Use of CD63 in preparation of kit for liver disease diagnosis or drug for preventing or treating liver diseases
A diagnostic kit and liver disease technology, applied in the field of medical bioengineering, can solve the problems of specific separation and purification of liver stem cells, cumbersome methods, and low purity of liver stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
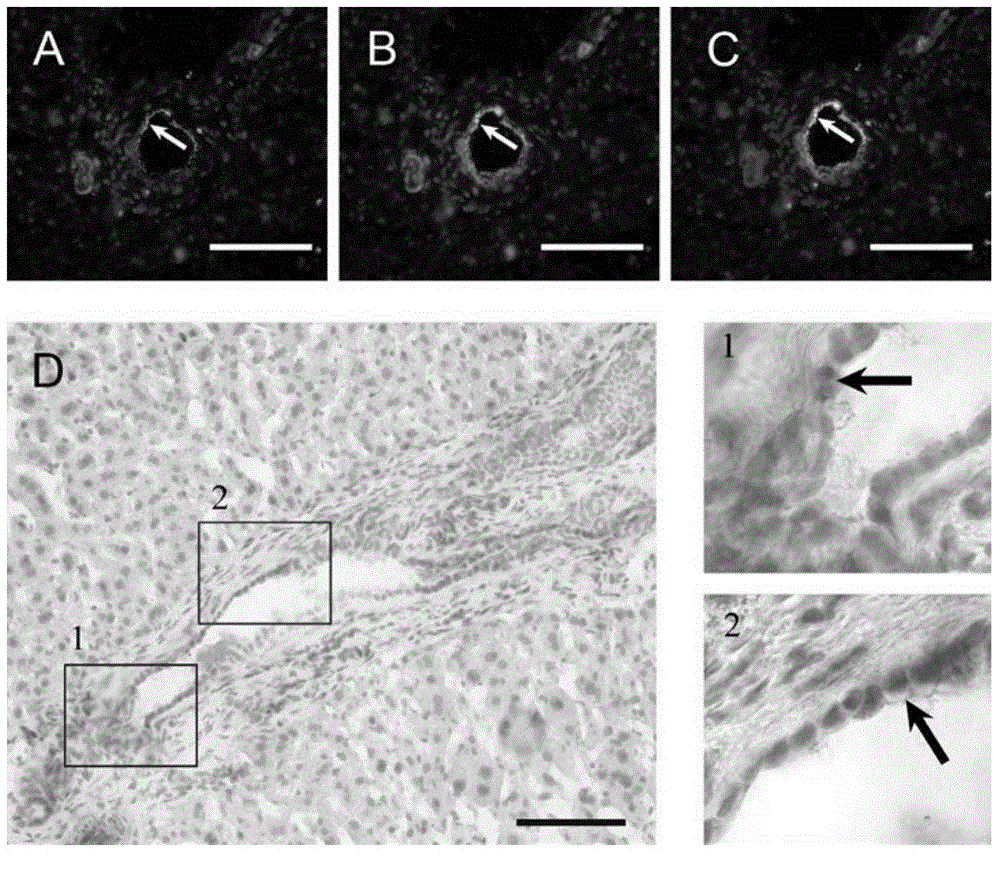
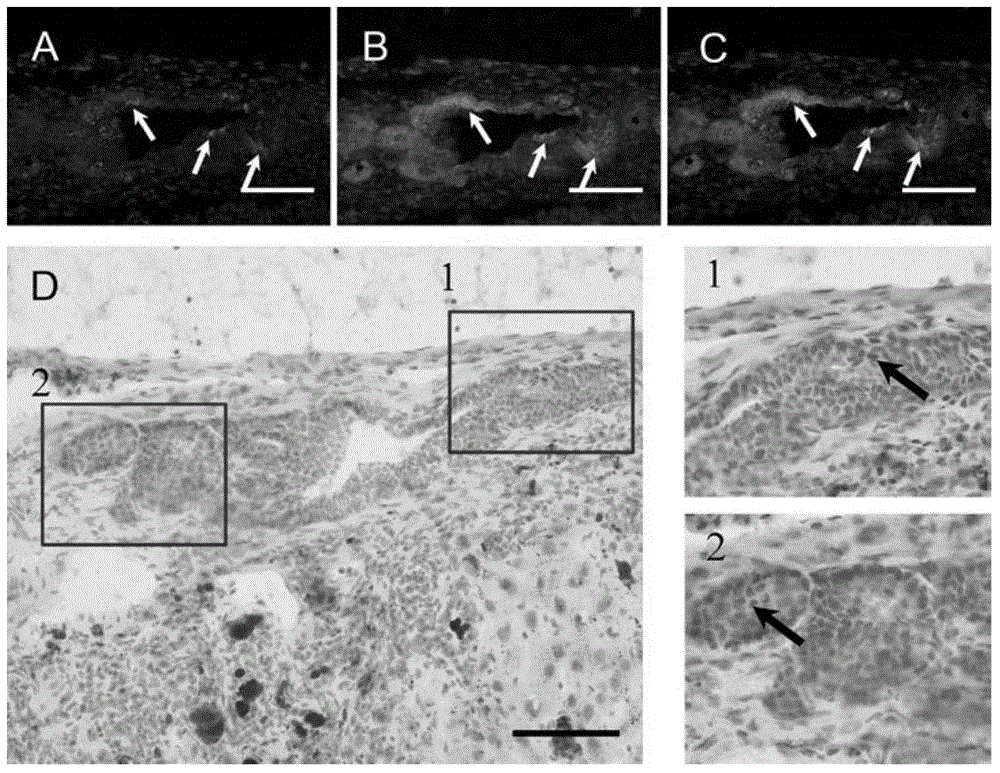
[0092] Example 1. Localization of CD63 hepatic stem cells in the liver
[0093] 1、正常肝脏和DDC诱导胆管反应3周后的肝脏(PreiseggerKH,FactorVM,FuchsbichlerA,StumptnerC,DenkH,ThorgeirssonSS,Atypicalductularproliferationanditsinhibitionbytransforminggrowthfactorbeta1inthe3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidinemousemodelforchronicalcoholicliverdisease,LabInvest.79(2):103-109) After embedding with OCT embedding agent (product number: 4583, purchased from SAKURA Company), frozen sections were 7um thick. Fix with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) (product number: P-6148, purchased from Sigma) at room temperature for 10 minutes, remove the fixative, and wash three times with PBS (product number: BS7016, purchased from Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.) , stored at 4°C for later use.
