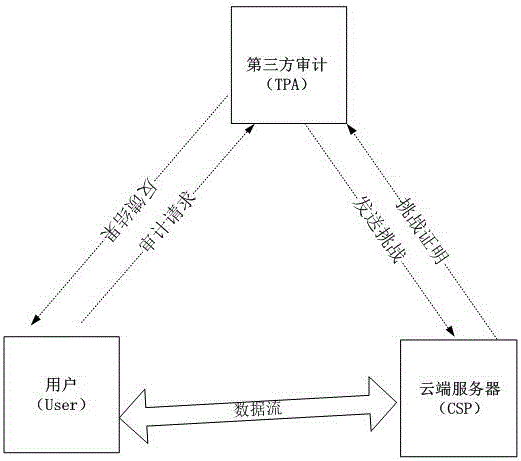
Dynamic verification method of cloud storage data using lattice-based linearly homomorphic signatures
A dynamic verification and cloud storage technology, applied in user identity/authority verification, homomorphic encryption communication, digital transmission system, etc., can solve problems such as not supporting dynamic data verification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
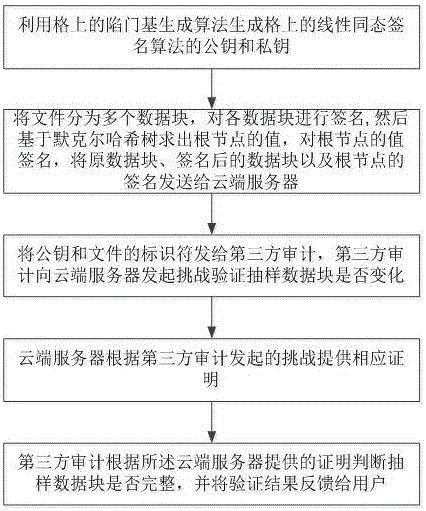
[0057] Such as figure 2 As shown, the dynamic verification method of cloud storage data based on lattice-based linear homomorphic signature includes data integrity verification, and the data integrity verification includes:
[0058] S01. Key generation: use the trapdoor base generation algorithm on the lattice to generate the public key and private key of the linear homomorphic signature algorithm on the lattice.
[0059] The keys are generated in the following way:
[0060] (pk,sk)←TrapGen(1 n )
[0061] p k = A ∈ Z q n * m , s k = T ∈ Z q m * m
[0062] In the formula, TrqpGen(1 n ) is the trapdoor base generation algorithm on the lattice, pk is the public key, sk is the private key, It is a group composed of m*m integer matrices in base q. Mat...
Embodiment 2
[0086] On the basis of Embodiment 1, in this embodiment, the dynamic verification method also includes modifying data: M represents the request information for data modification, and the user wants to change the data block u i change into As an example, the user will modify the data block Use the lattice-based linear homomorphic signature algorithm to find the corresponding signature order update information and will update the information sent to the cloud server;
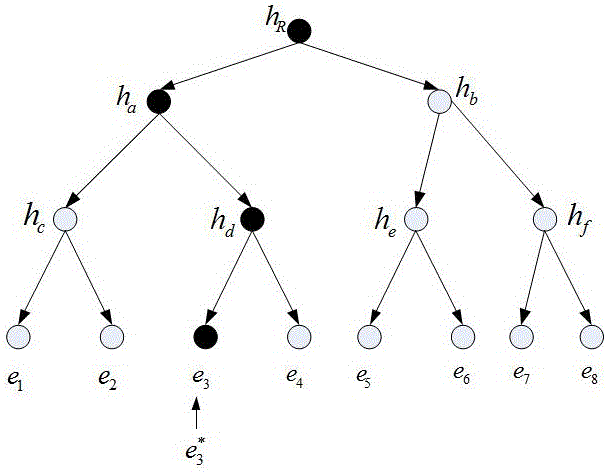
[0087] The cloud server executes the polynomial time algorithm ExeUpdate(F,Φ,Update), and the cloud server modifies the data block according to The subscript i of the data block u to be modified i Replace with Modified Data Block signature e i replace with get file signature collection According to the signature set Φ * Calculate the value of the new root node Such as image 3 As shown, the cloud server will prove Sent to user ;P Update It is the proof of whether the data sent by the clo...
Embodiment 3
[0091] On the basis of Embodiment 1, in this embodiment, the dynamic verification method also includes modifying data: I represents the request information for data insertion, so that the user can add data block u after the i-th data block *' as an example.
[0092] The dynamic verification method also includes inserting data: the user uses a lattice-based linear homomorphic signature algorithm to obtain the inserted data block u *' signature e *' , and update information Update={I,i,u *' ,e *'} to the cloud server;
[0093] The cloud server executes the polynomial time algorithm ExeUpdate(F,Φ,Update), and inserts the data block u *' Stored in the cloud server, the signature e *' put in signature e i After that, get the file signature collection Calculate the value of the new root node (Such as Figure 4 shown); the cloud server will sent to the user;
[0094] User according to (Ω i ,e i ) Find the value h″ of the root node of the Merkle hash tree R , judge ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com