A two-stage anaerobic digestion method for treating molasses alcohol wastewater
A technology for molasses alcohol wastewater and secondary anaerobic treatment, applied in anaerobic digestion treatment, chemical instruments and methods, natural water treatment, etc. Fermentation biogas and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving biogas yield and biomass energy recovery, good research and application prospects, and improving the effect of anaerobic treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
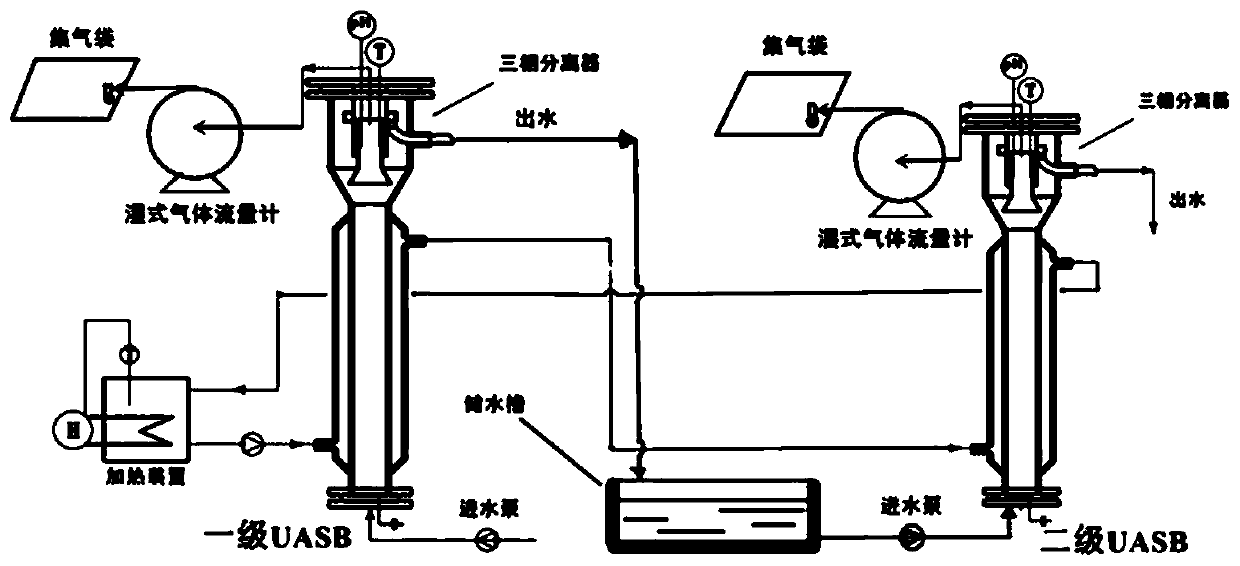
[0020] Example 1 Experimental device diagram
[0021] The temperature of the reaction system of the two-stage UASB reactor for the treatment of molasses alcohol wastewater is 35°C, and the initial pH of the influent is adjusted to 7.20-7.50 with sodium carbonate solution. The generated biogas is desulfurized by a water-sealed bottle, measured by a wet gas flow meter, and then collected by a gas collection bag to determine the gas composition and content. Before and after the anaerobic digestion reaction, the pH, COD concentration, sulfate concentration and sulfide concentration of the wastewater were measured; after the reaction, the biogas volume and methane content were measured, and the determination methods were analyzed by national standard methods (Table 1 ).
[0022] Table 1 Analysis items and methods
[0023]
[0024] The experimental design is that the effective volume of the primary anaerobic UASB reactor is 12L, the volume of the reaction zone is 7.7L, the volu...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2 Variation of anaerobic effluent pH
[0026] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the pH of the effluent of the two-stage anaerobic reactor is higher than the pH of the influent, and it shows an upward trend as the load increases. The reason for the increase of effluent pH value may be that the concentration of organic acids in the influent water is high. During the anaerobic digestion process, MPB and SRB directly use the organic acids in the wastewater to carry out metabolic activities such as methane production and sulfate radical reduction. The acid-producing bacteria are in In a weak position, the metabolic activity is inhibited, and the concentration of organic acids in the wastewater is reduced.
