Method of treating diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) using a beta-bromodomain inhibitor
A B-cell, diffuse technology for the treatment of lymphoma in mammals that addresses the lack of well-established, insufficiently characterized response predictors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
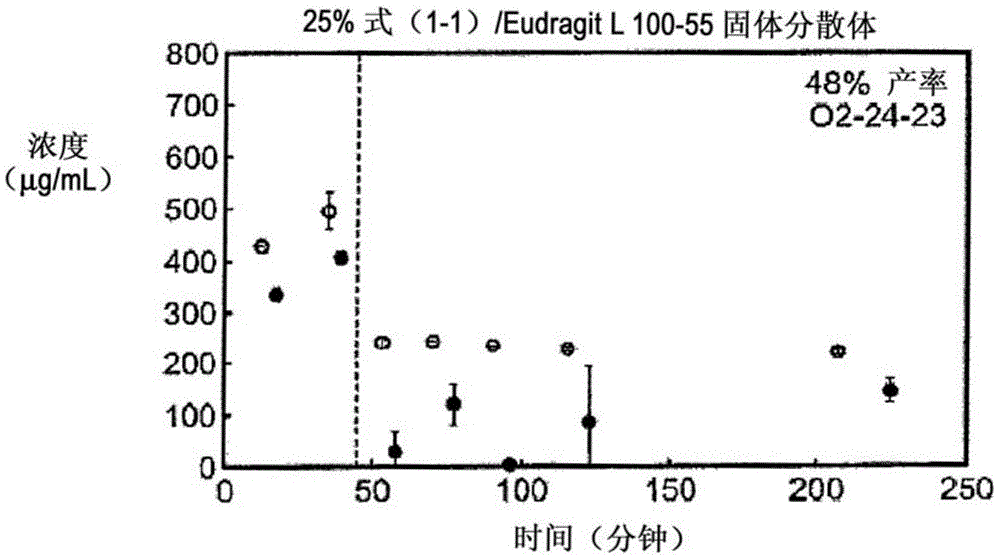
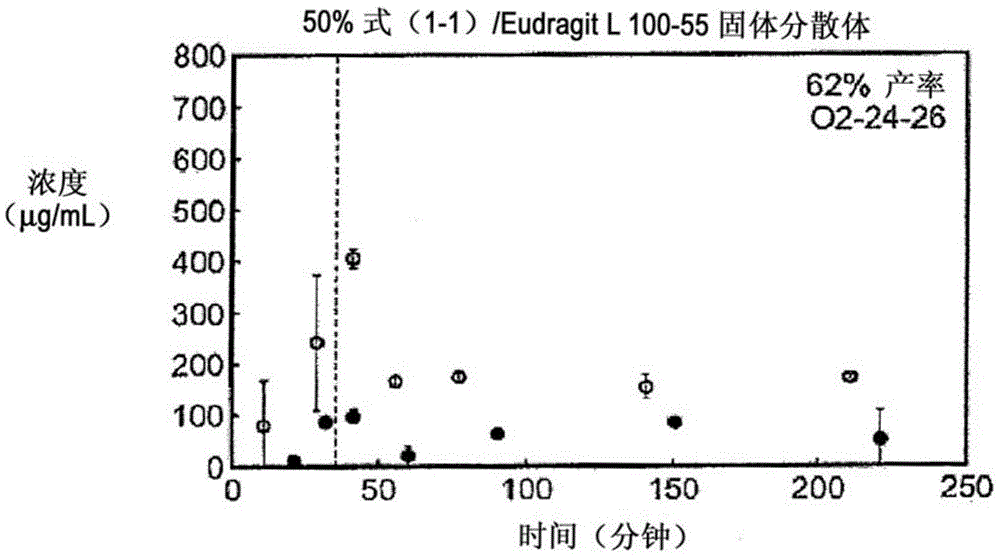
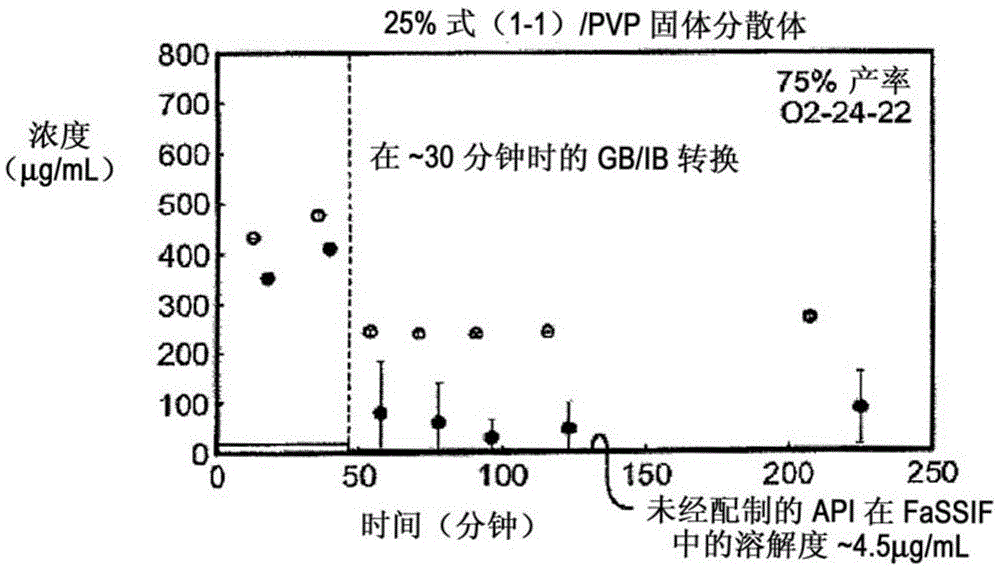
[0176] Example 1: In Vitro Screening of Solid Dispersion of Compound (1-1)
[0177] Ten solid dispersions were prepared using compound (1-1) and one of five polymers, including hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS-M), hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP-HP55), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), PVP-vinyl acetate (PVP-VA) and Eudragit L100-55, and for each polymer, compound (1- 1) The load factor is 25% and 50%. Solid dispersions were prepared by solvent evaporation using spray drying followed by secondary drying in a low temperature convection oven. The performance of each solid dispersion was evaluated by a non-sink dissolution performance test, which measures the total amount of drug and the amount of free drug present in solution over time. Non-sedimenting dissolution was chosen because it best represents the in vivo situation of low solubility compounds. The test involves "stomach shift" of the dispersion from gastric pH (0.1 N NaCl, pH 1.0) to i...
Embodiment 2
[0178] Example 2: In Vivo Screening of Solid Dispersion of Compound (1-1)
