Recombinant Streptococcus zooepidemicus for fermentation of micromolecule hyaluronic acid
A technology of Streptococcus zooepidemicus and hyaluronic acid, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of complex reaction conditions, low level of recombinant expression of hyaluronidase, difficulty in obtaining molecular weight, etc., and achieve the effect of wide application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Construction of recombinant plasmids secreting and expressing hyaluronidase
[0035] Primers HyaL-F and HyaL-R were designed, and a standard PCR amplification system and program was used to amplify the hyaluronidase gene Hyal whose sequence was obtained as shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
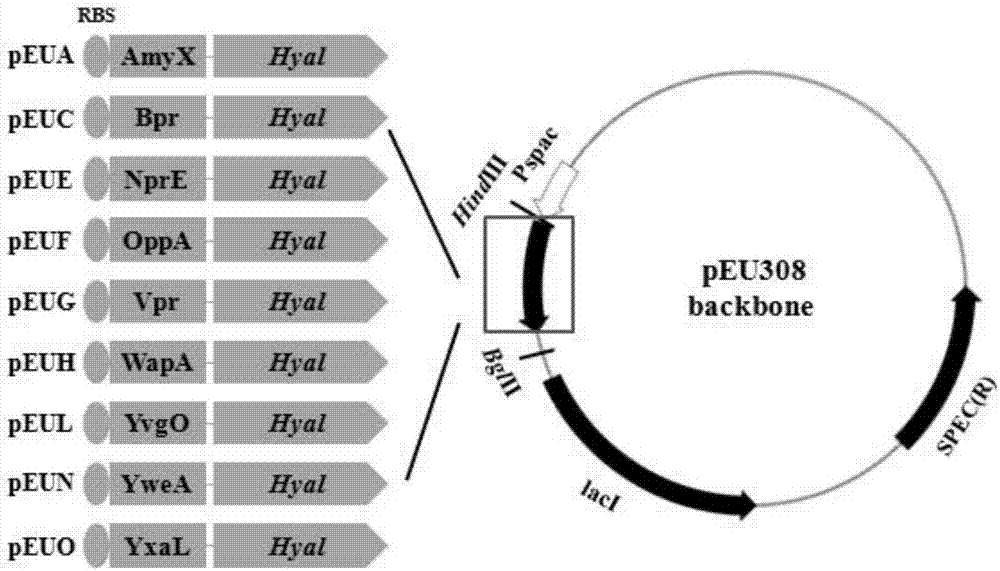
[0036]Design primers AmyX-F / AmyX-R, Bpr-F / Bpr-R, NprE-F / NprE-R, OppA-F / OppA-R, Vpr-F / Vpr-R, WapA-F / WapA-R, YvgO-F / YvgO-R, YweA-F / YweA-R, YxaL-F / YxaL-R, respectively with plasmid pMA0911-amyX, pMA0911-bpr, pMA0911-nprE, pMA0911-oppA, pMA0911-vpr, pMA0911-wapA , pMA0911-yvgO, pMA0911-yweA, pMA0911-yxaL as templates, using standard PCR system and procedures, amplified to obtain signal peptides AmyX, Bpr, NprE, OppA, Vpr, WapA, YvgO, YweA, YxaL (SEQ ID NO. 2-10), wherein the above-mentioned signal peptide upstream primers are all introduced into the streptococcal RBS sequence AAGGAGGATGT, and the downstream primers are all introduced into the N-terminal 20bp sequence of hyaluronidase Hya...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2 Shake flask culture and enzyme activity assay of 9 strains of recombinant Streptococcus zooepidemicus
[0061] Pick the 9 recombinant Streptococcus zooepidemicus strains constructed above and the control bacteria (transformed pEU308 empty plasmid), inoculate the monoclonal in 5mL seed medium, culture at 200rpm37°C overnight, then transfer to 250mL with 10% inoculum Erlenmeyer shake flask, the culture medium is the fermentation medium, the filling volume is 25mL, it is cultured at 200rpm at 37°C for 20h, and 0.1mMIPTG is added for induction.
