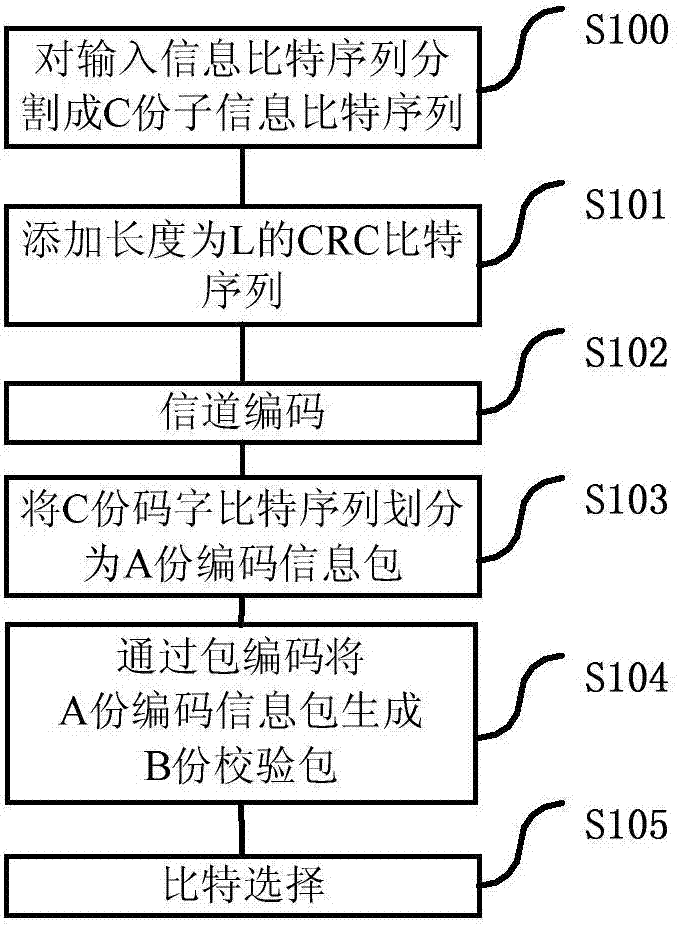
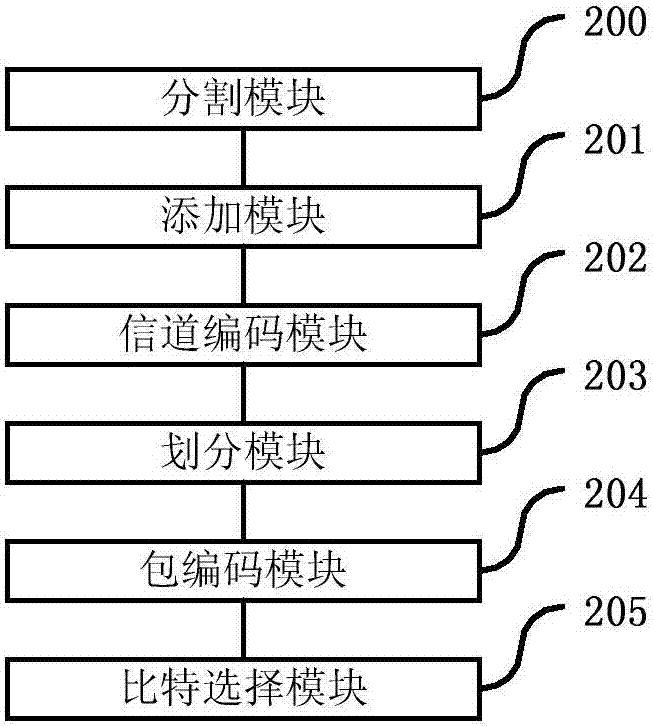
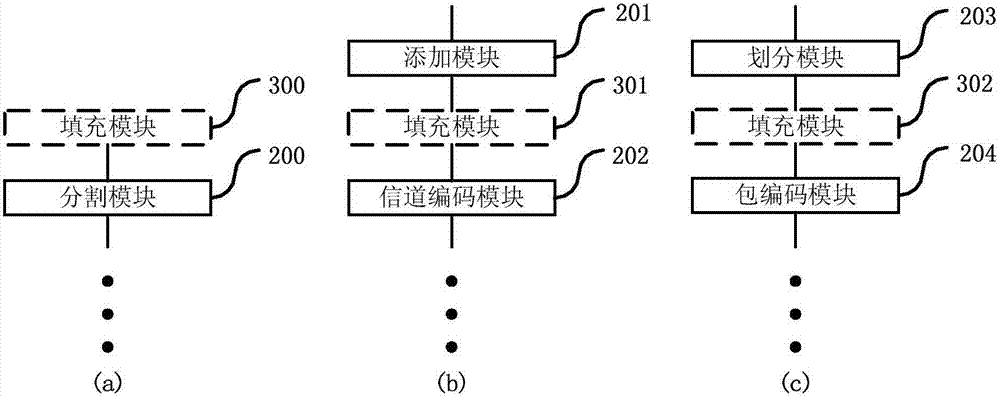
Data packet coding processing method and device, base station and use equipment
A processing method and data packet technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of reducing complexity, high throughput, increasing hardware complexity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0183] According to an aspect of this embodiment, it is used in a wireless data communication system, which can be used in a base station, including: an access point (AP), or may be called a node B (node B), a radio network controller (RNC) , Evolved Node B (Evolved Node B, eNB for short), Base Station Controller (BSC), Base Transceiver Station (BTS), Base Station (BS), Transceiver Function (TF), Radio Router, Radio Transceiver, Basic Services Cell (BSS), Extended Service Cell (ESS), Radio Base Station (RBS), or some other terminology.
[0184] Such as Figure 4 What is shown is a simple link embodiment of a wireless communication system adopting multiple aspects related to the embodiment of the present invention. The sending end 400 sends data to the receiving end 401, and the receiving end 401 sends a feedback signal to the sending end 400 according to the correctness of the received data. The sending end 400 is a base station, and other equipment or devices as descri...
Embodiment 2
[0205] According to one aspect of the present invention, this embodiment corresponds to the retransmission data processing method described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the maximum number of retransmissions is 3 times (including the first transmission, and the maximum number of transmissions is 4 times), and each The total number of bits of data transmitted for the second time is equal to the number of bits of data transmitted for the first time. In the processing method of the 1st or 2nd or 3rd retransmission data (the 0th retransmission data refers to the first transmission data), the number of codeword bit sequence bits and the number of check packet bits after rate matching are determined by the following parameters:
[0206] The number of data bits in the first transmission Q=12168, the number of codeword bit sequences C=10, the number of bits in the codeword bit sequence in the first transmission N1=1156, and the length of the first transmission check packet k...
Embodiment 3
[0213] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the number of bits in the codeword bit sequence after calculating the bit selection for each rate-matched part can be determined by the following parameters:
[0214] The total number of transmitted bits Y, the number of codeword bit sequences C=10 and the number of information bits k'=608 of B=1 check packet.
[0215] Let the total transmission bit number Y=16000, so the number of codeword bit sequence bits after the rate matching is: the number of bits of the former C1=2 shares is N1=1540 bits, and the number of bits of the rear C-C1=8 shares is N1-1 = 1539 bits, C1 and N1 are calculated as: C1=mod(Y-k',N1-1)=2.
[0216] Alternatively, it can be determined by the following parameters:
[0217] The modulation order M, the number of preset resources G, the number of codeword bit sequences C=10, and the number of information bits B=1 check packet k'=608.
[0218] Assume that the modulation o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com