Regulatory approaches to skyrmions in the hexagonal mnniga
A magnetic field and strip technology, applied in the field of regulation of skyrmions, can solve problems such as narrow temperature range, lack of zero-field stability, and disappearance of skyrmions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1) Preparation (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35 Sample: will (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35 The sample block was cut into rectangular pieces of 3 mm x 2 mm. In order to facilitate the direct observation of nano-sized skyrmions under the transmission electron microscope, the observation area of the sample was polished by sandpaper, pitter and polisher, and then thinned by an ion thinner, so that the thickness of the observation area of the sample was less than 100 Nano. Mount the sample with the thinned observation area on the electric field rod and insert it into the transmission electron microscope. Among them, the current can be applied to the sample through the Keithley ammeter, and the required magnetic field can be generated by the objective lens current of the transmission electron microscope, and the (001) crystal plane of the sample can be regulated as follows through the transmission electron microscope.
[0036] 2) Vertical (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35 A magnetic ...
Embodiment 2
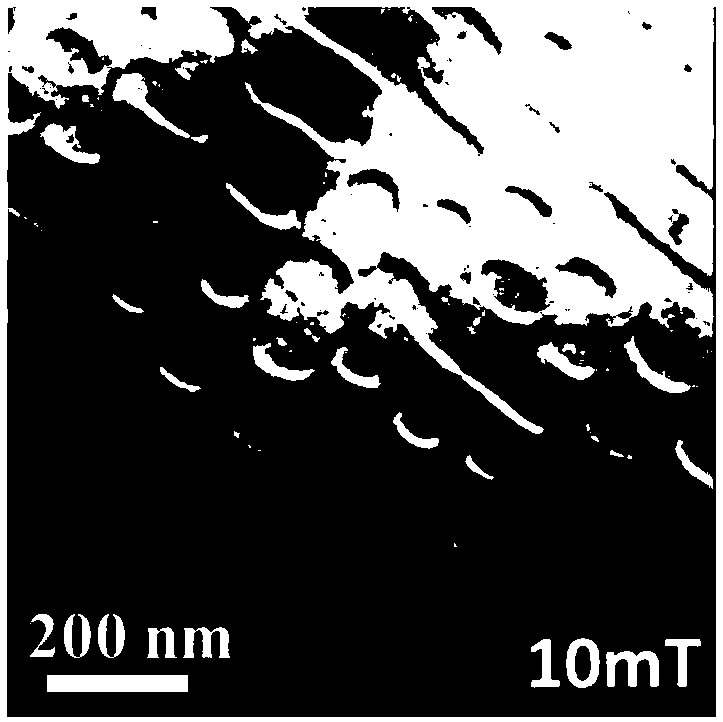
[0041] It is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that in step 2) a magnetic field of 10mT is applied (this magnetic field is not enough to make the hexagonal (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35 Strip magnetic domains in the transition into skyrmions). figure 2 is the magnetic domain structure diagram of the skyrmion obtained according to the above control method. After removing the external magnetic field, it is found that the formed skyrmions can still be stored stably, with non-volatile zero-field stability. Will (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35After the temperature is increased from room temperature to 330K or decreased to 100K, it is found that skyrmions can still exist stably, so the regulation method of the present invention forms skyrmions at room temperature in a wide temperature range.
Embodiment 3
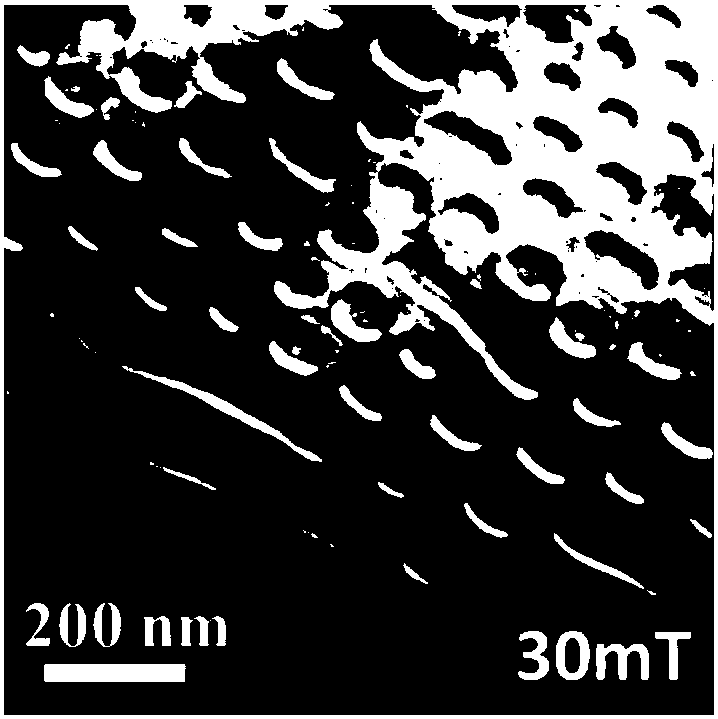
[0043] It is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that in step 2) a magnetic field of 30mT is applied (this magnetic field is not enough to make the hexagonal (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35 Strip magnetic domains in the transition into skyrmions). image 3 is the magnetic domain structure diagram of the skyrmion obtained according to the above control method. After removing the external magnetic field, it is found that the formed skyrmions can still be stored stably, with non-volatile zero-field stability. Will (Mn 50 Ni 50 ) 65 Ga 35 After the temperature is increased from room temperature to 330K or decreased to 100K, it is found that skyrmions can still exist stably, so the regulation method of the present invention forms skyrmions at room temperature in a wide temperature range.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com