L-lactic acid catalysis reaction system and preparation method of L-lactic acid
A technology of catalytic reaction and reaction system, applied in the field of enzyme catalysis production of L-lactic acid, can solve the problems of inconvenient industrial production and expensive substrates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0039] Experimental example 1. In vitro multi-enzyme catalyzed conversion of glucose into L-lactic acid
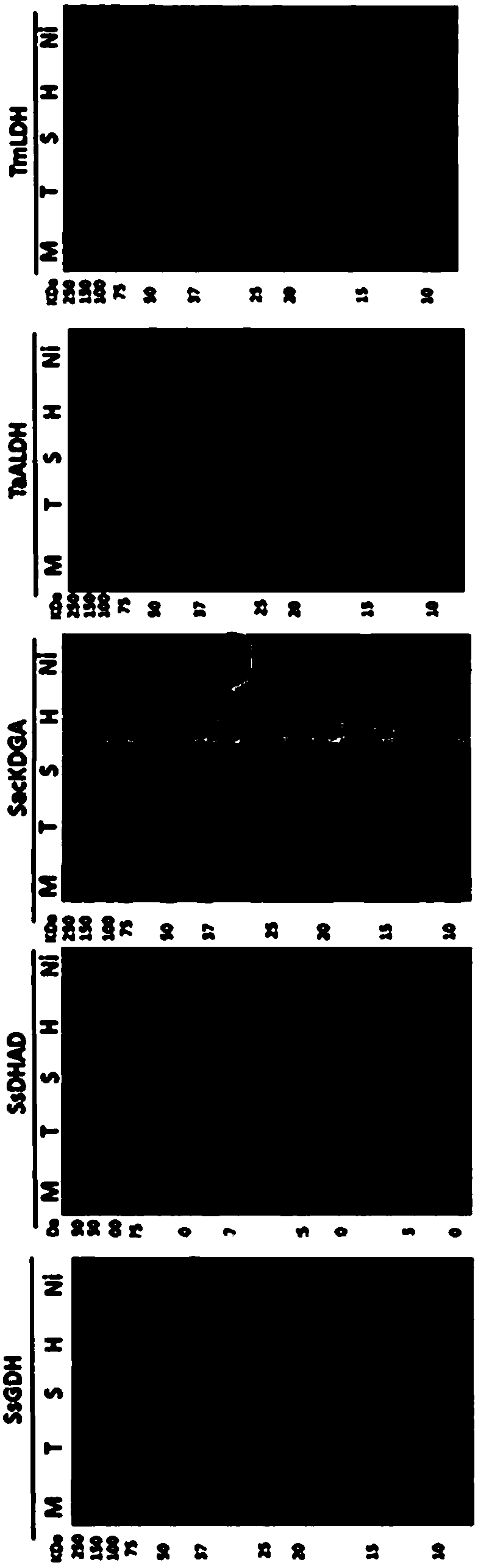
[0040] Combination of glucose dehydrogenase, dihydroxy-acid dehydratase, 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase, glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, dihydroxy-acid dehydratase and L-lactate dehydrogenase to establish L-lactate catalyzed reaction system.
