Saccharifying enzyme high-yield strain gene knockout recombinant bacteria with low trans-glycoside enzyme background as well as construction method and application thereof
A high-yield, gene-knock-out technology for glycosylase, applied in the direction of glycosylase, recombinant DNA technology, enzymes, etc., can solve the problem of undocumented glycosylase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
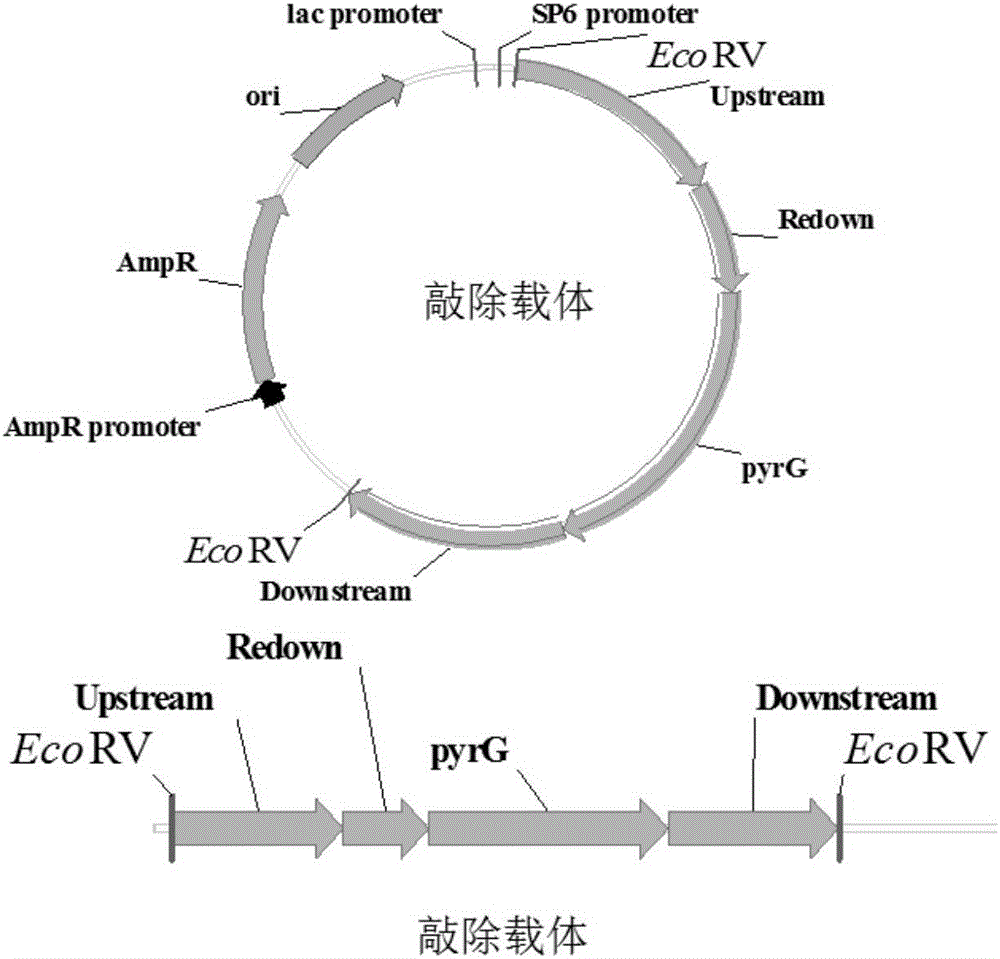
[0065] Example 1 Construction of Aspergillus niger α-glucosidase gene knockout vector
[0066]Using the Aspergillus niger SH-2 genome as a template, use primers Upstream-F and Upstream-R, Redown-F and Redown-R, Downstream-F and Downstream-R respectively to amplify to obtain an Upstream fragment of about 1000bp (to be The upstream homology arm of the gene to be knocked out), the Redown fragment of about 500bp (the partial repeat sequence of the downstream homology arm of the gene to be knocked out) and the Downstream fragment of about 1000bp (the downstream homology arm of the gene to be knocked out); to construct Aspergillus nidulans (Aspergillus nidulans) genome was used as a template, and a 1398bp pyrG fragment (as shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO: 8 in the sequence listing) was amplified with primer pairs pyrG-F and pyrG-R. After the gel was recovered, it was used as an Upstream fragment, Redown fragment and pyrG fragment were used as templates, and Upstream-F and pyrG-R wer...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Transformation and screening of homologous recombination knockout target gene
[0068] 1. Preparation of protoplasts: in CD liquid medium (glucose 2%; NaNO 3 0.3%; KCl 0.2%; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.05%; KH 2 PO 4 0.001%; agarose 0.05%; pH5.5; after sterilization, add 1 × uridine) to cultivate Aspergillus niger mycelia, and transfer to YPD liquid medium (peptone 2%; yeast powder 1 %; glucose 2%; add 1× uridine after sterilization). The mycelium balls were filtered from the culture medium with double-layer filter paper and washed with 0.8M NaCl. v), 1% helicase (w / v) and 0.5% lysozyme (w / v) in the enzymolysis solution. 30°C, 100rpm enzymatic hydrolysis for 1.5-3h. Then place the enzymatic hydrolysis solution containing protoplasts on ice, filter through four layers of lens paper and rinse with 5mL NaCl four times. The filtrate was centrifuged at 900×g at 4°C for 10 min, and the supernatant was discarded; with 20 mL of STC (10 mM Tris-HCl; 1.2 M sorbitol; 50 ...
