Agaricus bisporus cultivation method
A technology of Agaricus bisporus, cultivation method, applied in mushroom cultivation, cultivation, plant cultivation and other directions, can solve the problems of high use cost, production failure, inability to realize production, etc., achieves simple collection, low cost, and prevents the occurrence of Alternaria Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
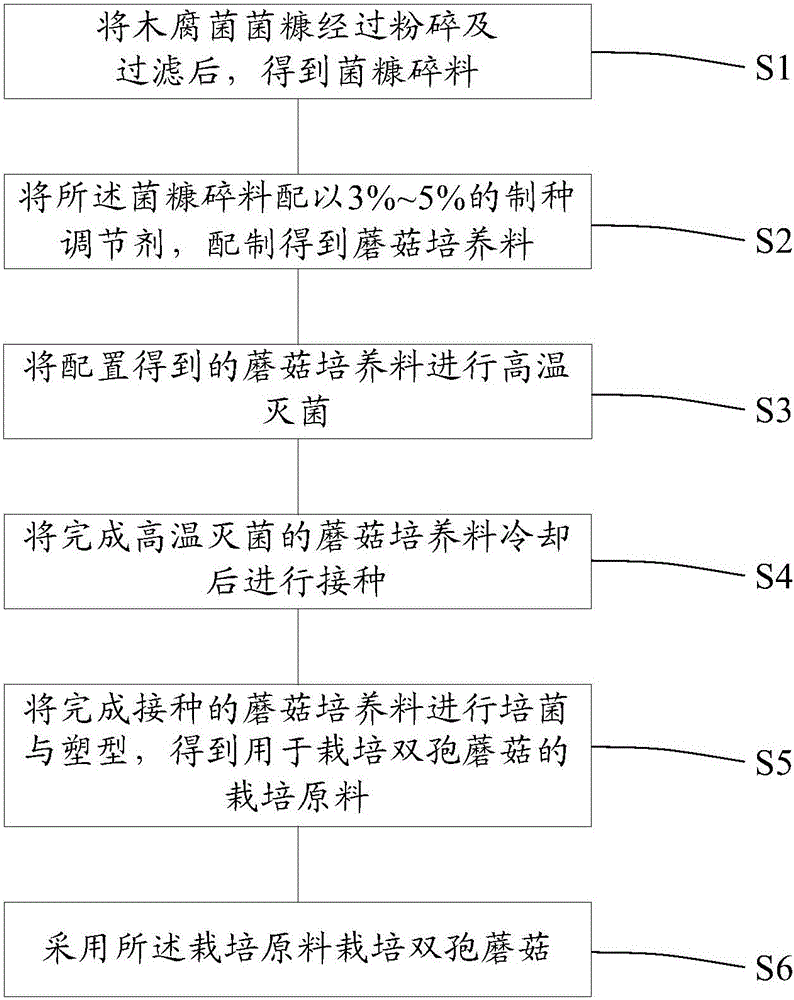
[0022] The cultivation method of Agaricus bisporus of the present invention comprises:
[0023] After crushing and filtering the chaff of wood rot fungus, the chaff fragments are obtained;
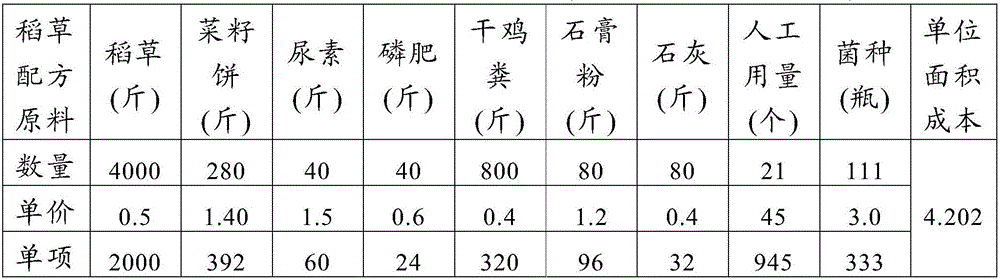
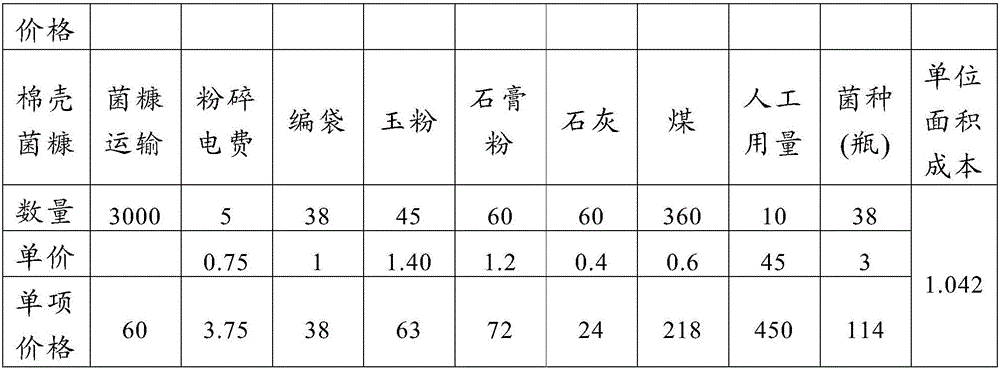
[0024] The mushroom chaff fragments are mixed with 3% to 5% seed production regulator to prepare mushroom compost;
[0025] Carrying out high-temperature sterilization of the mushroom compost obtained by configuring;
[0026] Inoculate after cooling the mushroom compost that has been sterilized at high temperature;
[0027] Cultivate and shape the inoculated mushroom compost to obtain cultivation materials f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com