Method for in-vitro rapid optimization of strain metabolic pathway
A pathway and strain technology, applied in the field of rapid optimization of strain metabolic pathways in vitro, can solve problems such as insufficient gene rearrangement diversity, and achieve the effects of rapid optimization of metabolic pathways, efficient and rapid joint analysis, and wide application fields.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of each functional gene fragment of β-carotene
[0041] Starting from the commercial vector pUC19, the DNA structure "loxPsym site-BsaI restriction site-RFP (red fluorescent protein gene)-BsaI restriction site-URA gene-loxPsym site" was amplified by overlapping PCR, and then passed the enzyme The method of cut ligation inserts the sequence into the multiple cloning site of pUC19 plasmid and assembles it into a universal vector pYW0120. This universal vector can quickly replace the RFP gene with the BsaI restriction sites at both ends of RFP, so that the exogenous function Gene fragments are quickly added to screening tags 1 and loxPsym sequences at both ends.
[0042] The functional gene fragment refers to the complete transcription unit of the target gene. Use PCR to amplify the functional gene on the genome template or use chemical methods to synthesize it from scratch, so that the end of the functional gene fragment carries a BsaI restrict...
Embodiment 2
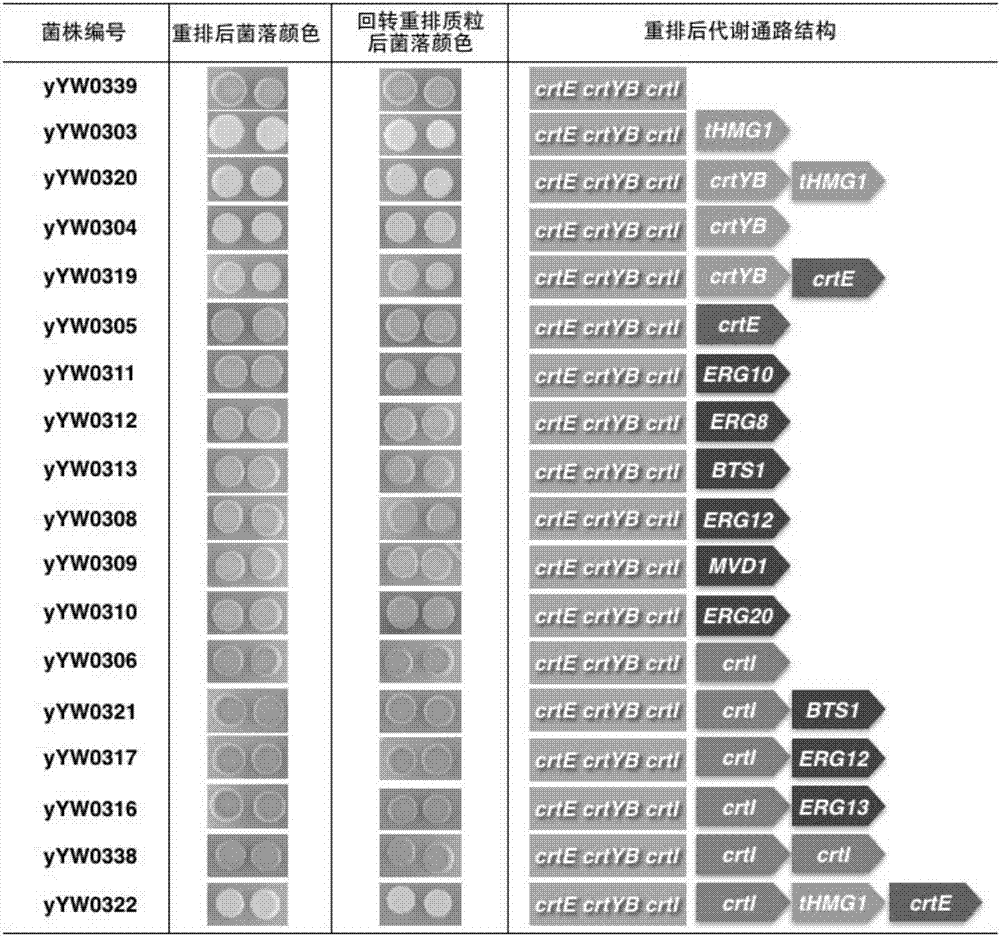
[0044] Example 2: Obtaining of rearranged plasmid libraries
[0045] According to the reaction system (50 μL) in Table 1, each functional gene fragment of β-carotene in Example 1 was mixed with the donor plasmid pYW0113, Cre enzyme, Cre enzyme buffer and ddH introduced loxPsym sequence and screening tag HIS. 2 O undergoes in vitro rearrangement.
[0046] Table 1 rearrangement reaction system
[0047] Element
[0048] According to the amount of each substance in the table (the mass of the above 11 fragments is 200ng, and the receiving vector pYW0113 is 400ng), add them into PCR tubes respectively, and mix well. React at 37°C for 60 minutes and inactivate at 70°C for 10 minutes, then the reaction of the rearrangement system is completed, and a rearranged plasmid library is obtained.
Embodiment 3
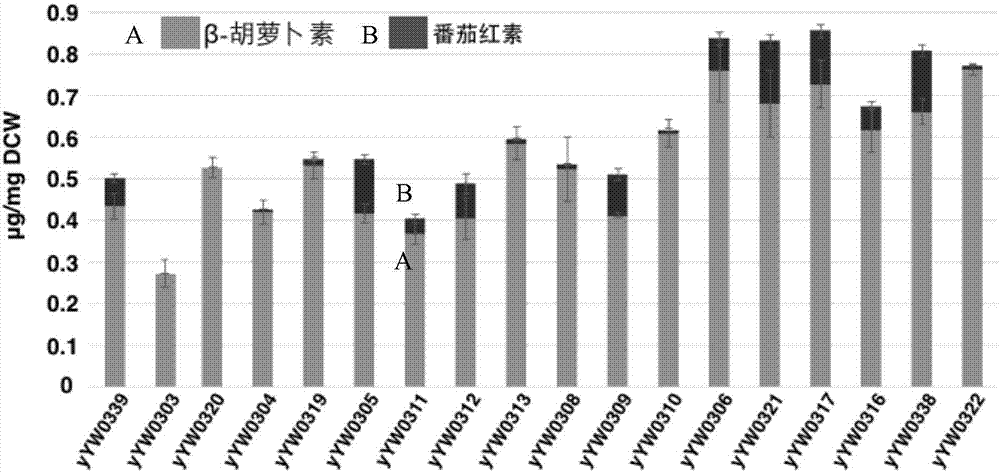
[0049] Embodiment 3: the acquisition of high-yielding bacterial strain
[0050] 1. Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with rearranged plasmid library
[0051] Pick a single colony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yYW0301 in 5mLYPD liquid medium, culture overnight at 30°C; measure the OD of Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture medium cultured overnight 600 , inoculate overnight culture solution into 5mL YPD (0.125OD 600 / ml), cultivated to OD at 30℃, 220rpm 600 Reach 0.5 (about 3.5-4.5h);
[0052] Pipette 1mL of Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture solution into a 1.5mL EP tube, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 2min, and collect the cells; resuspend the cells in 1mL of sterile water, centrifuge as above, and collect the cells; resuspend the cells in 1mL 0.1M LiOAc, centrifuge as above, and collect the cells; Remove 900 μL supernatant with a pipette, and resuspend the cells in the remaining 100 μL LiOAc, place on ice to obtain competent cells.
[0053] Prepare the transformation system:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com