Robust Frequency-Invariant Beamforming Method for Linear Constrained Minimum Variance Diagonal Loading
A minimum variance, linearly constrained technique, applied in transducer circuits, sensors, signal processing, etc., to solve problems such as computational complexity, beamformer performance degradation, and low desired signal resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, technical scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
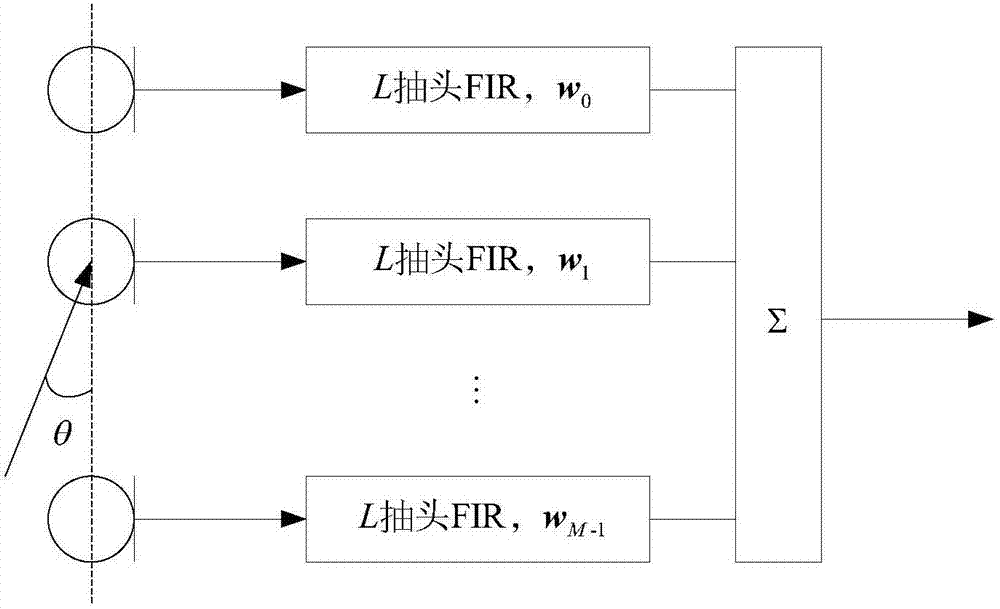
[0051] figure 1 is the schematic diagram of the microphone array broadband beamforming method, in figure 1 The received signal x(k) of the microphone array in the medium is processed by a broadband adaptive beamformer to obtain its output signal: y(k)=w H x(k); where the superscript H represents the conjugate transpose, w is the weight vector of the broadband beamformer, w=[w 11 ,...,w M1 ,...,w 1L ,...,w ML ] T ,w ML Indicates the Lth weight coefficient of the Mth microphone channel, the superscript T indicates the transpose, and k indicates the time sequence; x(k)=[x 11 (k),...,x M1 (k),...,x 1L (k),...,x ML (k)] T , x ML (k) represents the received signal of the Mth microphone channel Lth.
[0052] The response of the beamformer based on the filter-sum structure can be expressed as
[0053] P(f,θ)=|w T d(f,θ)| (1)
[0054] In the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com