Embodiment 3
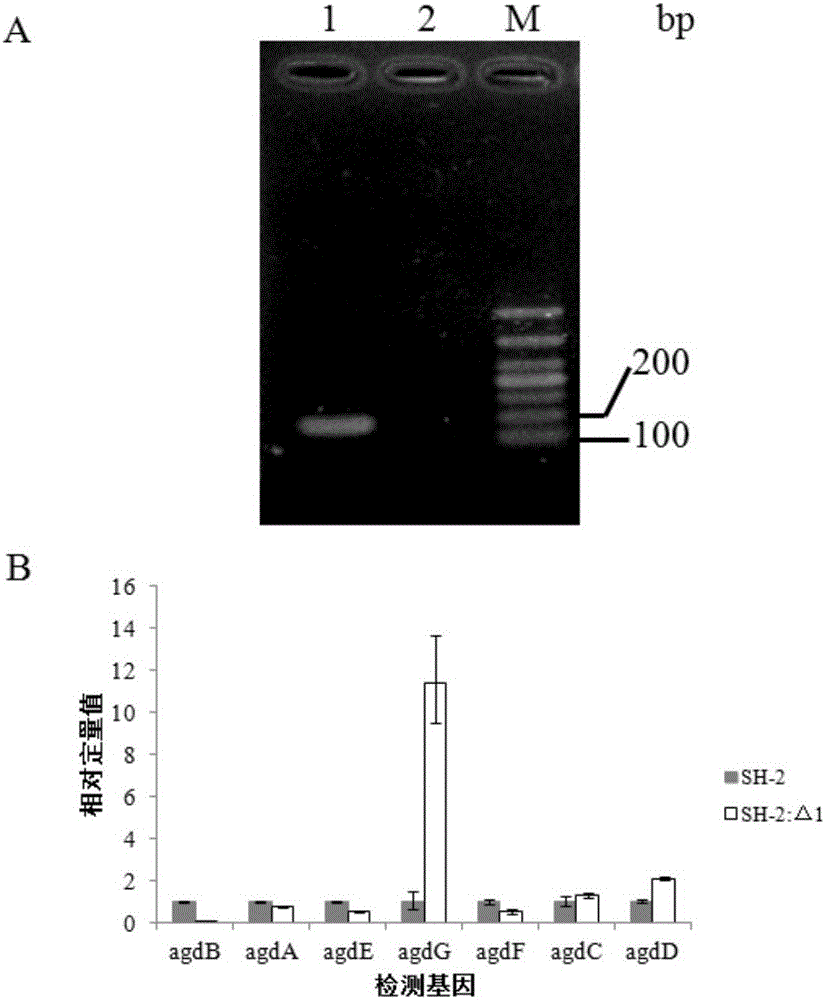
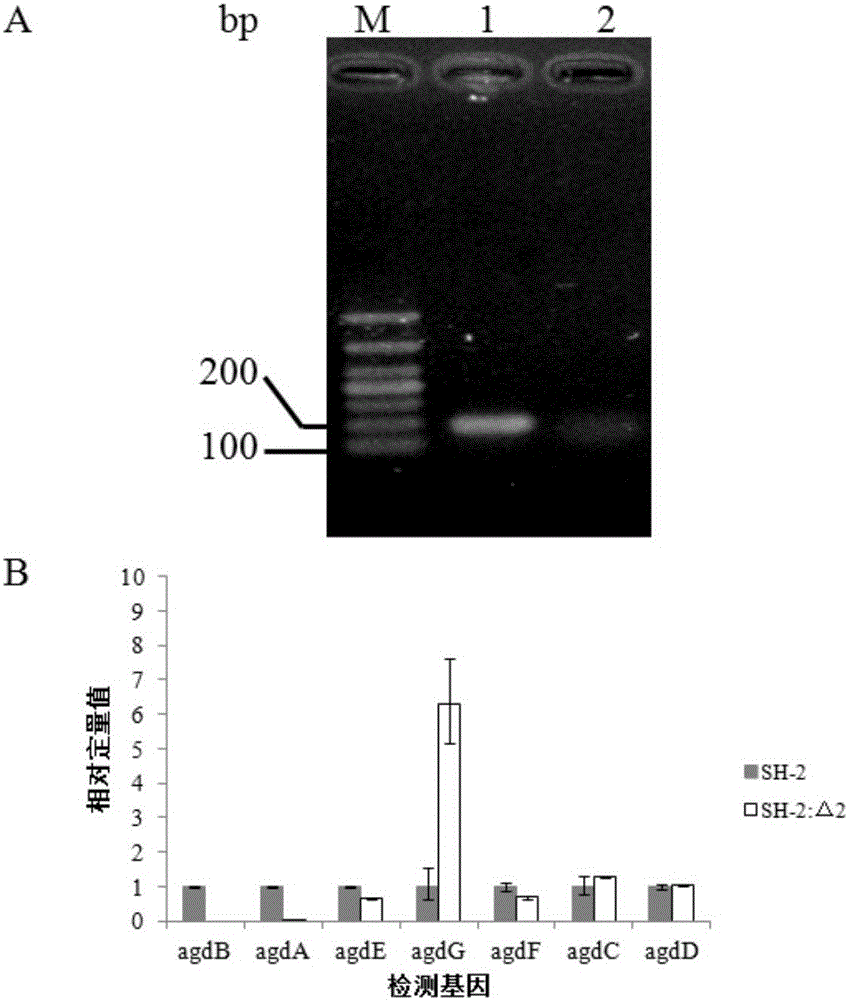
[0070] Example 3 Construction of Aspergillus niger SH-2: Δ1 and Aspergillus niger SH-2: ΔpyrGΔagdB strains and their functional identification (knockout gene agdB)
[0071] 1. Construction of Aspergillus niger SH-2:Δ1 and Aspergillus niger SH-2:ΔpyrGΔagdB strains
[0072] 1. Construction of knockout vector
[0073] (1) The relevant primer sequences for the construction of the agdB gene knockout vector are as follows:
[0074] Primer name
Sequence (5'→3')
Upstream(agdB)-F add EcoR V
gatatcTGCGCCTCAGTACTTGGGAG
Upstream(agdB)-R
ccctgtcaatggcaa ATCCCAGCTGGGTGGTCCCAGC
Redown(agdB)-F
ccaccccagctgggat TTGCCATTGACAGGGTTAGTG
Redown(agdB)-R
tctcgaggaagttgc GCTCGCCGGTCTGGCTTTG
pyrG(agdB)-F
gccagaccggcgagc GCAACTTCCTCGAGAACGCGC
pyrG(agdB)-R
cactaaccctgtcaatggcaa CCCTTTTAGTCAATACCG
Downstream(agdB)-F
cggtattgactaaaaggg TTGCCATTGACAGGGTTAGTG
Downstream(agdB)-R add EcoR V
ga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com