Alkaline phosphatase determination method based on carbon-dots fluorescence ''quenching-recovery''
A technology of carbon dot fluorescence and determination method, which is applied in the field of biological analysis and detection of nanomaterials, and can solve problems such as analysis and determination that have not yet been found.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
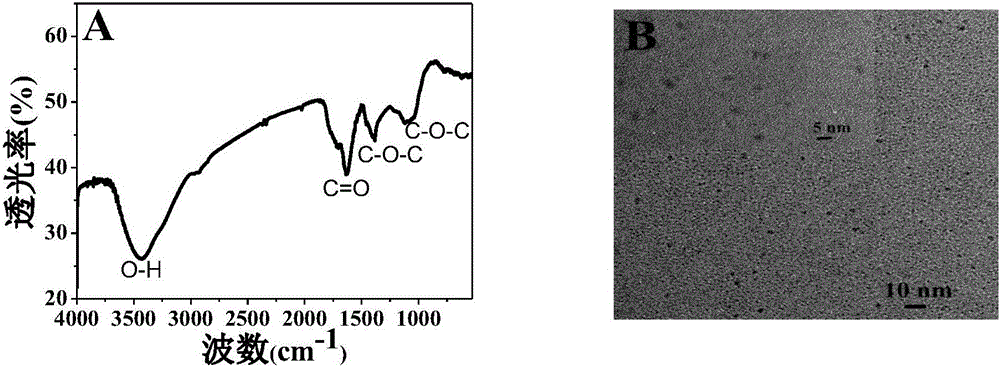
[0017] a. Weigh 1.1g of ascorbic acid and dissolve it in 25mL of ethanol solution, mix it with 25mL of ultrapure water, stir to form a uniform solution, transfer it to the reaction kettle, heat at 180°C for 4h, and cool the obtained dark brown solution with dichloro Methane was extracted, and the obtained solution was dialyzed with ultrapure water for 24 hours as a fluorescent probe;
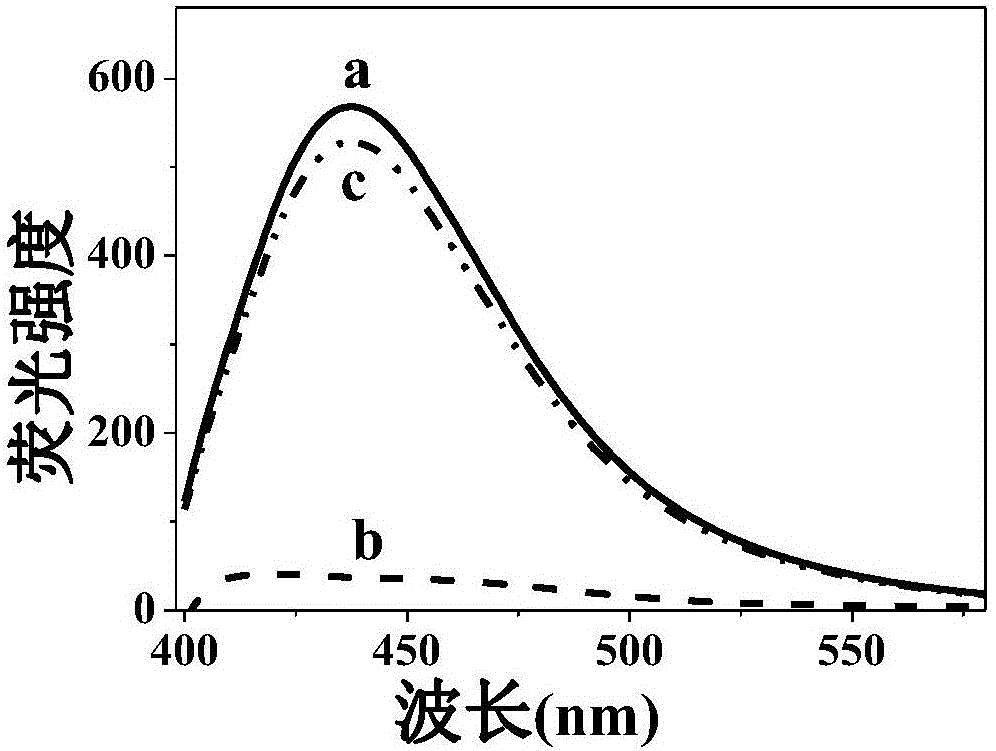
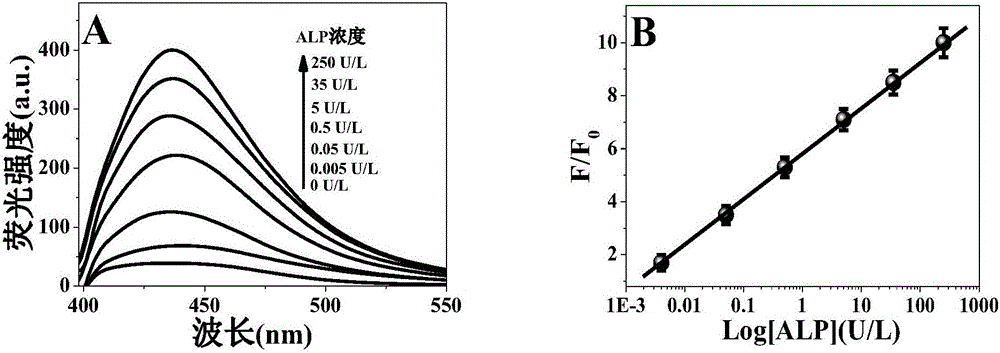
[0018] b. Add 50 μL 0.1mol / L trisodium ascorbic acid solution and 50 μL alkaline phosphatase solution of different concentrations into 400 μL Tris-HCl buffer solution with pH=8.5, and add 100 μL potassium permanganate (0.01 mmol / L) and 0.35mg / mL carbon dot mixture (the fluorescence intensity is recorded as F 0 ), and measure the fluorescence intensity after 2 min of reaction.
Embodiment 2
[0020] a. Add 25mL of milk to 20mL of ultrapure water, stir it into a uniform solution, transfer it to a reaction kettle, heat it at 180°C for 2h, filter it with a microporous filter after cooling, and dialyze the obtained solution with ultrapure water for 24h as Fluorescent probes;
[0021] b. Add 50 μL 0.1mol / L p-aminophenylphosphate sodium salt solution and 50 μL alkaline phosphatase solution of different concentrations to 400 μL Tris-HCl buffer solution with pH=8.5, react for 25 minutes and add 100 μL containing potassium permanganate ( 0.01mmol / L) and 0.35mg / mL carbon dot mixture (the fluorescence intensity is recorded as F 0 ), and measure the fluorescence intensity after 2 min of reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com