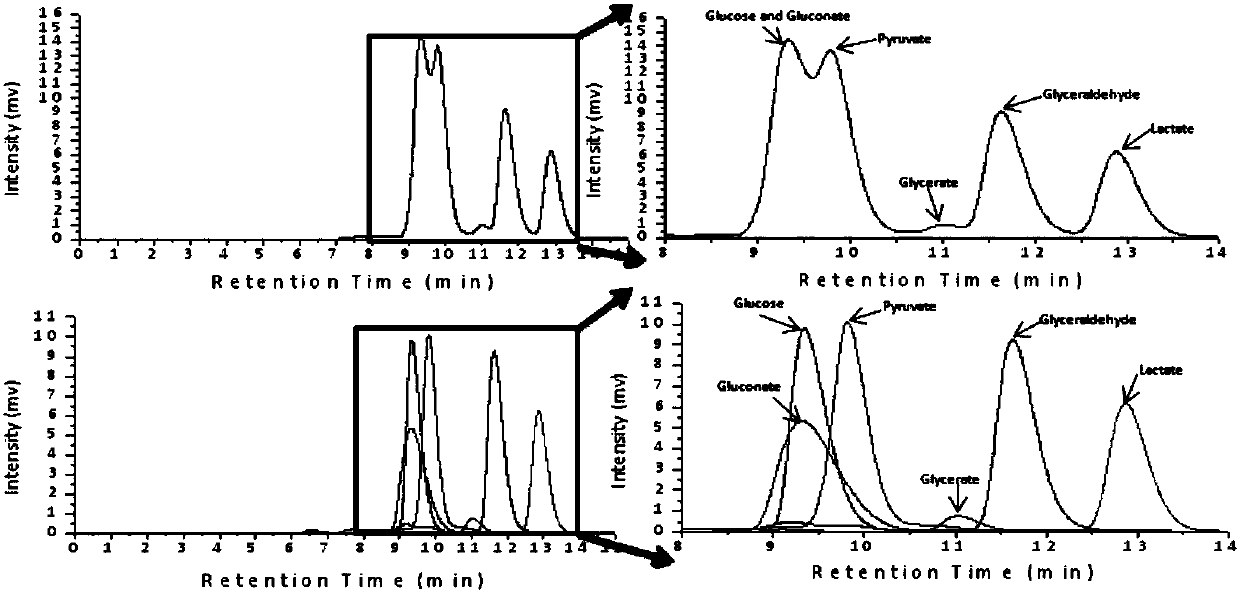
[0041] Glucose is converted into L-lactic acid by the L-lactic acid catalytic reaction system ( figure 1), including: (1) glucose dehydrogenase (GDH, EC 1.1.1.47), which catalyzes the production of gluconic acid from glucose; (2) dihydroxyacid dehydratase (DHAD, EC 4.2.1.9), which catalyzes the production of 2-ketone from gluconic acid -3-deoxygluconic acid (3) 2-keto-3-deoxygluconic acid aldolase (KDGA, EC4.1.2.14), catalyzes 2-keto-3-deoxygluconic acid to generate glyceraldehyde and pyruvate; (4 ) Glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH, EC1.2.1.3), which catalyzes glyceraldehyde to generate glyceric acid; (5) dihydroxy acid dehydrata...
experiment example 2
[0049] Experimental example 2. In vitro multiple enzymes catalyze the conversion of glucose into L-lactic acid (determination of enzyme concentration)
[0050] In a 1mL reaction system containing 100mM HEPES buffer (pH7.0), 5mM divalent magnesium ions, 5mM NAD + , 27.75mM glucose, the catalytic reaction was carried out at 50°C, and the reaction time was 12 hours. The proportions of different enzymes were changed respectively to finally determine the proportions of enzymes required in the reaction system.
[0051] After the reaction, if Figure 5 shown. First, optimize the amount of glucose dehydrogenase added. Only the added amount of glucose dehydrogenase is changed, and the added amount of other components in the reaction system does not change. After the reaction, the concentration of L-lactic acid is determined to determine the The optimal addition amount of hydrogenase was determined to be 1U / mL. After the addition amount of glucose dehydrogenase is determined, the ad...
experiment example 3
[0052] Experimental example 3. In vitro multi-enzyme catalyzed conversion of glucose into L-lactic acid (determination of coenzyme concentration)
[0053] After determining the amount of enzyme to be added in the reaction system, carry out coenzyme NAD + concentration optimization.
[0054] In a 1mL reaction system containing 100mM HEPES buffer (pH7.0), 5mM divalent magnesium ions, 27.75mM glucose, 1U / mL glucose dehydrogenase, 2U / mL dihydroxy acid dehydratase, 1U / mL 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase, 1U / mL glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, 1U / mL L-lactate dehydrogenase, catalyze the reaction at 50°C, and the reaction time is 12 hours . Altered coenzyme NAD + The addition ratio is 0-10mM, and finally determine the addition ratio of the required coenzyme in the reaction system.
[0055] After the reaction, by Image 6 It can be seen that when the coenzyme NAD + The production rate of lactic acid did not increase significantly after the addition amount of 5mM. Taking into cons...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com