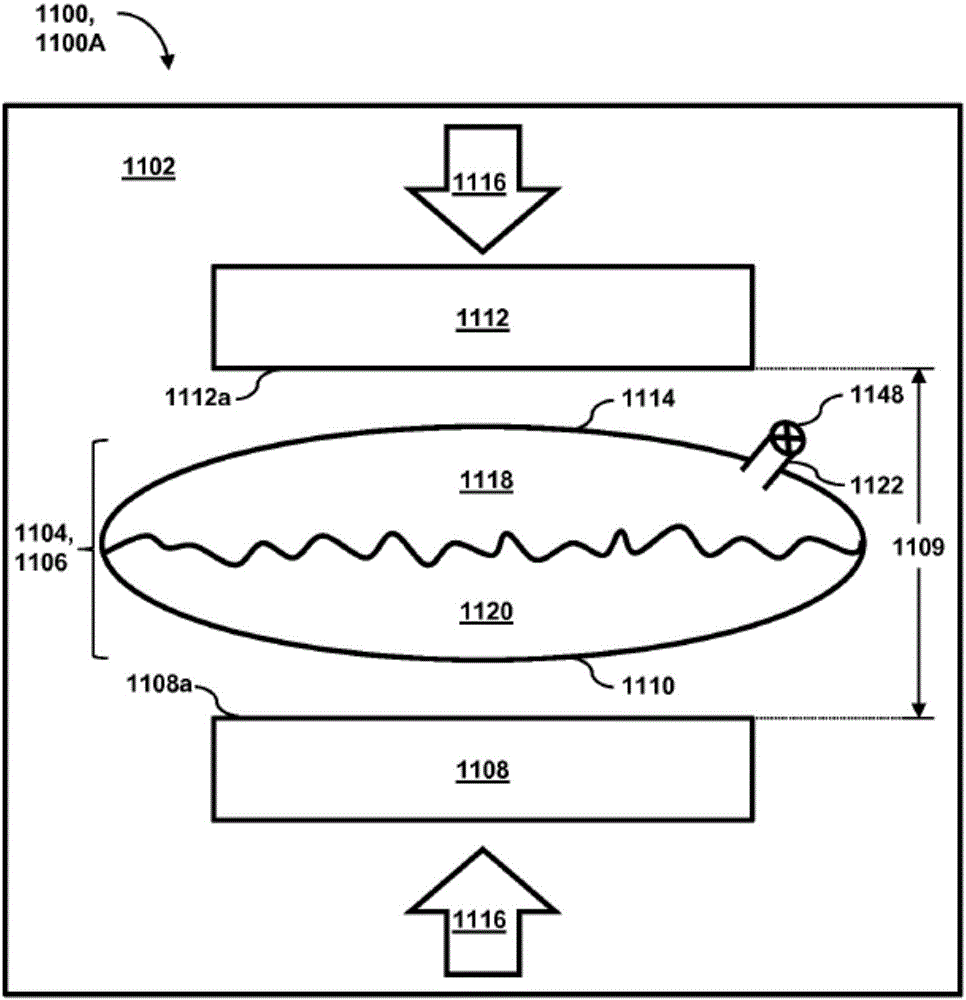
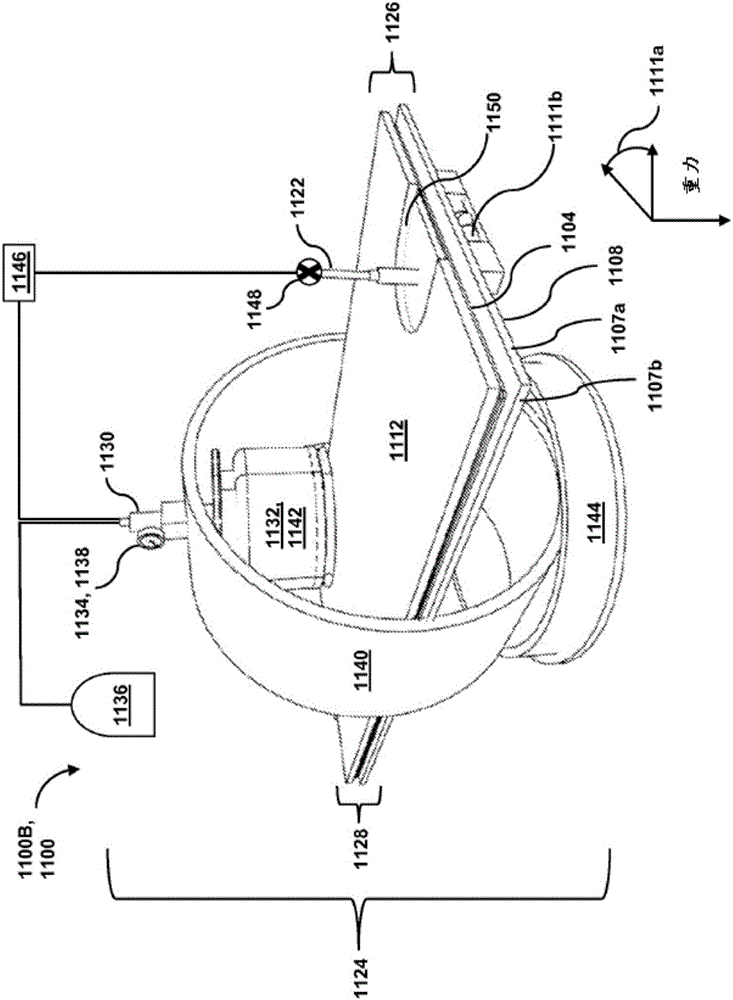
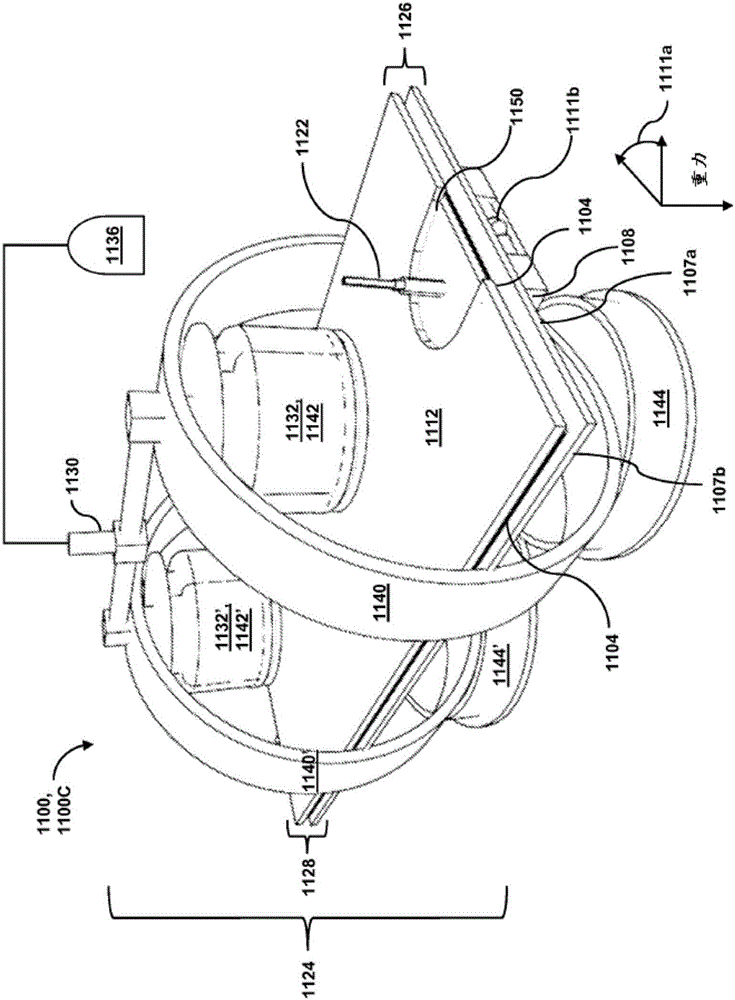
Passive separation of whole blood
A platelet and storage technology, applied in the field of passive separation of whole blood, can solve the problems of expensive, labor-intensive, and energy-intensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0166] Embodiment 1: CIF device is made
[0167] Desired device parameters were entered into custom-written MATLAB software, and the resulting design feature structural coordinates were exported for use in generating CAD for each device. A chrome-on-glass photomask designed by a CAD facility was then used to pattern the microchannel pattern in photoresist (SU8 3050, ~100-150 μm deep) that was spin-coated onto standard 4 on a silicon wafer and subjected to UV (i-line) exposure. An inverse polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS; SylGard 184, Dow Corning, Midland, MI) model of the wafer / photoresist master was created and passed Air plasma oxidation seals the model to a PDMS-coated glass slide. Input and output fluidic ports are created in ~5 mm thick PDMS by a biopsy punch prior to sealing. The particle suspension of interest is then introduced Previously, the PDMS device was treated with polyethylene glycol (PEG). Fluid was driven through the device by inserting an appropriate length of 1....
Embodiment 2A
[0169] Example 2A: CIF two-step design method for separation of polystyrene beads
[0170] In the first step, multiple filter channels are tested simultaneously, each with a different f 间隙 value. By observing that with f 间隙 changes in which particles are or are not maintained in the central channel, choosing an appropriate f 间隙 Values for patterning the entire device in a second step.
