Rare earth iron alloy and preparation method thereof
A ferroalloy and rare earth technology, which is applied in the field of rare earth ferroalloy and its preparation, can solve the problems of high local concentration of rare earth metals, affecting product consistency, and high requirements for melting temperature, and achieves broad development and market prospects, controllable rare earth content, and product quality high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
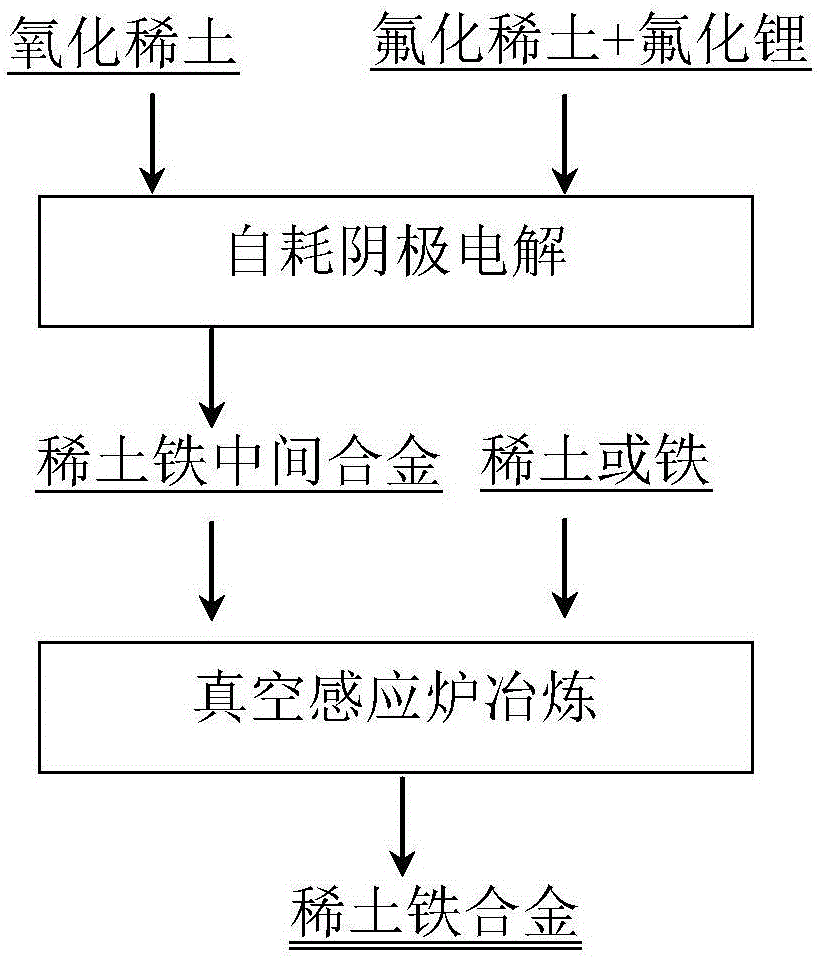
[0037] A preparation process for rare earth iron alloys for producing rare earth steels, comprising the following steps:
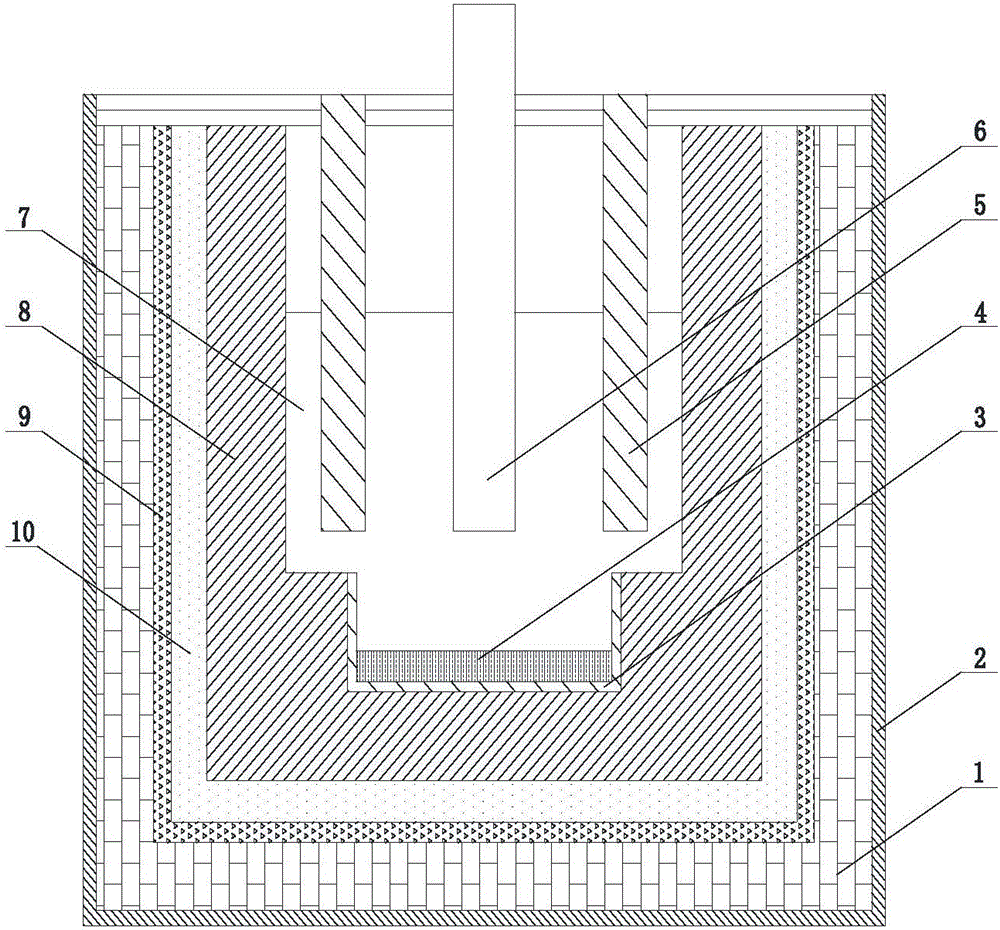
[0038] Step 1: Graphite is used as the electrolytic cell, the graphite plate is used as the anode, the iron rod is used as the self-consumable cathode, and there is a receiver containing the alloy under the cathode;
[0039] The material of the receiver can be one of iron, rare earth oxide, and boron nitride.
[0040] Step 2: In the fluoride molten salt electrolyte system of rare earth fluoride and lithium fluoride, the rare earth oxide is used as the electrolytic raw material, and the rare earth iron master alloy is obtained by direct current electrolysis;
[0041] Step 3: The rare earth iron master alloy and iron are used as raw materials, and the rare earth iron alloy is prepared by a melting method.
[0042] The equipment for melting rare earth iron master alloys into rare earth iron alloys is an intermediate frequency induction furnace. The melting ...
Embodiment 1
