Method of preparing porous ceramic through low-temperature sintering
A technology of porous ceramics and low-temperature sintering, applied in the field of porous ceramics, can solve the problems of insufficient ceramic strength, decreased pore permeability, complicated preparation process, etc., and achieve the effects of easy industrialization, high ceramic strength, and simple process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
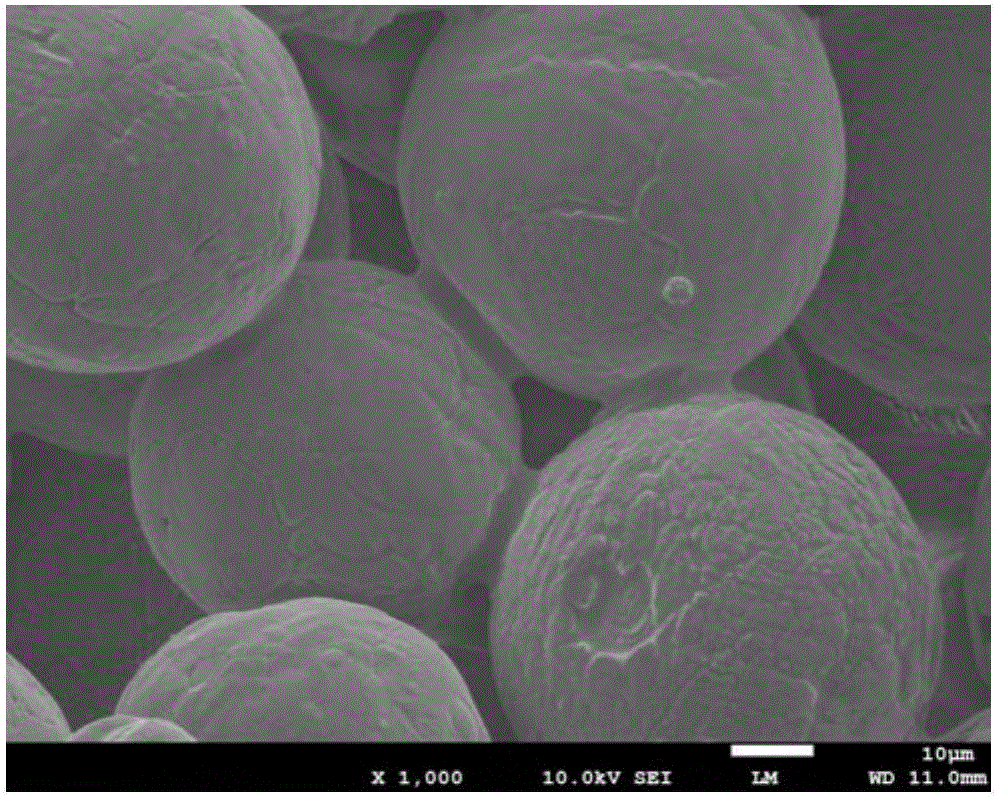
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
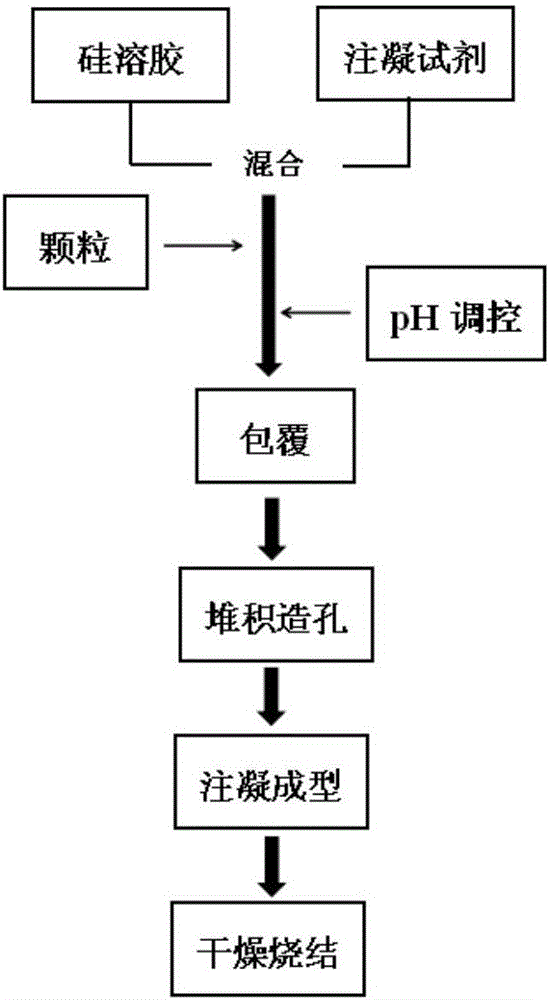
[0027] The preparation process of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings.
[0028] The flow chart of encapsulation-injection molding to prepare porous ceramics is attached figure 1 Shown:
[0029] (1) Dissolve the injection molding reagent in a silica sol solution with a concentration of 5-20wt.%, wherein the concentration of the organic monomer in the liquid phase is 2-20wt.%, and the mass ratio of MBAM to organic monomer is 1: 30-1:10, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 4 3-10% of the organic monomer mass fraction, TEMED and (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 4 The mass ratio is 1:1-1:6.
[0030] (2) Then, the ceramic powder is mixed with the liquid premix, the powder volume fraction is 50 vol%, and the particles are uniformly dispersed through mechanical stirring. During the stirring process, adjust the pH of the solution to a set value, and then continue stirring for 10 minutes to complete the coating process.
[0031] (3) The slurry is injected into the mold, and the c...
Embodiment 1
[0036] In a silica sol solution with a concentration of 5wt.%, injection molding reagent is added. The composition of the reagent is 2wt.% of organic monomer, and the mass ratio of MBAM to organic monomer is 1:30, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 4 Accounting for 3% of the mass fraction of organic monomer, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 4 The mass ratio with TEMED polyol is 1:1, and the mixture is prepared. Add the alumina powder to the premixed liquid, stir and disperse and adjust the slurry pH to 3 to complete the coating process. After the slurry was injected into the mold, the particles were piled up to make holes, and then placed at 80°C, and the polymerization reaction time was 10 minutes. After the green body is dried, it is sintered at 1300°C for 2 hours to obtain a porous ceramic with a porosity of 40% and a strength of 30MPa.
Embodiment 2
[0038] In a silica sol solution with a concentration of 15wt.%, injection molding reagent is added, the composition of the reagent is 10wt.% of organic monomer, and the mass ratio of MBAM to organic monomer is 1:20, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 4 Accounting for 7% of the mass fraction of organic monomers, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 4 The mass ratio to TEMED polyol is 1:3, and the mixed solution is configured. Add the alumina powder to the premixed liquid, stir and disperse and adjust the slurry pH to 3 to complete the coating process. After the slurry is injected into the mold, the particles are piled up to make holes, and then placed at 50°C, and the polymerization reaction time is 40 minutes. After the green body is dried, it is sintered at 1300°C for 2h to obtain a porous ceramic with a porosity of 39% and a strength of 35MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com