[0171] Figure 11 The results obtained from performing the first step on beads with various diameters in three microchannel arrays with different central channel widths (100 μm, 125 μm and 150 μm) are presented. In each case, a parallel array of 33 test devices was designed to explore a wide range of degrees of filtration for each gap, where the device f 间隙 Values range from 6.4x10 -5 (device #1) linearly down to 5.76x10 -4 (Device #33). A device array with given parameters was designed according to Equations 1 and 2 and created for testing. Visually by observing the f below which ...
Embodiment 2B
[0172] Example 2B: Application of a CIF two-step design based on polystyrene beads and platelet separation
[0173] The results in Example 2A give approximate guideline values that can be used to study more complex particle enrichment / filtration applications than simple beads in saline solution. One such application of widespread interest in fact is the further enrichment of platelets in a suspension of PRP to levels above the AABB standard in PC. Platelets have an approximately discoid and highly variable, heterogeneous and dynamic shape with an effective diameter of ~1.5-4 μm. research flow as Figure 11 Behavior of the same three arrays of PRPs described in , with particular focus on devices in the range #2 to #10, which correspond to ~1-2x10 -4 the f 间隙 value. The platelets of the subjects studied were consistently retained in the following device #9 (w c =100μm), #8 (125μm) and #5 (150μm) in the central flow channel, the device corresponds to 1.92x10 -4 , 1.76x10 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com