[0094] 2. Immunofluorescence staining: After blocking the liver section treated in step 1 with 1% BSA (product number: A1933, purchased from sigma company) at room temperature for 30 minutes, add dropwise the mouse a...
Embodiment 2
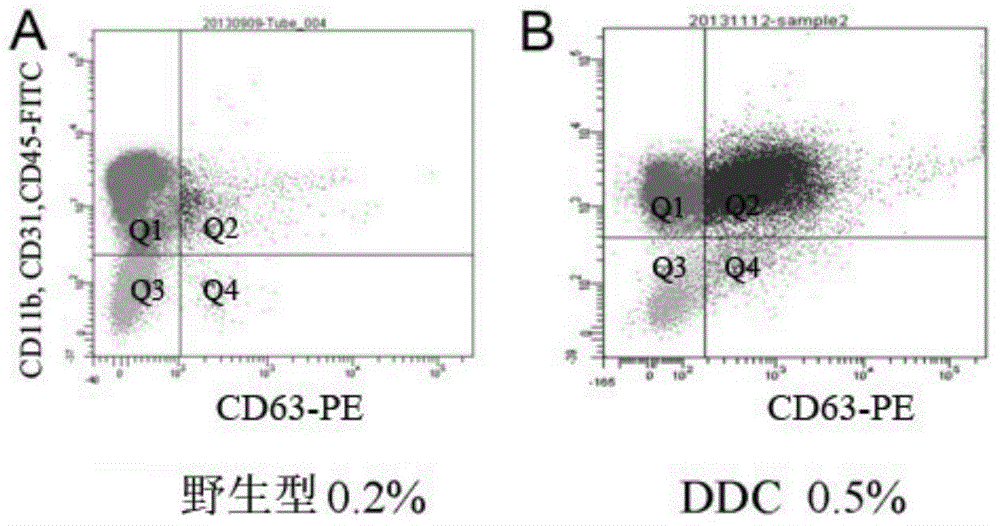
[0097] Example 2. Rapid isolation and expansion of CD63-positive hepatic stem cells
[0098] 1. Two-step in situ collagenase perfusion digested liver (WangMJ1, ChenF, LiJX, LiuCC, ZhangHB, XiaY, YuB, YouP, XiangD, LuL, YaoH, BorjiginU, YangGS, WangensteenKJ, HeZY, WangX, HuYP, Reversalofhepatocytesenescenceaftercontinuousinvivocellproliferation, Hepatology .60(1):349-361.), the digestion mixture was further incubated with 0.25% collagenase (product number: 11088858001, purchased from Roche) at 37° C. for 30 minutes.
[0099] 2. Centrifuge the digested cell suspension at 50g centrifugal force twice for 30 minutes at low speed, discard the precipitate (large hepatocytes), collect the supernatant and continue to centrifuge at 300g centrifugal force for 5 minutes, and use serum-free DMEM medium (product number: SH30022.01 , purchased from Hyclone Company) resuspended cells, counted, and diluted the cells to 10 7 / ml, using OptiPrep TM DensityGradientMedium (Catalog No.: D1556, s...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3. Differentiation of CD63-positive liver stem cells into mature hepatocytes
[0106] 1. Press 5×10 4 cells / cm 2 Sow CD63-positive hepatic stem cells on type 1 collagen-coated 35mm culture dishes, add SCM-A medium, and store at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in the incubator until the cells are congested, and change the medium every other day.
[0107] 2. After the cells are congested, replace the liver induction medium (DMEM / F12, 10% FBS, 10ng / mlHGF, 10ng / mlEGF, 10-7MDex, 1%DMSO, 10ng / mlOSM, 20% Matrigel) and continue to culture for 6 days , and change the liquid every other day.
[0108] 3. Detection of mature hepatocytes formed by induction and differentiation of CD63-positive liver stem cells: the cells formed after induction were collected to extract RNA, and Real-Time detection showed that the expression levels of markers (Abcg2, CK19, Gja1, Ggt1) of stem cells and cholangiocytes Compared with before induction, the expression levels of liver cell markers (Alb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com