[0179] Solid dispersions of the three most promising compounds (1-1) were prepared on a larger scale, namely 25% compound (1-1) in PVP, 25% compound (1-1) in HPMCAS- Dispersions in MG, and 50% compound (1-1) in HPMCAS-M for in vivo studies. Each formulation was evaluated in the in vitro dissolution test described in Example 1. To ensure that these dispersions were amorphous and homogeneous, each dispersion was evaluated by X-ray powder diffraction (PXRD) and modified differential scanning calorimetry (mDSC). Additionally, to understand the effect of water on the glass transition temperature (Tg) of various dispersions, samples first equilibrated at a set relative humidity (i.e., 25%, 50%, and 75% RH) for at least 18 hours were tested. mDSC. [Water can be used as a plasticizer for solid dispersions, and the hygroscopicity of systems caused by active compounds or polymers can affect the amount of wa...
Embodiment 3
[0185] Example 3: Preparation and Clinical Application of Capsules Comprising Solid Dispersion of Compound (1-1)
[0186] A 10 mg strength gelatin capsule was prepared for a preliminary clinical study in patients with hematologic malignancies. Based on the in vitro and in vivo test results of the solid dispersion of compound (1-1) described in Examples 1 and 2, the solid dispersion of 50% compound (1-1) in HPMCAS-M was selected for the development of capsules . Capsule development was initiated with a size 3 hard gelatin capsule targeting a fill weight of 190 mg, as this configuration could potentially increase capsule strength by filling larger sized capsules while maintaining the pharmaceutical composition. Empirically, 4 capsule formulations were designed with different amounts of disintegrant and with or without wetting agent. Since all 4 formulations showed similar disintegration and dissolution test results, the simplest formulation (with no wetting agent, and with t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com