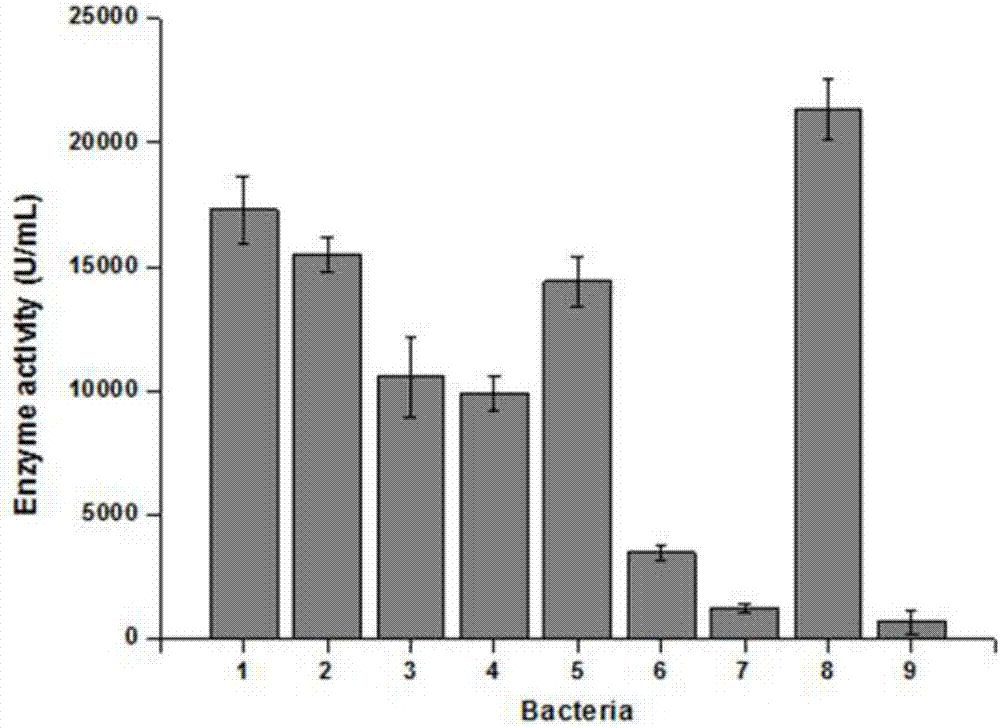
[0062] The 20h fermented liquid samples in shake flasks of 9 strains were taken respectively and centrifuged at 5000r / min at 4°C for 5min, the supernatant was retained, and the crude enzyme activity in the supernatant was determined. From attached figure 2 It can be seen that in the inducible promoter P spac Under the mediation effect, nine recombinant strains S.zooepidemicus HyalA, HyalC, S.zooepidemicus HyalE, S.z...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3 Determination of Hyaluronic Acid Production and Molecular Weight of Recombinant Streptococcus zooepidemicus
[0064] Take the fermentation broth samples of the recombinant bacteria fused with the signal peptide and the control bacteria to the 20th hour, centrifuge at 5000r / min, 4°C for 5min, save the supernatant, add 3 times the volume of 100% ethanol for precipitation, mix well and place After 30 minutes, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 10 minutes, add an equal volume of distilled water, and redissolve the precipitate at 4°C. This purification step is repeated three times. The content of hyaluronic acid was determined by the Bitter-Muir carbazole colorimetric method. Add 1 mL of borax sulfuric acid reagent and 200 μL of hyaluronic acid sample diluted by a certain multiple into the colorimetric tube, mix well and cook in boiling water for 15 min, and cool to At room temperature, add 50 μL carbazole reagent, mix well and cook in boiling water for 15 minutes, measur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com