[0049]A Φ650mm circular graphite electrolytic cell is used. The anode is composed of four graphite plates. In the electrolyte, scandium fluoride is 80wt%, lithium fluoride is 20wt%, the cathode is a 70mm pure iron rod, the average current intensity is 5000A, and the anode current density is 0.5- 1.0A / cm 2 , cathode current density 8-25A / cm 2 , the electrolysis temperature was maintained at 900-1050°C, the electrolysis was continued for 240 hours, 870 kg of scandium oxide was consumed, and 733 kg of scandium-iron alloy was obtained, with an average scandium content of 75% and a current efficiency of 82%. The alloy composition results are shown in Table 1.
[0050] Table 1 Rare earth iron master alloy composition analysis results / wt%
[0051] sc Fe C O P S Si mn 75.0 24.55 0.0085 0.0094 <0.01 <0.005 0.012 <0.005
[0052] Using the scandium-iron master alloy prepared in this example as a raw material, take 2 kg of scandium-iron master alloy, a...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A Φ650mm circular graphite electrolytic cell is used, the anode is composed of four graphite plates, the electrolyte contains 75wt% gadolinium fluoride and 25wt% lithium fluoride, the cathode is a 70mm pure iron rod, the average current intensity is 4500A, and the anode current density is 0.5- 1.0A / cm 2 , cathode current density 4-15A / cm 2 , the electrolysis temperature was maintained at 900-1050°C, the electrolysis was continued for 150 hours, 1223kg of gadolinium oxide was consumed, and 1287kg of gadolinium-iron alloy was obtained, with an average gadolinium content of 80% and a current efficiency of 78%. The alloy composition results are shown in Table 3.
[0057] Table 3 Rare earth iron master alloy composition analysis results / wt%
[0058] Gd Fe C O P S Si mn 80.10 19.48 0.0084 0.0092 <0.01 <0.005 0.010 <0.005
[0059] Using the gadolinium-iron master alloy prepared in this example as a raw material, take 3.8 kg of gadolinium-ir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com