Embodiment 3
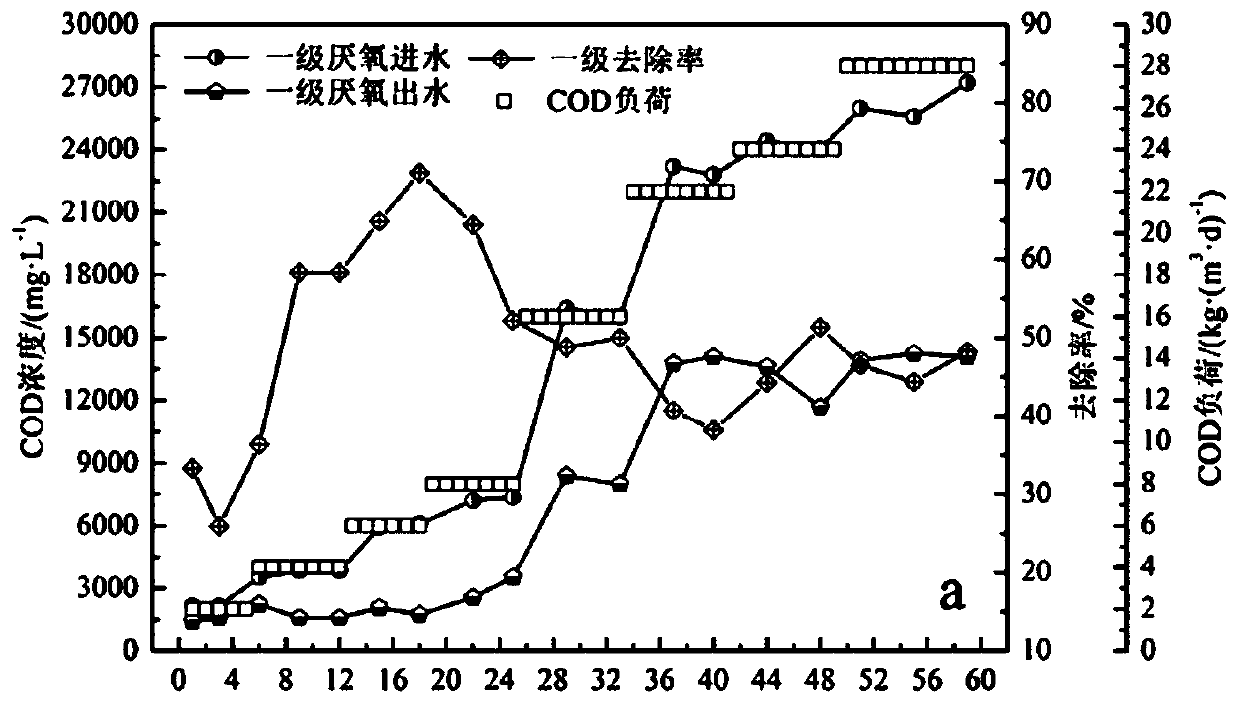
[0027] Embodiment 3 Influent and effluent COD concentration and COD removal rate variation
[0028] The degradation of wastewater COD is as follows: Figure 3-a and Figure 3-b shown. Depend on Figure 3-a It can be seen that with the increase of influent COD concentration, the removal of COD in the first-stage anaerobic digestion process first increases, then decreases and gradually stabilizes at about 45%. The COD removal rate of the primary anaerobic process was low at the initial stage of reactor operation, which may be due to the fact that the microorganisms in the sludge had not yet adapted to the molasses alcohol wastewater; when the reactor ran to the 9th day, the primary COD removal rate rose to 58.3%, indicating that the microorganisms had not yet adapted to the molasses alcohol wastewater; It basically adapts to wastewater, and can effectively use the organic matter in wastewater for metabolic activities; when the reactor runs to the 18th day, the primary COD rem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com