Bacterial strain for degrading diethyl terephthalate and application thereof
A technology of diethyl phthalate and bacterial strains, which is applied to bacterial strains and application fields that can efficiently degrade diethyl terephthalate, and can solve problems such as carcinogenicity, imperfect treatment process of diethyl terephthalate, and environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Isolation and screening of diethyl terephthalate degrading strain Delftia WL-3:
[0045] Take 5mL of sewage samples and place them in 100mL enrichment medium containing 500mg / L diethyl terephthalate, at 30°C, 180r min -1 Culture 7d. Measure the degradation situation of the diethyl terephthalate in the enrichment solution with an ultraviolet scanner, after confirming that the diethyl terephthalate is degraded, insert the solution containing 750mg / L diethyl terephthalate with 10% inoculum In the ethyl ester-rich medium, continue to enrich and measure the degradation, follow this method until the concentration of diethyl terephthalate increases to 1500mg / L, and pass for 3 times.
[0046] The diethyl terephthalate enrichment solution was serially diluted and spread on an inorganic salt plate with 1000 mg / L diethyl terephthalate as the sole carbon source, and cultured in a 30°C incubator for 3 to 4 days. Single colonies with different colony shapes were streaked on LB plat...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Identification and growth characteristics of strain Delftia WL-3 degrading diethyl terephthalate and its metabolites:
[0052] Identification of WL-3:
[0053] 16S rDNA identification of WL-3: Use primers 27F: 5`-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3` and 1492R: 5`-TACCTTGTTACGACTT-3` to amplify the 16S rDNA of strain WL-3, and connect it to the clone by T / A cloning Vector pMD19T, construct the recombinant cloning vector pMD19T-16S, transform it into the cloning host strain Escherich coli DH5α to obtain the recombinant microorganism Escherich coli DH5α (pMD19T-16S), sequence the exogenous fragment of the recombinant microorganism obtained, and compare the NCBI database 16S rDNA sequence, the strain WL-3 was identified to the genus Delftia at the molecular level, and the nucleotide sequence of its 16S rDNA is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence table.
[0054] Growth characteristics of WL-3:
[0055] Delftia WL-3 grows slowly on LB plate, 30℃, 48h can form a milky white colony with...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Degradation characteristics of diethyl terephthalate and its metabolite-degrading bacteria Delftia WL-3:
[0059] Pick a single colony of strain WL-3 from the LB plate, inoculate them in 3 mL LB liquid medium at 30°C, shaker 180r min -1 Cultivate for 12h. Then the culture solution of the bacterial strain was transferred to 100 mL of fresh liquid LB medium, and the culture was continued for 12 h. 6000r·min -1 Centrifuge for 10min, collect the bacteria, wash twice with sterilized inorganic salt medium, and make OD 600nm =1.0 bacterial suspension, that is, seed liquid. In the inorganic salt medium with a final concentration of diethyl terephthalate of 1000mg / L, insert OD at 5% inoculum 600nm =1.0 Strain WL-3 seed liquid, at 30°C, 180r·min -1 Shake the culture, take a sample every 24h, measure the OD 600nm and concentrations of diethyl terephthalate.
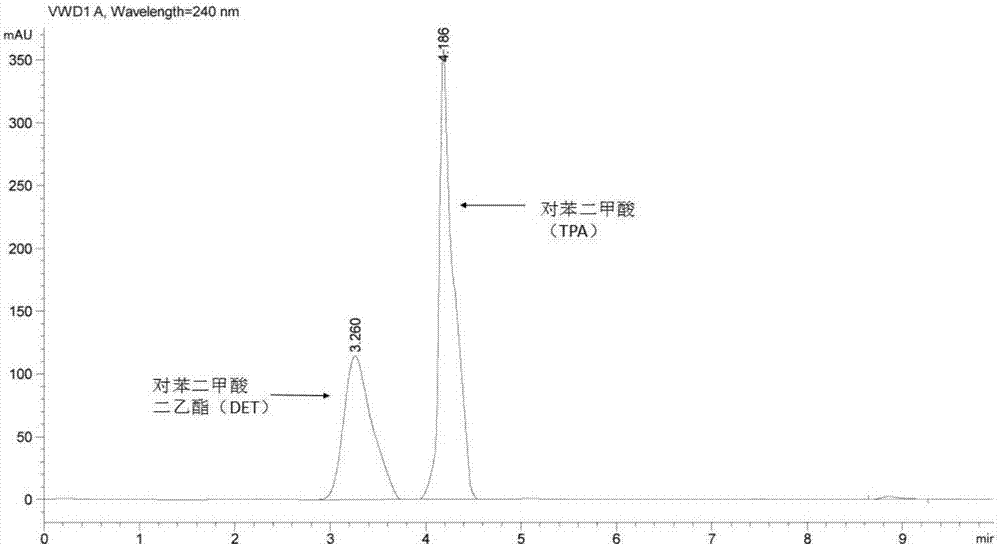
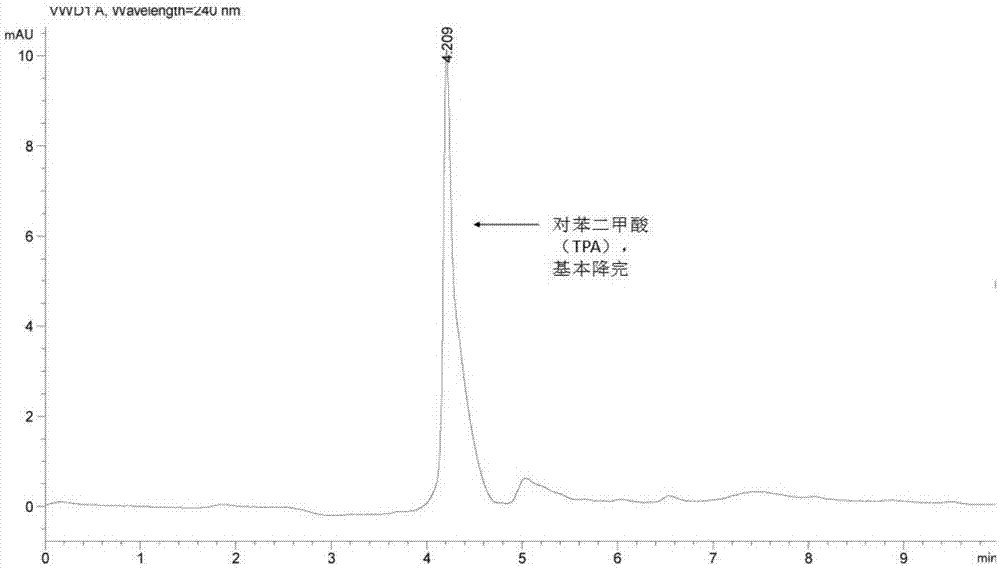
[0060] Depend on Figure 4a ~ Figure 4d It can be seen that the bacterial strain WL-3 was inoculated in the medium ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com