Method for cooperatively treating waste mercuric chloride contact agent through microwaves and ultrasonic waves
A collaborative processing and ultrasonic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, carbon compounds, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, low recovery rate of mercury chloride and low regeneration rate of activated carbon, and achieve short processing time, save processing time and The effect of process energy consumption and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
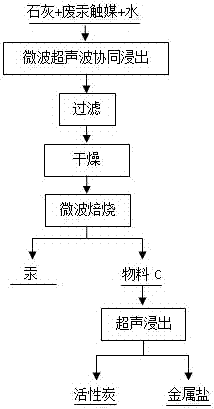
[0024] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 Shown, a kind of method of microwave and ultrasonic co-processing waste mercuric chloride catalyst, concrete steps are as follows:
[0025] (1) Mix 50g of spent mercuric chloride catalyst and 10g of quicklime to obtain mixture A. The mass ratio of spent mercury catalyst to quicklime in mixture A is 5:1; Ratio, add 0.12L water to mixture A and mix well to obtain mixture B;
[0026] (2) Under microwave and ultrasonic conditions, where the ultrasonic frequency is 20 Hz, the ultrasonic power is 30 W, and the microwave power is 50 W, the mixture B obtained in step (1) is leached for 20 minutes, filtered, and then placed at a temperature of 80 Dry under microwave conditions at ℃ for 40min;
[0027] (3) Under the condition of nitrogen, where nitrogen is fed from the bottom of the furnace, the nitrogen flow rate is 10L / min, and the nitrogen purity is 90%, the product obtained in step (2) is subjected to microwave roasting to obtain material C, which ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 Shown, a kind of method of microwave and ultrasonic co-processing waste mercuric chloride catalyst, concrete steps are as follows:
[0031] (1) Mix 50g of spent mercury chloride catalyst and 5g of quicklime to obtain mixture A. The mass ratio of spent mercury catalyst to quicklime in mixture A is 10:1; Ratio, add 1.1L water to mixture A and mix well to obtain mixture B;
[0032] (2) Under microwave and ultrasonic conditions, where the ultrasonic frequency is 1100 Hz, the ultrasonic power is 10 W, and the microwave power is 1200 W, the mixture B obtained in step (1) is leached for 100 minutes, filtered, and then placed at a temperature of 110 ° C Dry under microwave conditions for 18min;
[0033] (3) Under the condition of nitrogen, where nitrogen is fed from the bottom of the furnace, the nitrogen flow rate is 80L / min, and the nitrogen purity is 81%, the product obtained in step (2) is subjected to microwave roasting to obtain material C, whi...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 Shown, a kind of method of microwave and ultrasonic co-processing waste mercuric chloride catalyst, concrete steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) Mix 50g of spent mercuric chloride catalyst and 12.5g of quicklime to obtain mixture A. The mass ratio of spent mercury catalyst to quicklime in mixture A is 4:1; according to the liquid-solid ratio of water to mixture A, mL:g is 10:1 The ratio of 0.625L water is added to mixture A and mixed evenly to obtain mixture B;
[0038] (2) Under microwave and ultrasonic conditions, wherein the ultrasonic frequency is 2500 Hz, the ultrasonic power is 200 W, and the microwave power is 3000 W, the mixture B obtained in step (1) is leached for 240 minutes, filtered, and then placed at a temperature of 100 Dry under microwave conditions at ℃ for 10 minutes;
[0039] (3) Under the condition of nitrogen, where nitrogen is introduced from the surface of the raw material, the nitrogen flow rate is 180L / min, and the ni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com