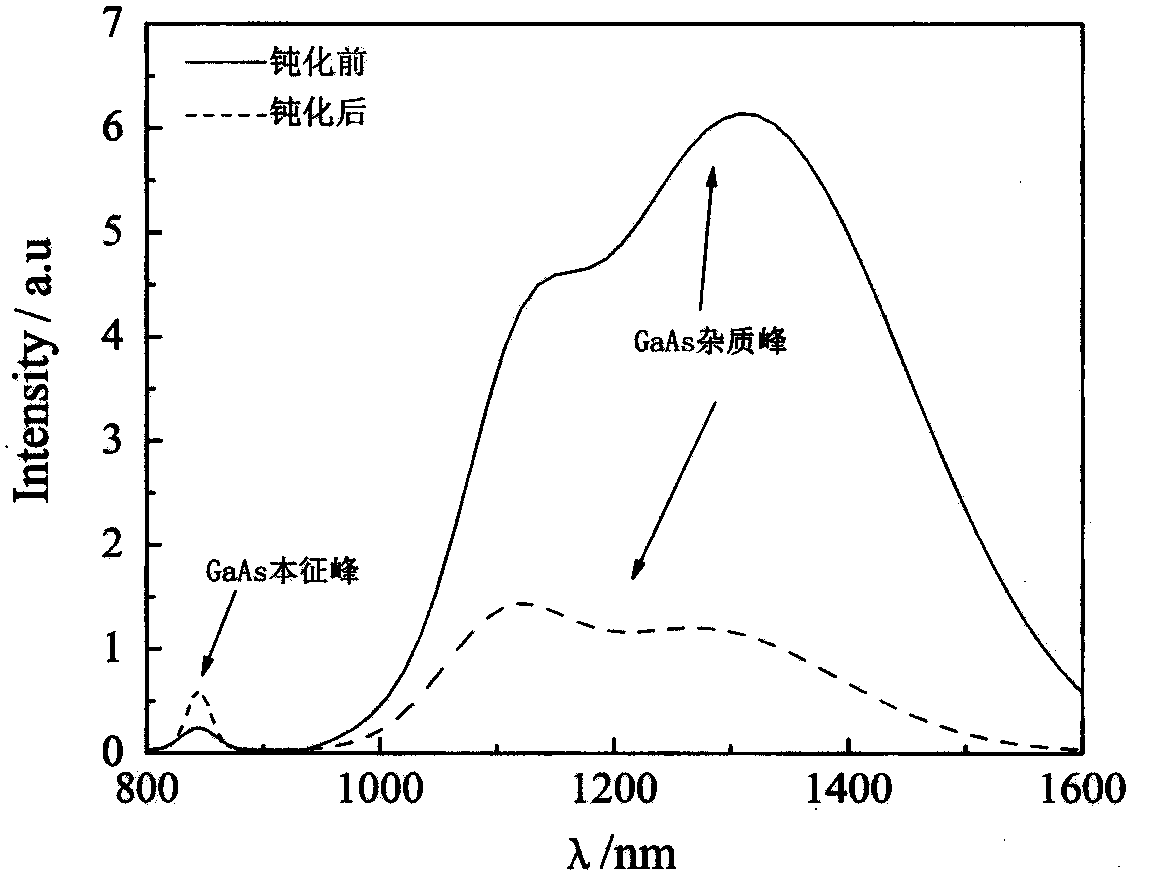
A semiconductor and wet process technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable subsequent application of III-V semiconductor materials, decreased passivation effect, and sodium ion pollution, and achieve enhanced passivation. Chemical stability, inhibition of oxidative corrosion, and reduction of volatilization of toxic gases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
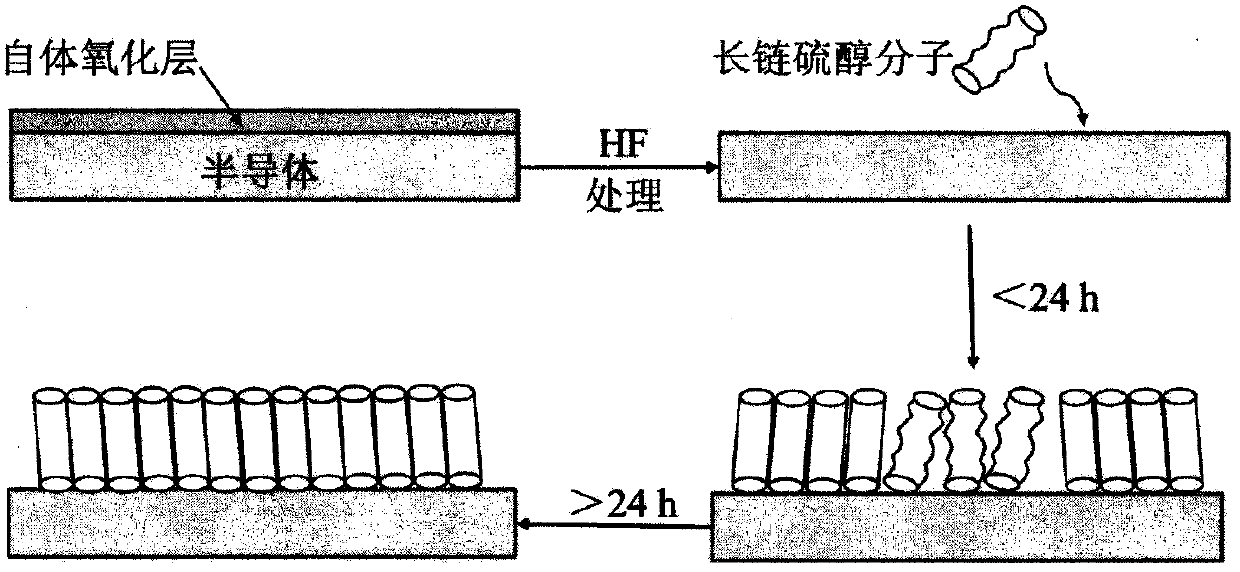
[0008] Step 1: Place the semiconductor wafer in acetone, ethanol, and deionized water for 5 to 10 minutes to ultrasonically clean it to remove organic contamination on the surface, and then rinse it with deionized water;
[0009] Step 2: Put the cleaned wafer into HF (HF:H 2 (O=1:1) soak in the solution for 3min to 10min to remove the thicker oxide layer on the wafer surface;
[0010] Step 3: Place the wafer in n-eicosanethiol (CH 3 [CH 2 ] 19 SH) in an ethanol solution, where the concentration of mercaptan is 5mM to 10mM, and the passivation is not less than 24h at room temperature;
[0011] Step 4: After the chip is taken out, put it into the isopropanol solution and sonicate it for not less than 5 minutes, and then dry it with high-purity nitrogen;
[0012] Step 5: The wafer is annealed under nitrogen condition, the temperature is 200±20°C, and the time is 30min±5min.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com