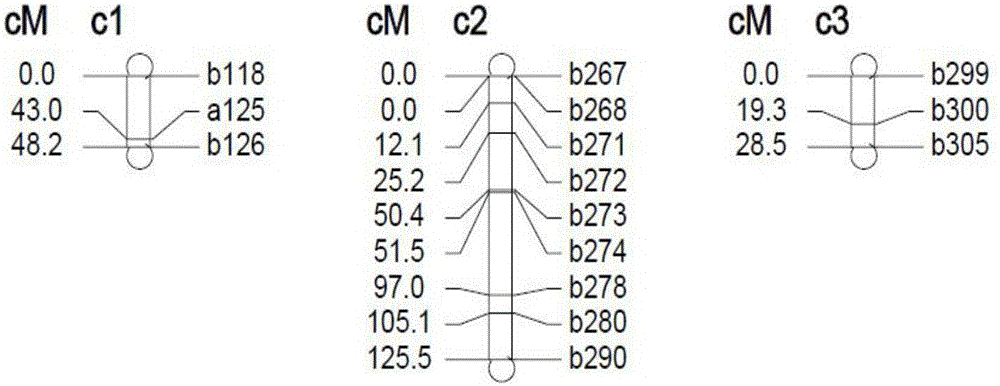
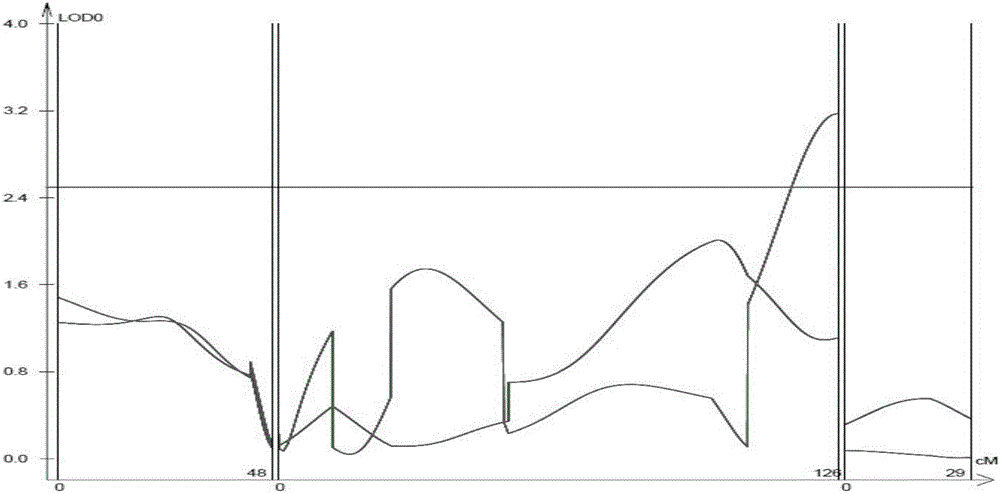
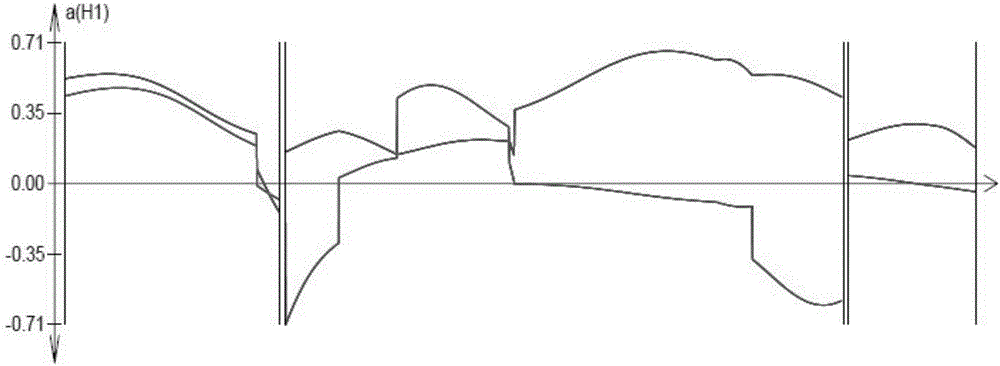
SSR mark linked with pseudoperonospora cubensis resistance main effect QTL and application of SSR mark
A technology for downy mildew and melon, which is applied in the field of SSR markers linked with the main effect QTL for downy mildew resistance in melon, can solve the problem of no molecular marker-assisted breeding, etc., and achieve the effects of improving the selection accuracy and shortening the breeding cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment one: the SSR marker linked with the main effect QTL of resistance to melon downy mildew
[0065] A kind of SSR marker linked with the main effect QTL of resistance to melon downy mildew, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0066] (1) Taking the melon resource PI390452 as the source of downy mildew resistance, the resistance gene was quantitatively inherited according to the genetic identification of resistance.
[0067] (2) The melon downy mildew-susceptible farm variety "Karaxai" was used as the female parent and the disease-resistant resource PI390452 was used as the male parent to obtain a hybrid F 1 .
[0068] (3) by Hybrid F 1 Self-pollination to obtain F 2 generation group, F 1 Crossbreed with "Karaxai" to get BC S , F 1 BCr was obtained by hybridization with PI390452.
[0069] (4) To PI390452, "Karaxai", F 1 、BC S , BCr and F 2 Carry out disease resistance identification, investigate the disease situation after inoculating the conid...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Embodiment two: the application of the molecular marker linked with the main effect resistance gene of melon downy mildew
[0090] The application of the molecular marker linked with the main effect resistance gene of melon downy mildew, by the molecular marker SSR-pc provided by the above-mentioned embodiment one 283 Be used for the genotype detection of muskmelon variety or line, be used for judging whether this kind or line is resistant to melon downy mildew, comprises the following steps:
[0091] (1) The disease-resistant resource PI390452 was crossed with other melons and propagated to F 2 generation above;
[0092] (2) Genomic DNA is extracted from the single muskmelon plant obtained by step (1), and the SSR-pc 283 This marker is amplified by PCR to detect whether a 283bp specific band appears, and if a specific band occurs, it is predicted that the melon plant is resistant to downy mildew.
Embodiment 3
[0093] Embodiment three: the construction of genetic segregation population and downy mildew inoculation method and disease classification
[0094] 1. Construction of F2 population
[0095] (1) F 1 , F 1 F 2 . By pair of parents, F 1 Generation and F 2 The generation groups were inoculated manually and the incidence of each individual plant was counted.
[0096] (2) Inoculation of downy mildew and disease classification: Spray inoculation with conidia suspension. Collect natural early diseased leaves from the field, brush the sporangia on the back of the leaves with a soft brush, place them in a beaker filled with sterile water, inoculate them on the cotyledons of susceptible varieties by spot grafting, and then put them in the light Propagate in the incubator. After a large black mold layer grows on the back of the cotyledon, use a soft brush to pick up the sporangia on the back of the leaf, put them in a beaker filled with sterile water, stir them evenly, and count th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com