Method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and astaxanthin, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, etc., can solve the inevitable problems of incomplete recovery of organic solvents, long extraction time, complicated process, etc., achieve ideal cutting force and wall breaking efficiency, improve Grinding and wall breaking effect and easy operation steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
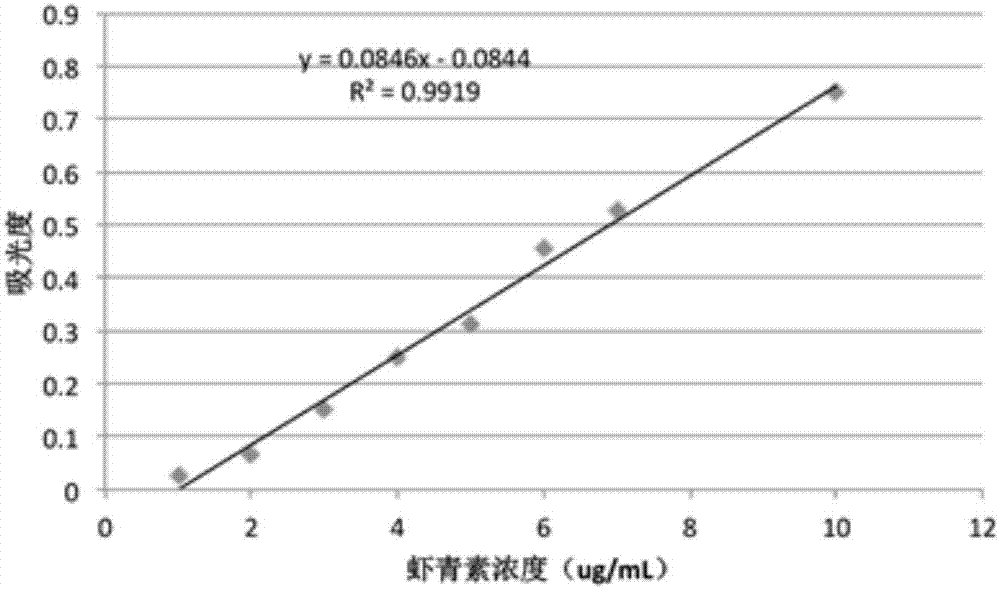
[0032] Example 1 Effect of different solid-liquid ratios of algae powder and extractant oil on the extraction effect of astaxanthin
[0033] The solid-liquid ratio of algae powder and extractant oil affected the concentration of astaxanthin oil and the extraction rate of astaxanthin. The increase of extractant oil can increase the extraction rate of astaxanthin, but it will reduce the concentration of astaxanthin oil, and the reduction of astaxanthin oil concentration will lead to the increase of transportation cost, raw material cost and storage cost of astaxanthin oil for subsequent application. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the concentration of astaxanthin oil as much as possible, but as the amount of algae powder increases, the loss rate of extractant oil increases, and the volume of effective astaxanthin oil decreases, resulting in a decrease in the extraction rate of astaxanthin. Therefore, a Appropriate material-to-liquid ratio.
[0034] Get 6 parts of 10ml ca...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 The influence of water bath temperature on the extraction effect of astaxanthin
[0039] Accurately weigh 4.0g Haematococcus pluvialis algae powder, add 10ml camellia seed oil and 0.4g glass beads with sizes of 50 mesh and 270 mesh respectively (the mass ratio of the two glass beads with different sizes and specifications is 1:1), set Oscillate on a vortex oscillator for 15 minutes, the oscillation frequency is 2800r / min, put it in a water bath for 15 minutes, and set the temperature of the water bath to 0°C, 15°C, 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C, 90 ℃, 100 ℃, shake once every 5 minutes during the water bath, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 3 minutes after the water bath, take the upper liquid and filter it on the glass fiber membrane to obtain astaxanthin oil. Observe the effect of water bath temperature on the extraction effect of astaxanthin, the results are shown in figure 2 .
[0040] From figure 2It can be seen that as the temperature of the water bat...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 The influence of water bath time on the extraction effect of astaxanthin
[0042] Accurately weigh 4.0g Haematococcus pluvialis algae powder, add 10ml camellia seed oil and 0.4g glass beads with sizes of 50 mesh and 270 mesh respectively (the mass ratio of the two glass beads with different sizes and specifications is 1:1), set Vibrate on a vortex oscillator for 15 minutes, the oscillation frequency is 2800r / min, put it into a water bath for water bathing, the water bath temperature is 70°C, the water bath time is 0-60min, oscillate once every 5min during the water bath, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 3min after the water bath is over , take the upper liquid and filter it on a glass fiber membrane to obtain astaxanthin oil. Observe the effect of water bath time on the extraction effect of astaxanthin, the results are shown in image 3 .
[0043] From image 3 It can be seen that as the water bath time prolongs, the concentration of astaxanthin oil increases, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com